The Environmental Challenges Facing Express Logistics Channels

Online shopping keeps getting bigger. This makes express logistics channels busier than ever. The effect on the environment is now a big worry.
Metric | Value/Statistic |
|---|---|
Express parcel volume (2023) | |
Logistics carbon emissions | Over 55 million tons (2022) |
More online shopping means more work for express logistics channels, but only 16% of companies can see their supply chain in real time.
If nothing changes, global freight emissions could go up by 160% by 2050.
As online shopping grows, it is important to care about sustainability, so new ideas from leaders like JUSDA are very important.
Key Takeaways
Express logistics channels hurt the environment a lot. They make a lot of carbon emissions and more packaging waste. This problem gets worse as online shopping grows fast.
Smart solutions can help fix these problems. Route optimization, green vehicles, sustainable packaging, and rail transport can cut down pollution and waste in logistics.
Companies like JUSDA are leading by using new technology and greener ways. They make express delivery faster, cleaner, and better for the Earth.
Environmental Impact of Logistics

People are worried about how logistics affects the environment. As global trade and e-commerce grow, this problem gets bigger. Logistics moves goods every day across cities and countries. This creates emissions and waste. These things hurt air quality and the climate. They can also harm people’s health.
Carbon Emissions in Express Delivery
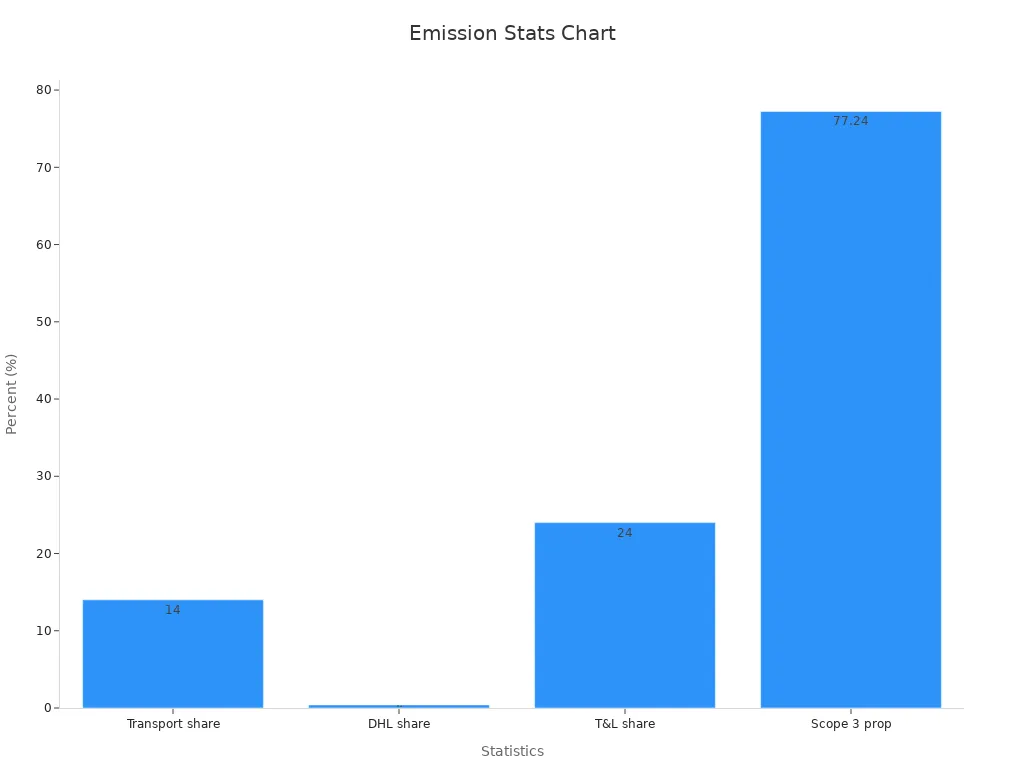
Logistics is a big source of greenhouse gas emissions. Transport and logistics together make up about 24% of global CO2 emissions. The transport sector alone is 14% of global carbon emissions, based on DHL data. Trucks, planes, ships, and trains move goods fast to meet demand. Express delivery uses air and road transport the most. These ways create more emissions than rail or sea.
Statistic Description | Value | Source/Notes |
|---|---|---|
Transport sector share of global carbon emissions | 14% | DHL data, includes all emission scopes, aligned with GHG protocol |
DHL's share of transport sector emissions | 0.4% | DHL's internal and externally audited data, disclosed to CDP |
Transport and logistics sector share of global CO2e emissions | ~24% | Broader industry perspective from DHL's sustainability trends report 2024 |
DHL's Scope 3 emissions proportion | 77.24% | Represents majority of DHL's emissions in 2019, highlighting challenges in accounting Scope 3 |
Express delivery makes it easy to get things fast. But it also increases emissions from logistics. Fast shipping means more trucks and planes are used. This leads to higher CO2 emissions. Every delivery adds to the total, especially in busy cities. In 2018, express delivery logistics made 13.7 million tons of CO2e. Over 80% came from online shopping parcels. Most emissions come from intercity deliveries, which are 99% of the total.
JUSDA knows about these problems and tries to help. The company uses smart planning and technology to cut emissions. JUSDA’s China-Europe Express Rail service uses trains instead of planes or trucks. Trains make less pollution than air or road delivery. This helps lower the carbon footprint when moving goods between continents.
Packaging Waste Issues
Packaging waste is another big problem for logistics. Every package needs something to protect it during delivery. Billions of parcels are shipped each year, so packaging waste keeps growing. In China, about 50.7 billion parcels were shipped in 2018. 80% were from online shopping. Corrugated boxes, plastic bags, and envelopes make up most of this waste.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Parcel shipments in China (2018) | ~50.7 billion parcels, 80% from online shopping |
Packaging types (by weight) | Corrugated boxes 53.5%, Plastic bags 33.5%, Envelopes 5.4%, Others 7.6% |
Top packaging volumes | Small corrugated boxes: 10.6 billion; Large plastic bags: 8.0 billion; Medium corrugated boxes: 7.8 billion |
Packaging material weight proportion | >20% of total parcel weight (excluding goods) |
Scrap packaging generated (2018) | 8.8 million metric tons (3.9% of China’s municipal solid waste) |
Packaging waste composition (by weight) | Corrugated boxes 90.8%, Plastic bags 5.9%, Envelopes 1.7%, Others 1.6% |
Recycling rates | Corrugated boxes ~80%, Plastic bags ~1.5% |
Disposal of unrecycled packaging | 57% landfill, 41% incineration, 2% open dumps |
GHG emissions from express delivery logistics (2018) | 13.7 million tons CO2e (~7% of logistics industry emissions) |
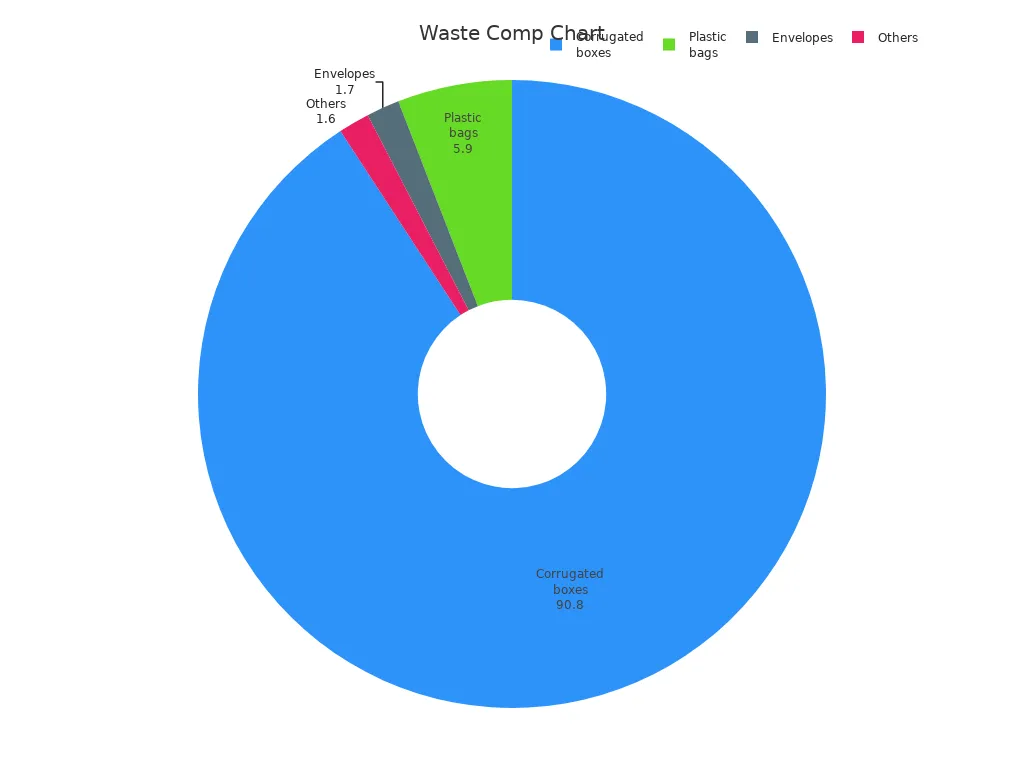
Corrugated boxes are more than half of all packaging by weight. Plastic bags are also used a lot. In 2018, over 8.8 million metric tons of scrap packaging were made. This was almost 4% of China’s municipal solid waste. About 80% of corrugated boxes get recycled. But only 1.5% of plastic bags are recycled. Most packaging that is not recycled goes to landfills or is burned. This makes environmental problems worse.
The impact of logistics on the environment grows as more people shop online. Fast delivery means more emissions and more waste. Packaging waste and greenhouse gas emissions are big worries, especially in cities with lots of deliveries.
JUSDA works on these problems with new ideas. The company uses sustainable packaging and recycling programs. JUSDA also uses technology to make packaging smaller and create less waste. By working on both emissions and waste, JUSDA helps make logistics better for the environment.
Express Logistics Channels and Urban Challenges
Last-Mile Delivery Impact
Express logistics channels affect city environments a lot. Last-mile delivery means taking packages from a local center to your home. This step uses vans or trucks that drive short distances. These vehicles stop many times to deliver packages. Each delivery puts more vehicles on city streets. More vehicles cause more emissions and hurt the environment. Delivery trucks often wait in traffic or park on busy roads. This makes emissions go up and air quality get worse. Many deliveries in one place can also make noise and safety problems for people nearby.
Traffic and Air Quality
Express logistics channels change how traffic works in cities. Studies from Europe and North America show warehouses are now farther from city centers. Trucks have to drive longer to deliver packages. This makes emissions go up and hurts the environment more. More trucks on the road cause more traffic jams and slower cars. These changes mean higher emissions, more air pollution, and bigger risks for the environment. People in cities notice more noise and bad air from deliveries. The environment has more problems as delivery vehicle emissions rise. Cities need to find ways to lower the environmental impact of express logistics channels and keep air clean for everyone.
Impact of Logistics on the Environment
Energy Consumption in Facilities
Warehouses and distribution centers use lots of energy each day. They need power for lights, heating, cooling, and machines. Many places work all day and night to ship things fast. Using so much energy makes more greenhouse gas emissions. Old equipment or bad insulation wastes even more energy. Some companies now use energy-saving lights and smart systems. These changes help lower the harm to the environment. Solar panels and better building designs also help use less energy. Companies that save energy can help the planet and spend less money.
Resource Use and Land Redundancy
Logistics facilities need big pieces of land. Companies build warehouses, parking lots, and loading docks for goods. Sometimes, they build more buildings than they really need. This is called land redundancy. Empty or barely used buildings waste land and resources. Studies show that planning models can help companies use land better. These models help companies use land and resources in smart ways. They also check if buildings work well during problems. For example, a study in Morocco used these models to help ambulance services. The same ideas help logistics companies waste less and lower their impact. Good planning keeps land safe and helps the environment stay healthy.
Consumer Demand and Express Delivery
Fast Shipping and Environmental Cost
People like to get their online orders fast. This makes companies change how they deliver packages. When people pick same-day or next-day shipping, trucks leave more often. These trucks do not carry many packages each time. So, there are more trips and more pollution. A study in Mexico found fast shipping makes CO2 emissions go up by 15%. It also makes logistics cost 68% more. Trucks leave before they are full, so they waste gas and space. In California, freight causes one-fourth of greenhouse gas emissions. Wanting fast shipping puts more trucks on the road. Many trucks are not full, so pollution gets worse. Expert Miguel Jaller from UC Davis says every fast shipping choice adds to traffic and pollution. People who shop online do not always see this, but it gets bigger with every order.
Returns and Failed Deliveries
Many people return things they buy online. Sometimes, packages cannot be delivered if no one is home. These problems make trucks drive more trips. More trips mean more pollution and higher costs. Last-mile problems, like failed deliveries, are up to 28% of transport costs and about 25% of supply chain emissions. The chart below shows how these problems hurt the environment and business:
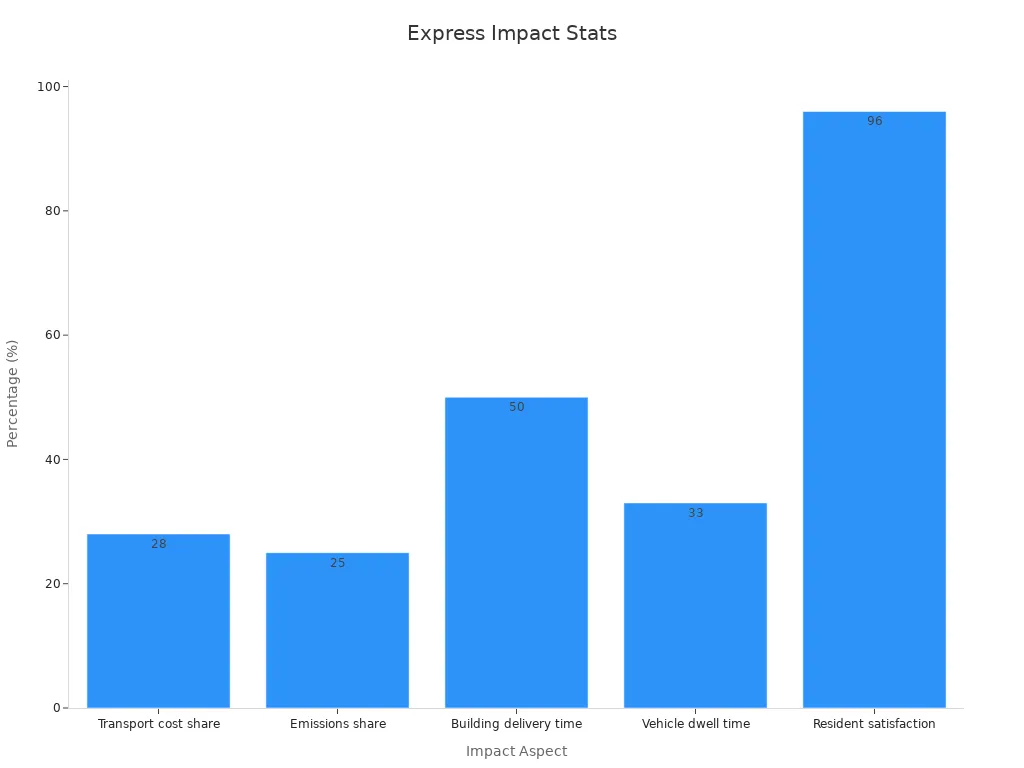
Parcel lockers help stop failed deliveries. They cut delivery time in buildings by half and lower wait time at the curb by one-third. In New York, delivery companies paid $123 million in parking fines in 2019 because of parking issues. When people return things, trucks must pick up and move them again. This makes more pollution. Studies show that better ideas, like parcel lockers, can help stop wasted trips and make shipping better.
Solutions for Reducing Environmental Impact

Route Optimization and Smart Planning
Route optimization and smart planning help companies pollute less and work better. Logistics teams use special models to pick the best truck routes. These models check road types, speed limits, and local rules. They also find ways to move goods with fewer stops and less time.
Researchers made a carbon emission model that uses route optimization and follows traffic rules. This model helps companies measure and lower emissions in express logistics.
Case studies show that using the shortest expressway routes with fewer transfers makes the least carbon emissions. These routes also follow local traffic laws.
High-grade roads and shorter routes are important for green logistics. They help companies reach their sustainability goals.
The best route for low emissions is not always the fastest or cheapest. Smart planning balances cost, speed, and emission targets.
Many studies, including those using P-median and neuro-fuzzy models, show that route optimization lowers emissions in road freight.
Real-world data from Turkey and China show that better vehicle routing can cut travel distance and fuel use. Truck upgrades and good routes can save up to 11.2% in carbon emissions.
New models now include traffic rules, making emission reduction plans more real and useful.
Smart planning and route optimization are key for green logistics. They help companies lower their carbon footprint and support sustainability.
Green Vehicles and Alternative Energy
Green vehicles and alternative energy are changing logistics. Electric vehicles, hybrid trucks, and trucks using renewable fuels help lower greenhouse gas emissions. Many companies now use these vehicles to support green logistics.
A review of 34 studies shows that electric vehicles lower emissions a lot. These studies compare electric vehicles, hybrids, and regular trucks in different countries. The results show that electric vehicles can lower global warming potential and help sustainability. But the benefits depend on the local electricity grid and how far the vehicles go. Some places see bigger improvements than others.
Another study looks at the full life cycle of vehicles. It finds that electric vehicles, plug-in hybrids, and hybrids all lower emissions compared to regular trucks. The study uses data from Norway, the US, and China. It shows that green vehicles do not fix every problem, but they help make transportation more sustainable.
Companies that use green vehicles and alternative energy make their operations more sustainable. They also give green delivery choices to customers who want to help the environment.
Sustainable Packaging Innovation
Sustainable packaging innovation helps cut waste in logistics. Companies design new packaging that uses less material and protects products better. This makes shipping more efficient and lowers waste sent to landfills.
A packaging innovation scorecard helps companies check how well their packaging supports sustainability. The scorecard looks at volume and weight efficiency. Better packaging means fewer damaged products and less waste. It also means trucks can carry more packages at once, which lowers emissions.
Sustainable packaging also helps green logistics by making the supply chain cleaner. Companies that use these ideas help lower greenhouse gas emissions and improve transport efficiency. They also show customers that they care about sustainability.
Companies that focus on sustainable packaging lead the way in green logistics. They set an example for others in the industry.
Collaborative Logistics Models
Collaborative logistics models bring companies together to share resources and lower environmental impact. When companies work together, they can fill trucks more and plan better routes. This lowers the number of trips and cuts emissions.
Shared delivery networks help companies reach more customers with fewer vehicles.
Joint warehousing lets companies use space better.
Data sharing helps everyone plan better and avoid empty trips.
Collaboration supports sustainable strategies and helps companies reach their sustainability goals. It also makes green logistics work better by lowering waste and emissions. When companies join forces, they can offer sustainable transportation to more customers.
Collaboration is a strong tool for building a greener future in logistics. It helps companies save money and protect the environment at the same time.
JUSDA and China-Europe Express Rail
Rail Transport for Lower Emissions
Rail transport is better for the environment than trucks or planes. Trains can carry lots of goods using less fuel. This means fewer emissions and helps the planet. One ton of freight can go almost 500 miles on one gallon of fuel by train. Union Pacific saved 18 million gallons of fuel in 2023 with smart energy systems. Rail freight makes up to 75% less CO2 than road freight. It also makes up to 90% less CO2 than air freight. In the UK, rail takes away 7 million truck trips each year. This saves 1.4 million tonnes of CO2.
Comparison | Rail vs Road Freight | Rail vs Air Freight | Example Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
CO2 Emissions Reduction | 75% less | Up to 90% less | Walmart cut 11 million truck miles by using rail |
Freight Volume Impact | 7 million fewer trucks | N/A | UK saves 1.4 million tonnes CO2 yearly |
JUSDA’s China-Europe Express Rail uses these green benefits. The service is fast, not too expensive, and better for the environment. Companies can ship goods quickly and make less pollution.
JUSDA’s Sustainable Supply Chain Solutions
JUSDA is a leader in making supply chains greener. The company uses rail transport and smart planning. The China-Europe Express Rail connects China and Europe in 15 to 20 days. This is faster than sea freight and cleaner than air. JUSDA uses technology to plan routes and save energy. The company also uses green packaging and smart warehouses. These actions help lower emissions and waste. JUSDA’s new ideas and smart choices show they care about a cleaner future for trade.

JUSDA Solutions
To provide you with professional solutions and quotations.
The effect of express logistics channels on the environment gets bigger every year.
This industry makes about one-fourth of the world’s carbon emissions and uses a lot of resources that cannot be replaced.
Green logistics, such as JUSDA’s rail solutions, help make less harm to the environment.
People can choose brands that care about the planet and make choices that help the environment.
See Also
Paving The Way For Logistics Through Digital Innovation
Understanding Emerging Trends In Logistics Risk Management
Overcoming Supply Chain Growth Issues In A Connected World
How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Future Logistics
