China's Railway Freight: Moving Forward Through Transformation

China's railway freight system is evolving into a modern logistics powerhouse. You can see this transformation in its adoption of digital and intelligent technologies. These advancements improve operations, reduce costs, and enhance environmental sustainability.
Rail freight emits up to 80% less carbon dioxide per kilometer-ton compared to road transport, making it a greener choice.
In 2020, over 12,400 cargo trains carried more than 1 million TEUs between China and Europe, marking a 50% increase from 2019.
The market size of China's intelligent logistics surged from 35.67 billion yuan ($5.11 billion) in 2020 to 128.05 billion yuan by October 2022, with an annual growth rate of over 70%.
These numbers reflect how railway freight reshapes China's logistics landscape while fostering global trade and environmental goals.
Key Takeaways
Rail freight is better for the environment. It produces 80% less carbon dioxide than trucks, making it a smart choice for businesses.
China's rail system is getting better with new digital tools. These tools make deliveries faster and cheaper.
The Belt and Road Initiative helps China trade with other countries. It increases cargo shipments and creates more jobs.
Using advanced tools like AI and IoT will make China's railways more reliable and eco-friendly.
Updated railways help the economy grow and protect the environment. This matches China's goals for green development.
Current State of China's Railway Freight

Scale and Infrastructure of the Railway System
China boasts one of the most extensive railway systems in the world. Its total railway length reached 139,000 kilometers (86,371 miles) as of 2019. Among these, 59% are double-tracked, and 71.9% are electrified, ensuring efficient and sustainable operations. The high-speed rail network spans an impressive 35,000 kilometers (21,748 miles), making it the longest globally. This advanced infrastructure supports both passenger and freight transport, with high-speed rail accounting for over 60% of total railway passengers in 2019.
Despite the focus on passenger transport, freight operations remain a vital component of China's railway system. Cargo volumes have experienced fluctuations over the years. After a period of stagnation in 2012 and a significant drop in 2015, freight volumes began recovering in 2017. This recovery highlights the system's resilience and its importance in supporting China's economic and trade activities.
Challenges in the Existing Freight Network
While China's railway freight system has achieved remarkable progress, it faces several operational challenges. One major issue is the incompatibility of rail gauges, which adds 2-3 days to transit times. This delay increases shipping costs by approximately 15% per shipment. Additionally, transport costs in regions like Central Asia are 25% higher than in the European Union due to inefficiencies caused by non-standardized systems.
These challenges hinder the seamless movement of goods across borders, affecting international trade and logistics efficiency. Addressing these issues is crucial for China to fully leverage its railway infrastructure and maintain its position as a global logistics leader.
Transformative Changes in Railway Freight
Digital and Intelligent Transformation
China's railway freight system is embracing digital and intelligent technologies to revolutionize operations. These advancements are transforming railways from traditional "transportation pipes" into "digital arteries." You can see this shift in the widespread adoption of technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and predictive maintenance. These tools enhance operational efficiency by enabling real-time monitoring, asset tracking, and optimized scheduling. For example, predictive maintenance reduces downtime by identifying potential issues before they occur, ensuring smoother freight operations.
The integration of advanced signaling technologies and smart logistics equipment has further improved cargo visibility and safety protocols. Automated systems, such as smart gantry cranes and bulk cargo robots, have significantly reduced loading and unloading times. This innovation not only lowers costs but also boosts efficiency. Additionally, the development of intelligent freight cars with higher cargo capacity has enhanced single-trip transportation capabilities.
The impact of these changes is evident in the numbers. For instance, the annual rail freight volume between the Greater Bay Area (GBA) and Europe has increased by 15% since 2011. The total value of goods transported by rail from Guangzhou to Europe reached $12.3 billion in 2022. These figures highlight how digital transformation is driving growth and strengthening China's railway freight network.
Statistic Description | Value | Year |
|---|---|---|
Annual increase in rail freight volume between GBA and Europe | 15% | Since 2011 |
Total value of goods transported by rail from Guangzhou to Europe | $12.3 billion | 2022 |
Reduction in average lead time for rail transportation | 10-15 days | Compared to maritime shipping |
Policy Reforms and International Trade Initiatives
Policy reforms and international trade initiatives have played a pivotal role in shaping China's railway freight system. The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has been a cornerstone of this transformation, fostering connectivity and expanding global trade routes. Through the China-Europe Railway Express, you can witness the tangible benefits of these efforts. Since its inception in 2011, the number of trains and cargo volume has steadily increased, showcasing the success of this initiative.
These reforms have also addressed logistical challenges, such as non-standardized systems and limited port capacities. By streamlining customs procedures and enhancing cross-border cooperation, China has reduced transit times and improved trade efficiency. Even during the COVID-19 pandemic, the China-EU-China route maintained stable cargo volumes, demonstrating the resilience of the railway freight network.
However, the redirection of cargo due to sanctions against Russia in 2022 highlights the adaptability of China's railway expansion. By diversifying trade routes and strengthening partnerships with other countries, China has ensured the continued growth of its railway freight system. These initiatives not only support economic growth but also create jobs and enhance connectivity across regions.
Sustainability and Green Energy Integration
China's railway freight system is setting new standards for sustainability by integrating green energy solutions. High-speed railways (HSR) have significantly reduced fossil fuel consumption and carbon emissions, making rail transport an eco-friendly alternative to road transportation. This shift aligns with China's commitment to environmental sustainability and its broader economic goals.
The positive environmental impacts of HSR extend beyond reduced emissions. By decreasing traditional resource consumption along railway routes, HSR promotes eco-friendly development. Third-tier cities and non-megacities have particularly benefited from these sustainable practices, showcasing the widespread impact of China's railway expansion.
Technological innovation and improved labor productivity have further enhanced eco-sustainability. For instance, the use of renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies in railway operations has minimized the environmental footprint. These efforts not only support China's green development agenda but also position its railway freight system as a global leader in sustainable transportation.
🚆 Tip: Choosing rail freight over road transport can reduce carbon emissions by up to 80%, making it a greener choice for businesses and consumers alike.
Benefits of Railway Freight Transformation

Boosting Economic Growth and Trade
China's railway freight transformation has become a driving force for economic growth and trade expansion. By modernizing its freight network, China has enhanced its ability to move goods efficiently across domestic and international markets. This improvement supports industries like mining, construction, and manufacturing, which rely heavily on reliable transportation systems.
Rail freight volumes increased by 3.6% year-on-year, with 1.3 billion tonnes moved from January to April 2025.
Coal shipments accounted for over half of the total freight, with 672 million tonnes transported, primarily for power plants.
Mining and construction material shipments rose by 29.3%, while metallurgical goods increased by 10.7%.
Rail-water container shipments surged by 19.1% year-on-year, reaching 5.38 million TEUs.
The Belt and Road Initiative has further amplified these benefits by connecting China to global trade routes. The China-Europe Railway Express and China-Central Asia freight train networks have seen significant operational increases, with the latter growing by 21% in 2024. These developments not only boost trade volumes but also create jobs and strengthen connectivity across regions.
🚆 Note: China's railway expansion is a cornerstone of its economic growth strategy, enabling seamless trade and job creation while fostering global connectivity.
Environmental Advantages of Modernized Railways
Modernized railways in China offer significant environmental benefits. Rail transport accounts for only 1.6% of total greenhouse gas emissions, making it a greener alternative to road or air transportation. Expanding railway infrastructure reduces reliance on high-carbon industries and supports China's environmental governance goals.
High-speed rail (HSR) plays a pivotal role in this transformation. By reducing fuel energy consumption, HSR minimizes emissions and promotes eco-friendly development. This shift benefits cities of all sizes, particularly third-tier cities, which experience improved air quality and sustainable growth.
Railway freight modernization also integrates renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies. These innovations lower the environmental footprint of transportation while aligning with China's green development agenda. Choosing rail freight over road transport can reduce carbon emissions by up to 80%, making it an ideal choice for businesses aiming to adopt sustainable practices.
Enhanced Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
China's railway freight system has achieved remarkable efficiency and cost-effectiveness through modernization. Advanced technologies like predictive maintenance and automated systems reduce delays and improve reliability. These innovations streamline operations, allowing goods to reach their destinations faster and at lower costs.
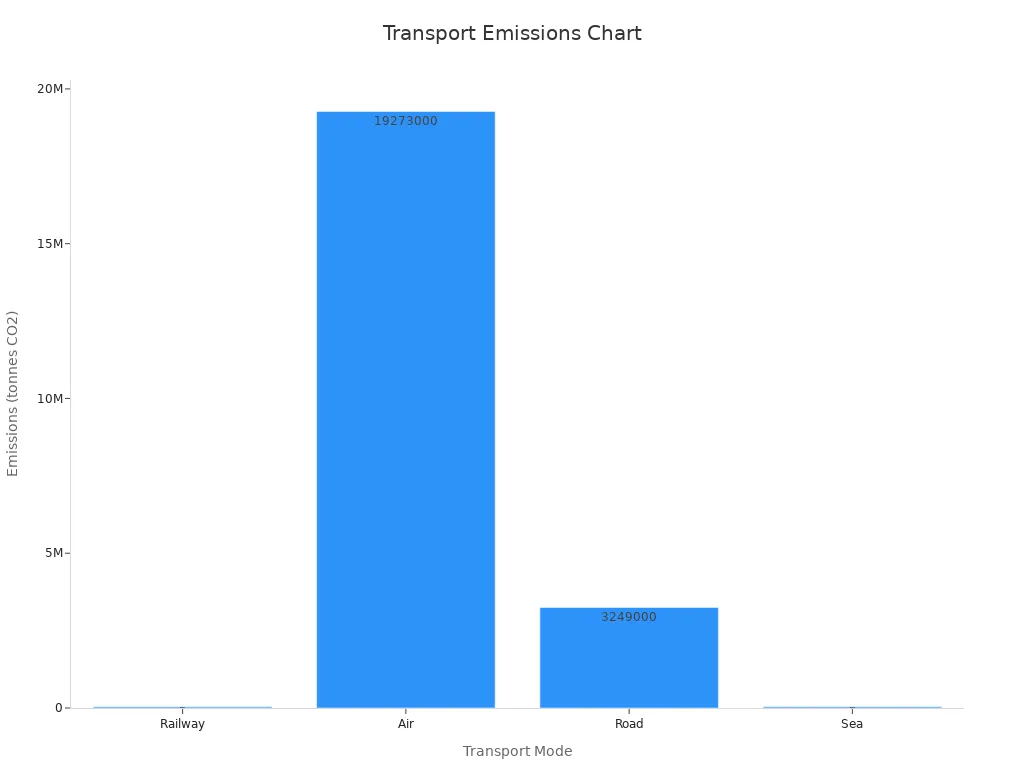
Transport Mode | Emissions (tonnes CO2) |
|---|---|
Railway | |
Air | 19,273,000 |
Road | 3,249,000 |
Sea | 36,500 |
A Chinese home appliance manufacturer reduced transport time from 45 days to 20 days, cutting transportation costs by 30%. These improvements stem from efficient border procedures and optimized logistics networks. The integration of smart logistics equipment, such as automated cranes and intelligent freight cars, further enhances operational efficiency.
China's railway expansion ensures that businesses benefit from reduced costs and faster delivery times. This transformation strengthens the country's position as a global logistics leader while supporting economic growth and trade.
Challenges and Future Outlook for China's Railway Freight
Overcoming Infrastructure and Funding Barriers
China's railway freight network faces significant infrastructure and funding challenges. Addressing these barriers requires innovative solutions and strategic planning. Diversified financing options, such as public-private partnerships (PPPs) and support from multilateral development banks, can reduce reliance on single funding sources. These partnerships encourage investment and ensure sustainable railway infrastructure development.
Improving regulatory transparency is another critical step. Clear and consistent policies attract foreign investment, fostering international trade and connectivity. Lifecycle cost analysis can help prioritize maintenance projects, minimizing long-term expenses and enhancing operational efficiency. Currently, maintenance funding in Central Asia accounts for only 20% of infrastructure budgets, far below the global average of 35%. Increasing these allocations will reduce inefficiencies and improve the reliability of cross-border rail freight services.
China's railway expansion also benefits from cost-efficiency measures. By optimizing maintenance schedules and adopting advanced technologies, you can lower operational costs and improve service quality. These efforts strengthen the foundation for economic growth and job creation, ensuring the railway freight system remains competitive in the global logistics landscape.
Future Trends in Railway Freight Development
China's railway freight system is poised for transformative growth. Emerging trends highlight the integration of advanced technologies and market-driven strategies. The Improved Comparative Static Model (ICSM) forecasts the impact of macroeconomic policy reforms on China Railway Corporation (CRC). Short-term analyses focus on government policy adjustments, while long-term projections emphasize market mechanisms with minimal intervention.
Tax policy plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of railway freight. The ICSM reveals that tax policies are more sensitive to price impacts than investment subsidies. Careful tax policy design can prevent social welfare losses and support trade volume growth. These insights guide policymakers in creating balanced strategies that promote economic growth and supply chain integration.
The Belt and Road Initiative continues to drive expansion. By connecting the Silk Road Economic Belt with global trade routes, China enhances cross-border rail freight operations and strengthens international partnerships. This connectivity fosters job creation and boosts trade volumes, positioning China's railway freight system as a leader in global transportation.
Technological advancements will further shape the future. Innovations like predictive maintenance, automated systems, and renewable energy integration will enhance efficiency and sustainability. These developments align with China's commitment to green growth and logistics modernization, ensuring the railway freight network remains a vital component of the nation's economic strategy.
China's railway freight system stands as a beacon of transformation, redefining logistics through digitalization and sustainability. You can see its impact in the revitalized Silk Road, which connects European companies to Chinese markets, fostering economic cooperation and creating new business opportunities. Enhanced rail infrastructure is projected to increase trade volume in the Greater Bay Area by 10% by 2025, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
This transformation also reshapes global trade dynamics. The China-Europe rail freight network offers faster transit times compared to maritime transport, making it a preferred choice for businesses. Continued innovation and investment will unlock even greater potential, ensuring China's railway freight system remains a cornerstone of economic growth, environmental sustainability, and global connectivity.
FAQ
What makes railway freight in China more sustainable than other transport modes?
Railway freight in China emits significantly less carbon dioxide compared to road or air transport. High-speed railways use renewable energy and energy-efficient technologies, reducing their environmental footprint. This makes rail freight a greener choice for businesses and consumers.
How does digital transformation improve railway freight operations?
Digital tools like IoT and AI enhance real-time monitoring and scheduling. Predictive maintenance prevents delays by identifying issues early. Automated systems, such as smart cranes, reduce loading times. These advancements make China's railway freight system faster and more reliable.
Why is the Belt and Road Initiative important for railway freight?
The Belt and Road Initiative connects China to global trade routes. It reduces transit times and improves cross-border logistics. This initiative strengthens international partnerships and boosts trade volumes, making China's railway freight system a key player in global logistics.
How does railway freight support economic growth in China?
Railway freight ensures efficient transportation of goods across domestic and international markets. Industries like mining and manufacturing rely on it for reliable logistics. This network creates jobs, supports trade, and strengthens China's economy.
What are the future trends in China's railway freight system?
Future trends include integrating advanced technologies like AI and renewable energy. The Belt and Road Initiative will continue expanding trade routes. These developments will enhance efficiency, sustainability, and global connectivity for China's railway freight system.
See Also
Navigating Tomorrow: Digital Innovations in Logistics Ahead
Exploring 2024: Latest Developments in Sea Freight Logistics
Transforming Logistics: The Impact of AI on Supply Chains
Future Innovations: Breakthroughs in Logistics Technology Explored
