Logistics Management is Leveling up with Generative AI
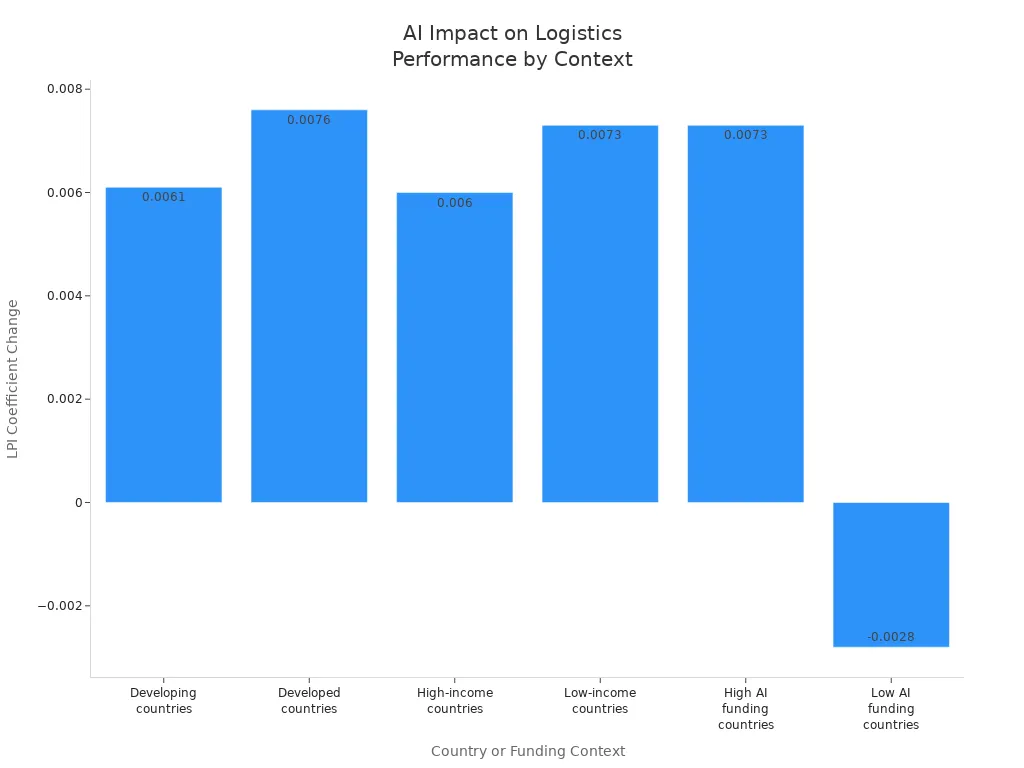
Generative AI is reshaping logistics management. Companies now see faster deliveries, smarter resource use, and new job opportunities. A recent survey found that logistics professionals value generative AI for automating communication and improving demand forecasting. The following table shows how AI investments boost logistics efficiency in different countries:
Context | AI Impact on Logistics Performance (LPI Coefficient) | Significance & Notes |
|---|---|---|
Developing countries | Positive and significant impact indicating AI investments improve logistics efficiency. | |
Developed countries | +0.0076 | Stronger positive effect, showing greater benefits in developed economies. |
High-income countries | +0.0060 | Significant positive impact on logistics performance. |
Low-income countries | +0.0073 | Even stronger positive effect, highlighting AI's potential in less developed regions. |
High AI funding countries | +0.0073 | Significant positive impact, emphasizing the importance of substantial AI investment. |
Low AI funding countries | -0.0028 | Negative and not significant, suggesting insufficient AI investment fails to improve logistics. |
Key Takeaways
Generative AI helps logistics companies improve demand forecasting, route planning, and inventory management, leading to faster deliveries and lower costs.
AI-powered tools like chatbots, robots, and automation systems increase warehouse speed and accuracy while reducing errors and labor costs.
Smart AI systems optimize delivery routes and load management, saving fuel, cutting emissions, and boosting shipment capacity.
AI creates new job roles in logistics, requiring workers to learn skills in data analysis, AI management, and automation supervision.
Companies must address challenges like high implementation costs, data privacy, and worker training to successfully adopt AI and stay competitive.
Generative AI in Logistics

Immediate Impact
Generative AI is changing logistics management in many ways. Companies use it to predict demand, plan production, and select suppliers. For example, generative AI analyzes sales data and market trends to forecast customer needs. This helps teams keep the right amount of stock and avoid shortages. AI also creates better production schedules by looking at demand and resources. This reduces bottlenecks and improves efficiency.
Logistics teams use generative AI to spot risks before they happen. The technology studies data from markets, weather, and global events. It then simulates crisis scenarios and suggests ways to avoid problems. Supplier selection also benefits from AI. Walmart uses chatbots to negotiate with suppliers, saving money and improving payment terms.
Generative AI helps design new products quickly. It tests different materials and shapes, making innovation faster and more sustainable.
Companies like UPS Capital use AI to plan delivery routes. The system checks traffic and weather to find the best path, saving fuel and time. Toyota’s AI platform predicts when vehicles need repairs, which saves thousands of work hours each year. Dematic uses AI to organize warehouses and forecast inventory needs, making operations more agile.
Key Technologies
Many technologies support generative AI in logistics. AI-powered chatbots answer customer questions, track shipments, and schedule deliveries. These chatbots work across different channels and languages, improving customer service.
Document automation tools read invoices and bills, entering data and fixing errors. Hyperautomation combines AI with robotic process automation to handle tasks like scheduling and tracking shipments. Large language models help with demand forecasting, supply planning, and inventory management. Some systems even automate freight execution, moving toward “touchless load” operations.
AI-powered robots pick, pack, and move products in warehouses. Amazon uses robots like Hercules and Titan to carry shelves and avoid collisions.
Autonomous mobile robots transport heavy carts and work together for efficient loading.
AI systems optimize packaging, sorting, and labeling, ensuring correct loading onto trucks.
These technologies make logistics faster, more accurate, and less costly.
Operational Efficiency
Generative AI brings new levels of operational efficiency to logistics. Companies now use smart systems to optimize routes, manage loads, automate warehouses, and forecast demand. These improvements help reduce costs, speed up deliveries, and make better use of resources.
Route Optimization
AI-powered route optimization tools help logistics teams find the fastest and most efficient paths for deliveries. These systems use real-time data, such as traffic, weather, and vehicle location, to adjust routes on the fly. A logistics company that used AI-driven route planning saw a 20% drop in fuel costs and a 30% improvement in delivery times. Shipping companies also report a 10% reduction in fuel use by choosing better routes.
AI route optimization not only saves money but also cuts down on carbon emissions by reducing unnecessary travel and idling.
Many companies have seen other benefits:
Freight companies save thousands each year by avoiding backtracking and extra stops.
Municipal fleets cut overtime costs by rerouting vehicles based on live updates.
Grocery and retail networks improve on-time deliveries, which builds customer trust.
Urban delivery fleets avoid traffic jams, preventing delays during busy hours.
Load Management
Generative AI helps logistics teams maximize shipment capacity and reduce costs. It automates carrier onboarding by checking credentials and performance, making carrier selection faster and more reliable. AI also enables real-time communication between carriers and shippers, improving route planning and supply chain visibility.
The following table shows how generative AI optimizes load management:
Aspect | How Generative AI Optimizes Load Management | Impact on Costs and Shipment Capacity |
|---|---|---|
Dynamic Route Optimization | Recalculates routes in real time using live data (weather, traffic, driver availability) to avoid delays and reduce fuel costs | Reduces operational costs and improves delivery times |
Fleet Coordination | Synchronizes multiple vehicles to maximize load efficiency and avoid redundant trips | Increases shipment capacity by better utilizing fleet resources |
Predictive Maintenance | Uses sensor data combined with environmental and operational factors to forecast maintenance needs | Minimizes downtime and unexpected repair costs |
Warehouse & Inventory Layout | Optimizes warehouse layout and inventory positioning based on demand, item size, and picking speed | Enhances picking speed and space utilization, increasing throughput |
Freight Audits & Onboarding | Automates verification, compliance, and carrier onboarding processes | Streamlines operations, reduces manual workload, and improves accuracy |
AI-driven systems also conduct freight audits and generate reports for demand forecasting and route planning. For example, one warehouse saved nearly $1 million a year by automating freight processing.
Warehouse Automation
Warehouse automation powered by AI has changed how companies handle inventory and orders. Robots now process orders three times faster than humans. Automated systems can handle three to five times more orders in the same space. AI-powered inventory tracking and sorting reach 99.9% accuracy, which means fewer mistakes like overstocking or misplacing items.
Aspect | Evidence Detail | Impact on Labor Productivity and Error Reduction |
|---|---|---|
Processing Speed | AI-driven robots process orders 3x faster than humans. | Significantly increases throughput and order handling capacity. |
Order Volume Capacity | Automated systems handle 3-5 times more orders within the same warehouse footprint. | Enables scalability without proportional labor increase. |
Accuracy Rates | AI-powered inventory tracking and sorting achieve 99.9%+ accuracy. | Minimizes costly errors like overstocking, understocking, and misplacements. |
Labor Cost Reduction | Automation reduces dependency on manual labor, cutting operational costs. | Frees human workers for higher-value tasks, improving overall productivity. |
Real-World Examples | Amazon uses 750,000+ AI robots; DHL robotic sortation sorts 1000+ parcels/hour with near-zero errors. | Demonstrates practical efficiency gains and error reduction in large-scale operations. |
Error Reduction | UPS reduces sorting errors by 99% using AI vision systems. | Enhances customer satisfaction and reduces returns. |
Labor Optimization | Automation handles repetitive tasks; humans focus on complex problem-solving and quality control. | Improves job satisfaction and addresses labor shortages. |
Automated warehouses operate around the clock, increasing throughput and reducing errors. Human workers can focus on solving problems and quality control, while robots handle repetitive tasks.
Demand Forecasting
AI-based demand forecasting tools help companies predict what products customers will need and when. These tools use real-time data from many sources, such as sales trends, weather, and social media. AI forecasting improves accuracy by 20-50% compared to traditional methods. This leads to better stock alignment, fewer shortages, and less waste.
Aspect | AI-Based Demand Forecasting | Traditional Forecasting Methods |
|---|---|---|
Forecast Accuracy | Improves accuracy by 20-50% | Relies heavily on historical data, less adaptive |
Inventory Cost Reduction | Reduces inventory costs by 20-50% | Higher costs due to overstock and stockouts |
Data Utilization | Uses real-time, structured & unstructured data | Primarily historical data, manual processes |
Adaptability | Quickly adapts to market changes and disruptions | Struggles with sudden market shifts |
Operational Efficiency | Automates forecasting, reduces manual errors | Labor-intensive, prone to human error |
Inventory Management | Enables precise inventory optimization | Less precise, higher risk of phantom inventory |
Scalability | Scales with data volume and business growth | Limited scalability |
Customer Satisfaction | Enhanced through better stock alignment | Can suffer due to inaccurate forecasts |
Traditional forecasting relies on past sales and manual calculations, which can lead to errors and slow responses to market changes. AI forecasting uses machine learning to spot patterns and adjust quickly. Companies like Walmart use AI to analyze sales and events, keeping shelves stocked and customers happy.
AI-driven demand forecasting reduces overstock and stockouts, cuts inventory costs, and improves customer satisfaction.
Sustainability
Reducing Emissions
Logistics companies use smart technology to lower emissions and save fuel. AI systems help plan delivery routes that avoid traffic and cut down on travel distance. For example, Amazon reduced its CO2 emissions intensity by 34% while doubling its revenue. Uber Freight uses AI to match return trips with nearby pickups, which cuts empty miles by up to 15%. Off-peak deliveries scheduled by AI avoid traffic jams, lowering fuel use and idle time. A transportation provider using Apexon's AI fleet management platform saw an 18% drop in fuel costs and a 12% reduction in delivery times. These changes help companies reduce their carbon footprint and save money.
Companies can cut up to 10% of their carbon emissions by using AI to choose low-emission routes and optimize load distribution.
Waste Minimization
AI helps companies reduce waste in many ways. It improves demand forecasting by studying sales and market trends, which helps balance supply and demand. This means fewer stockouts and less extra inventory. AI-driven inventory systems lower surplus and overstocking, making supply chains more responsive. Companies like Amazon use AI to design smaller packages with sustainable materials, which reduces packaging waste. AI also tracks damaged items and food, helping companies throw away less. When customers return products, AI decides if items should be repaired, recycled, or disposed of, cutting down on unnecessary waste.
AI improves apparel fit, which lowers the number of returns and reduces waste from unwanted goods.
Accenture built an AI solution that collects supplier data to track carbon emissions and help companies manage environmental waste.
Supply Chain Transparency
AI makes supply chains more transparent by tracking products and their carbon footprints. It connects with blockchain to show where products come from and how much energy they use. Companies can see which suppliers use less energy or produce fewer emissions. Ikea uses AI to measure emissions from purchased products and works with partners to improve sustainability. Target uses AI to manage energy but faces challenges with reporting transportation emissions. AI also helps companies choose suppliers based on sustainability scores, making it easier to meet environmental goals.
Benefit | How AI Supports Transparency | Example Companies |
|---|---|---|
Product Tracking | Monitors origins and carbon footprints | Ikea, Amazon |
Supplier Evaluation | Rates partners on sustainability metrics | Target, Accenture |
Emissions Reporting | Aggregates data for Scope 3 tracking | Accenture, Ikea |
Compliance Management | Ensures supply chain meets green standards | Amazon, Target |
Transparent supply chains help companies meet sustainability targets and build trust with customers.
Workforce Transformation
New Roles
Logistics organizations see big changes in job roles as AI tools become more common. Many tasks, such as inventory management, warehouse layout design, and route planning, now use automation. Workers spend less time on repetitive jobs and more time on complex problem-solving. AI systems handle data-heavy work, so employees can focus on tasks that need human judgment. New positions appear, such as AI system managers, data analysts, and automation supervisors. These roles require people to oversee AI outputs and make sure results match business goals.
AI automates routine customer service, letting staff handle difficult questions.
Workers now monitor AI-driven demand forecasts and adjust plans as needed.
Teams use AI to spot risks and suggest solutions before problems grow.
Human oversight stays important to keep AI decisions accurate and fair.
Skills and Training
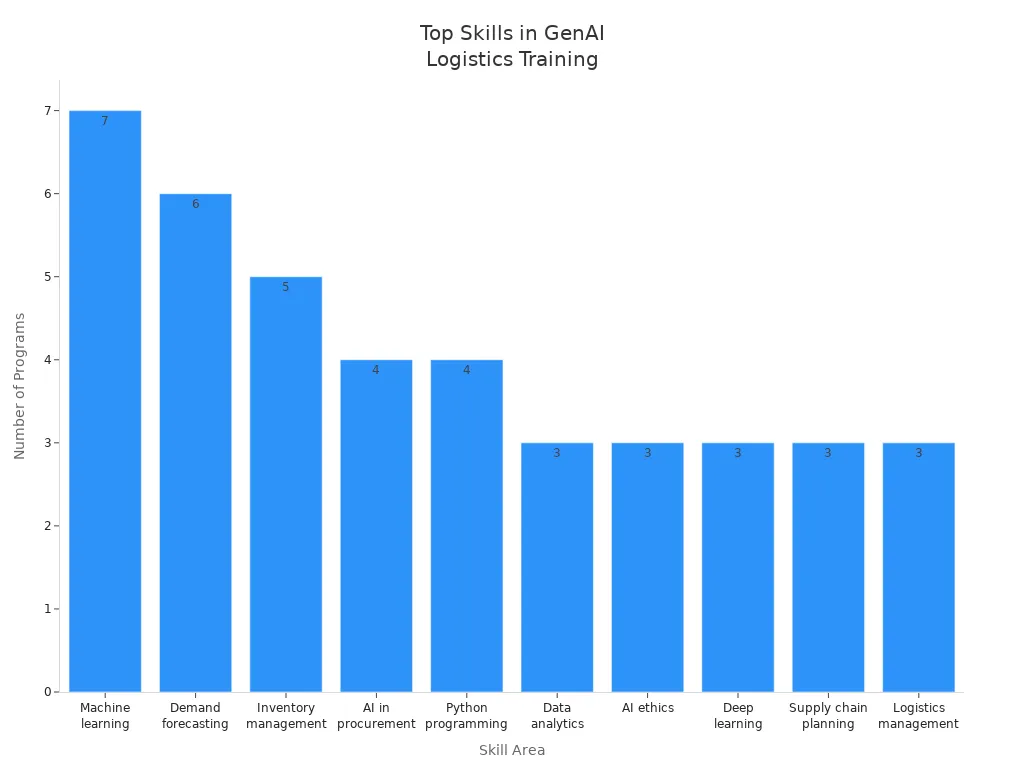
Modern logistics teams need new skills to work with AI systems. Data science, machine learning, and AI ethics are now in high demand. Professionals must understand supply chain operations and know how to manage change. Many training programs teach these skills, from short online courses to advanced degrees.
Course / Program Name | Certifying Organization | Key Skills and Training Focus | Duration | Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Generative AI in Supply Chain Management | Indian Institute of Management Mumbai | Demand forecasting, procurement, inventory management, pricing decisions | 15 hours live online | None specified |
Master of Science in Applied Artificial Intelligence for Supply Chain Management | International University of Applied Sciences | Machine learning, AI in supply management, Python programming, statistics | 12-24 months | Undergraduate degree, math and Python knowledge |
AI for Logistics and Maritime | Netherlands AI Coalition | AI applications in logistics, measuring AI results | 4 hours | None specified |
ChatGPT/Generative AI for Supply Chain Masterclass | Udemy | Demand forecasting, inventory optimization, ROI measurement, ethics | 1.5 hours | Basic SCM understanding |
Training also covers how to use AI tools with existing systems like ERPs and warehouse management software. Ethical training helps workers spot bias and keep AI results trustworthy.
Human-AI Collaboration
Teams in logistics now work closely with AI tools to improve results. AI helps with route optimization, document processing, warehouse management, and predictive maintenance. These tools give real-time insights and automate routine tasks. Workers use AI-powered dashboards to track shipments and spot issues quickly.
AI acts as a co-pilot, suggesting actions while humans make final decisions.
Teams start with small projects, clean data, and review AI outputs for trust.
No-code platforms let staff build custom AI tools without deep programming skills.
Companies see up to 15% better supply chain efficiency and 12% lower costs.
DHL and Honeywell use AI to boost delivery speed and warehouse accuracy.
Human-AI collaboration leads to higher productivity, better service, and more satisfied customers.
Challenges
Implementation Costs
Logistics companies face high upfront costs when they start using new AI tools. These costs include buying hardware, software licenses, and paying experts. Training staff and building AI models also add to expenses. Many companies see big savings after they start using AI. One logistics company saved $2.1 million each year by reducing staff and errors. Another gained $3.4 million in extra revenue by increasing shipment capacity. Error rates dropped from 4% to 0.8%. Most companies see a return on investment between 30% and 200% within three years. Many systems pay for themselves in one to one and a half years. Scaling up adds 15-25% to initial costs, but future expansion costs drop by 40-60%.
Aspect | Details / Figures |
|---|---|
Upfront Implementation Costs | Moderate compared to healthcare and finance industries |
Operational Savings | $2.1M annual savings from reduced staff and error rate improvements |
Revenue Gains | $3.4M additional revenue from increased shipment capacity |
Error Rate Reduction | From 4% to 0.8% in logistics example |
ROI Range | 30% to 200% within three years; many systems pay for themselves within 1 to 1.5 years |
Scalability Costs | Add 15-25% to initial costs but reduce future expansion costs by 40-60% |
Industry Cost Variations | Healthcare: $750K-$2M; Finance: $600K-$1.8M; Manufacturing: $500K-$1.5M; Retail: $350K-$1.2M |
Regulatory Impact | Adds ~23% to AI implementation costs in regulated industries |
Companies must align AI projects with business goals to maximize returns. Cross-team collaboration helps find the best uses for AI.
Data Privacy
Protecting data is a major concern for logistics companies. Large datasets can expose sensitive information and increase the risk of identity theft. Companies use privacy policies, encryption, and access controls to keep data safe. Regular privacy audits test how well data is anonymized. Clear communication about data use and user rights builds trust. Regulations like GDPR and CCPA require strict data handling. Companies limit data collection and use synthetic data to lower risks.
AI models often train on limited or redacted data to reduce exposure.
Controlled environments help test AI before full use.
Strong access controls and risk assessments prevent leaks.
Employees learn cybersecurity best practices.
Privacy techniques like anonymization and memory scrubbing protect user data.
Closed-source models in closed systems limit data handling.
Companies encourage users to review privacy settings and understand how their data is used.
Change Management
Adopting new AI tools brings big changes to logistics teams. Many workers resist change. A recent survey found that 72% of failed AI projects happened because workers did not accept new systems. Lack of AI knowledge is common, especially in small companies. Skill gaps and data quality problems slow progress.
Companies explain what the AI tool does and how it helps.
Leaders identify who will use the tool and offer training.
Clear timelines set expectations for when to use new tools.
Open communication about benefits builds trust.
Strong leadership supports employees and encourages them to become ambassadors.
Training and safe spaces for experimentation help workers gain confidence.
Agile pilot projects allow teams to learn and adapt.
Success is measured and celebrated to build momentum.
Companies must focus on education, integration, and proving business value to succeed with AI.
Generative AI brings major changes to logistics management. Companies see better demand forecasting, smarter route planning, and improved inventory control. Key challenges include data quality, high costs, and the need for skilled workers.
Professionals should use advanced AI models, connect real-time data, and train teams for new tools.
The future of logistics will rely on ongoing AI innovation, helping teams work faster, safer, and more sustainably.
FAQ
What is generative AI in logistics?
Generative AI uses smart computer programs to help companies plan, predict, and solve problems in moving goods. These tools learn from data and suggest better ways to manage deliveries, warehouses, and inventory.
How does generative AI improve delivery times?
AI checks traffic, weather, and order details. It then finds the fastest routes for drivers. Companies see fewer delays and faster deliveries.
AI helps drivers avoid traffic jams and roadblocks.
Is generative AI safe for private data?
Most companies use strong security tools like encryption and access controls. They also follow privacy laws.
Regular audits check for risks.
Employees learn how to keep data safe.
What new jobs does generative AI create in logistics?
New Role | Main Task |
|---|---|
AI System Manager | Oversees AI tools |
Data Analyst | Studies and explains AI results |
Automation Supervisor | Checks robots and smart systems |
These jobs need people who can work with technology and solve problems.
See Also
Discovering Hidden Opportunities Of AI Within Logistics
How AI Is Transforming The Future Supply Chain
Insights Into AI Integration For Future Supply Chains
Machine Learning And Big Data Changing Supply Chain Management
