A guide to the future of manufacturing technology and its implications
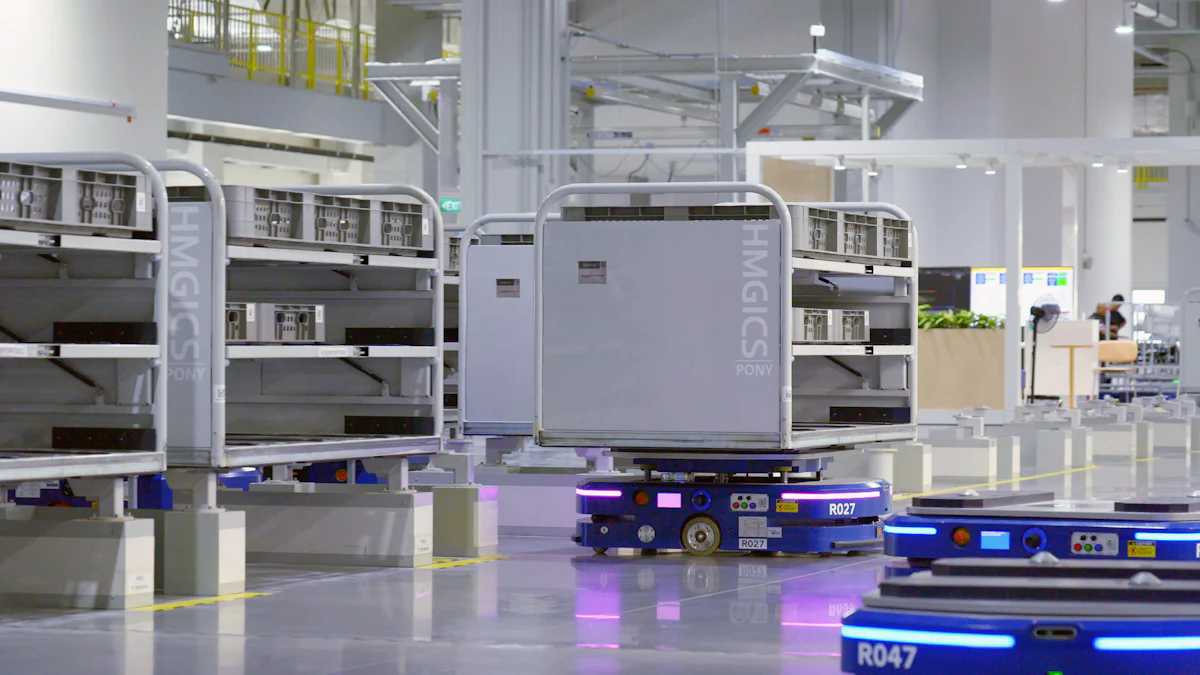

The future of manufacturing technology is rapidly reshaping industries globally. Cutting-edge technologies like AI, robotics, and IoT are driving a revolution in production processes. AI algorithms have the capability to swiftly analyze data, identifying crucial patterns and trends. Automation and smart manufacturing empower manufacturers to enhance both productivity and precision. It is essential for businesses to grasp upcoming trends in manufacturing technology to maintain their competitiveness. The fusion of advanced technologies leads to streamlined operations, influencing a wide range of products from aircraft components to pharmaceuticals.
Key Technologies Shaping the Future of Manufacturing Technology
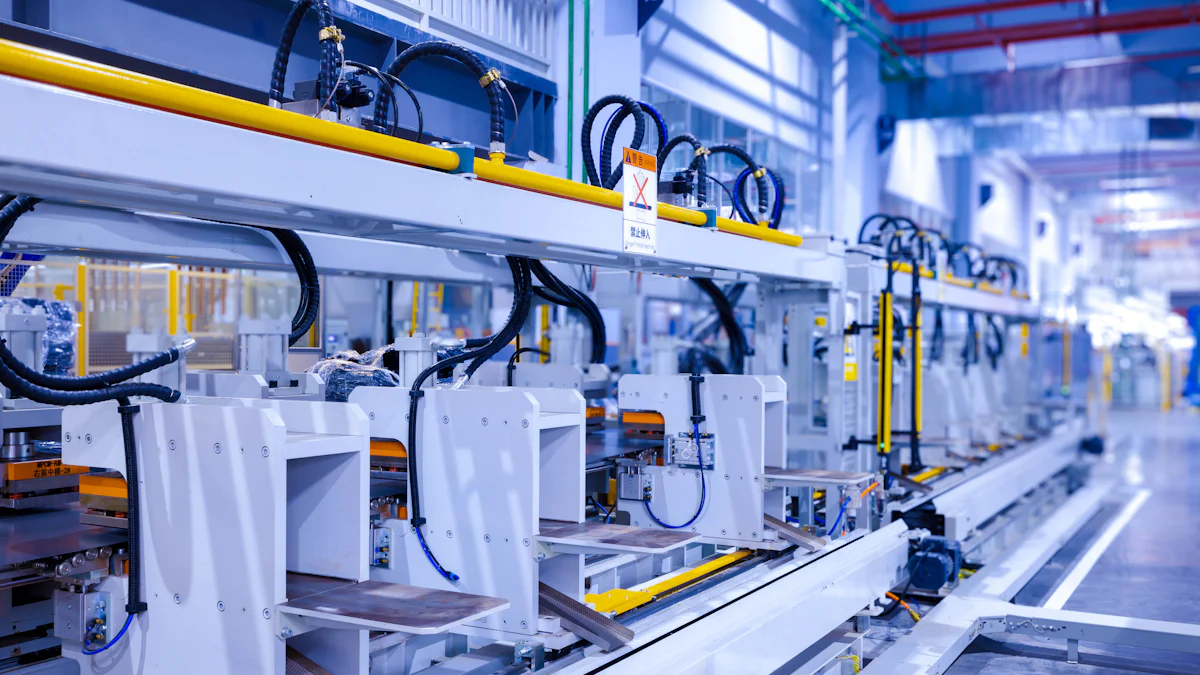

Automation and Robotics
Advanced Robotics
Advanced robotics play a crucial role in modern manufacturing. These systems enable precision movement, precision joining, and heavy lifting. Robotics excel in tasks that are hazardous for human workers. Automated robotic systems improve consistency across production units. This technology enhances product quality by reducing errors and defects.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside human operators. Cobots enhance productivity and safety in manufacturing environments. These robots handle repetitive tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more complex activities. Cobots are designed to be user-friendly and easily programmable. This makes them accessible to a wide range of industries.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Innovations in Materials
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is revolutionizing the future of manufacturing technology. Innovations in materials have expanded the applications of 3D printing. Advanced materials such as metals, ceramics, and composites are now used in 3D printing processes. These materials offer greater strength, durability, and flexibility. This technology enables the creation of complex geometries that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
Applications in Various Industries
3D printing has found applications in various industries. The aerospace industry uses 3D printing to produce lightweight and complex components. The medical field benefits from 3D-printed implants and prosthetics tailored to individual patients. The automotive industry leverages 3D printing for rapid prototyping and custom parts production. These applications demonstrate the versatility and potential of additive manufacturing.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Manufacturing
IoT-Enabled Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming manufacturing into a smart and connected environment. IoT-enabled devices collect and transmit data in real-time. Sensors embedded in machinery monitor performance and detect anomalies. This data-driven approach allows for proactive maintenance and reduces downtime. IoT technology enhances operational efficiency and productivity.
Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance
Data analytics play a pivotal role in smart manufacturing. Advanced algorithms analyze data collected from IoT devices. Predictive maintenance uses this data to forecast equipment failures before they occur. This approach minimizes unplanned downtime and extends the lifespan of machinery. Data analytics also optimize production processes by identifying inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI in Quality Control
Artificial intelligence (AI) significantly enhances quality control in manufacturing. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data from production lines. This analysis identifies defects and inconsistencies in real-time. Manufacturers can address issues immediately, reducing waste and improving product quality. AI systems also predict potential problems before they occur. This predictive capability minimizes downtime and maintains consistent production standards.
AI-powered vision systems inspect products with high precision. These systems detect minute defects that human eyes might miss. The integration of AI in quality control ensures higher accuracy and reliability. Manufacturers benefit from reduced error rates and enhanced customer satisfaction. AI-driven quality control represents a critical advancement in the future of manufacturing technology.
Machine Learning for Process Optimization
Machine learning (ML) optimizes manufacturing processes by analyzing data patterns. ML algorithms identify inefficiencies and suggest improvements. These insights lead to more efficient use of resources and energy. Manufacturers achieve higher productivity and lower operational costs. ML models continuously learn and adapt to changing conditions. This adaptability ensures ongoing process optimization.
Manufacturers use ML to monitor equipment performance. Predictive maintenance schedules reduce unexpected breakdowns. This proactive approach extends machinery lifespan and reduces maintenance costs. ML also enhances supply chain management by predicting demand and optimizing inventory levels. The application of ML in manufacturing drives significant advancements in the future of manufacturing technology.
Benefits of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Reduced Downtime
Advanced manufacturing technologies significantly reduce downtime. Predictive maintenance systems, powered by AI, forecast equipment failures before they occur. This proactive approach minimizes unexpected breakdowns. Manufacturers can schedule maintenance activities during non-peak hours. This ensures continuous production and maximizes uptime.
Enhanced Precision and Accuracy
Enhanced precision and accuracy are crucial benefits of advanced manufacturing technologies. Robotics and automation systems execute tasks with high precision. These systems eliminate human errors and inconsistencies. AI-driven quality control systems detect defects in real-time. This ensures that products meet stringent quality standards. Manufacturers achieve higher consistency and reliability in their production processes.
Cost Reduction
Lower Labor Costs
Lower labor costs result from the implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies. Automation and robotics handle repetitive and hazardous tasks. This reduces the need for manual labor. Manufacturers can allocate human resources to more strategic roles. This shift enhances overall productivity and efficiency.
Material Savings
Material savings are another significant advantage. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, optimizes material usage. This technology creates products layer by layer, minimizing waste. Manufacturers can produce complex geometries without excess material. This leads to substantial cost savings and resource efficiency.
Environmental Sustainability
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a key benefit of advanced manufacturing technologies. IoT-enabled devices monitor energy consumption in real-time. Data analytics optimize energy usage across production lines. Manufacturers can identify and eliminate energy inefficiencies. This reduces operational costs and environmental impact.
Waste Reduction
Waste reduction is essential for sustainable manufacturing. Advanced technologies enable precise control over production processes. AI and machine learning optimize resource utilization. This minimizes waste generation and enhances sustainability. Manufacturers can achieve eco-friendly production practices while maintaining high-quality standards.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementation Costs
Initial Investment
Implementing advanced manufacturing technologies requires a substantial initial investment. Companies must purchase new equipment and software. The cost of integrating these technologies into existing systems can be high. Businesses need to budget for these expenses to avoid financial strain.
Ongoing Maintenance
Ongoing maintenance of advanced manufacturing technologies also incurs costs. Regular updates and repairs are necessary to keep systems running smoothly. Companies must allocate funds for these activities. Proper maintenance ensures the longevity and efficiency of the technology.
Workforce Adaptation
Skill Gaps
The adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies creates skill gaps in the workforce. Many workers lack the necessary skills to operate new machinery and software. This gap poses a challenge for companies looking to modernize their operations. Businesses must identify these gaps and develop strategies to address them.
Training and Education
Training and education are crucial for workforce adaptation. Companies must invest in training programs to upskill their employees. These programs should focus on the specific technologies being implemented. Continuous education ensures that workers stay updated with the latest advancements. This investment in human capital enhances overall productivity and efficiency.
Cybersecurity Risks
Protecting Intellectual Property
Cybersecurity risks pose a significant threat to advanced manufacturing technologies. Protecting intellectual property is a primary concern. Companies must implement robust security measures to safeguard their innovations. Unauthorized access to proprietary information can lead to competitive disadvantages. Strong cybersecurity protocols are essential to prevent such breaches.
Ensuring Data Privacy
Ensuring data privacy is another critical aspect of cybersecurity. Advanced manufacturing technologies generate vast amounts of data. This data includes sensitive information about production processes and business operations. Companies must ensure that this data remains confidential. Implementing encryption and access controls helps protect data privacy. These measures build trust with customers and partners, ensuring long-term business success.
Future Predictions and Trends in Manufacturing Technology
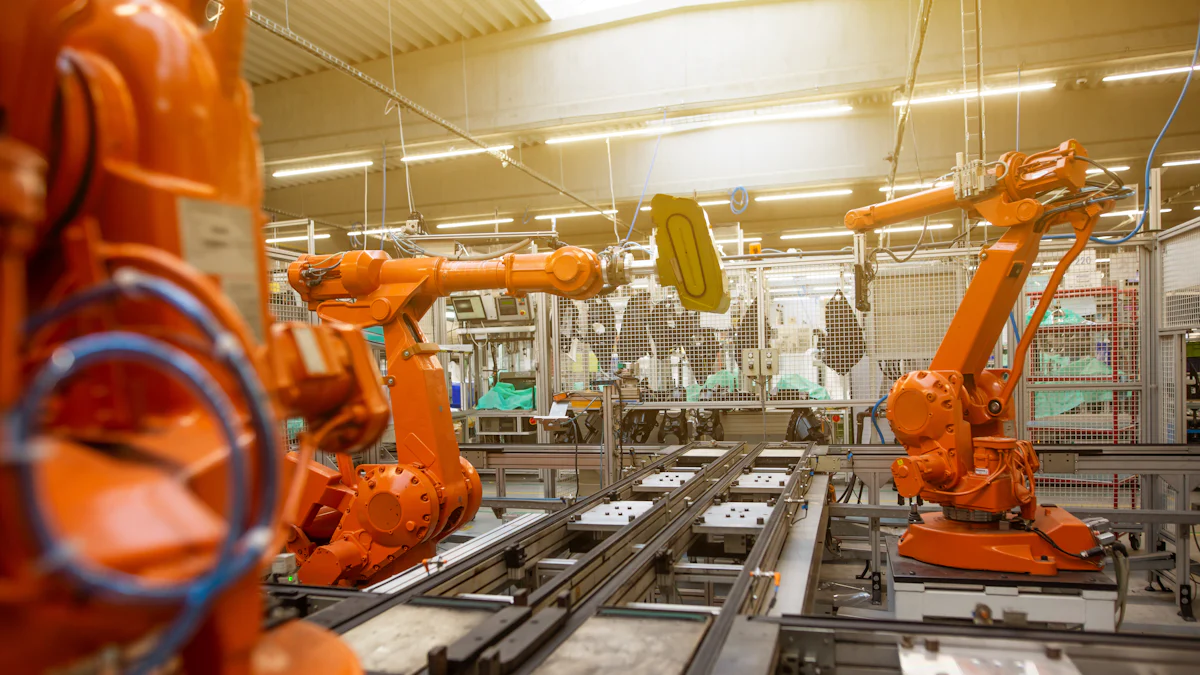

Emerging Technologies
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing promises to revolutionize the future of manufacturing technology. Quantum computers can process complex calculations at unprecedented speeds. This capability will enable manufacturers to optimize production processes with greater precision. Quantum algorithms can simulate material properties, leading to the development of new materials. These advancements will enhance product quality and reduce production costs.
Biotechnology in Manufacturing
Biotechnology is another emerging technology shaping the future of manufacturing technology. Biotechnology integrates biological processes into manufacturing. This approach can produce bio-based materials and chemicals. Manufacturers can use biotechnology to create sustainable and eco-friendly products. Biotechnology also enables the production of personalized medicines and medical devices. These innovations will transform industries such as healthcare and agriculture.
Industry 4.0 and Beyond
Integration of Cyber-Physical Systems
Industry 4.0 involves the integration of cyber-physical systems in manufacturing. Cyber-physical systems combine physical processes with digital technologies. These systems enable real-time monitoring and control of production processes. Manufacturers can achieve higher efficiency and flexibility through this integration. Cyber-physical systems also facilitate the implementation of smart manufacturing practices.
Evolution of Smart Factories
Smart factories represent the next phase in the evolution of manufacturing technology. Smart factories utilize advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and robotics. These technologies enable autonomous and self-optimizing production processes. Smart factories can adapt to changing conditions and demands in real-time. This adaptability enhances productivity and reduces operational costs. The evolution of smart factories will drive the future of manufacturing technology.
Global Implications
Economic Impact
The future of manufacturing technology will have significant economic implications. Advanced technologies will increase productivity and reduce production costs. These improvements will enhance the competitiveness of manufacturers. The adoption of new technologies will also create high-skilled jobs. However, there may be a displacement of low-skilled workers. Policymakers must address these challenges to ensure inclusive economic growth.
Social and Ethical Considerations
The future of manufacturing technology raises important social and ethical considerations. The widespread use of automation and AI may lead to job displacement. Society must address the potential impact on workers and communities. Ethical considerations also arise regarding data privacy and security. Manufacturers must implement robust measures to protect sensitive information. Ensuring ethical practices will be crucial for the sustainable development of manufacturing technology.
JUSDA's Role in the Future of Manufacturing Technology
JusLink Platform
Full-Chain Supply Chain Visibility
JusLink offers full-chain supply chain visibility. This platform allows real-time monitoring of all supply chain nodes. Clients can identify and mitigate risks promptly. JusLink enhances transparency, ensuring efficient resource utilization. This visibility supports better decision-making processes.
AI-Driven Collaborative Intelligent System
JusLink features an AI-driven collaborative intelligent system. This system addresses common pain points in supply chain management. AI algorithms optimize operations by analyzing vast amounts of data. The system facilitates seamless collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, and customers. This integration drives the future of manufacturing technology forward.
SMART JusLink
Supply Chain Management Solution
Real-World Applications and Performance
Case Example: Global Presence and Network
JUSDA operates 155 service points worldwide. The company manages over 2.5 million square meters of warehousing space. JUSDA maintains more than 2,000 international service routes. This extensive network supports global supply chain operations. The company's reach exemplifies its role in the future of manufacturing technology.
Data-Driven Improvements
JUSDA leverages data to drive continuous improvements. The company uses data analytics to enhance supply chain efficiency. Predictive models forecast demand and optimize inventory levels. Data-driven insights help reduce operational costs. These improvements ensure that JUSDA remains at the forefront of manufacturing technology.
Strategic Developments and Future Goals
Revenue and Profit Growth
JUSDA aims for significant revenue and profit growth. The company focuses on expanding its global footprint. Strategic investments in technology drive this growth. JUSDA's commitment to innovation ensures sustained profitability. The company adapts to market changes to maintain its competitive edge.
Technological Advancements
JUSDA prioritizes technological advancements. The company invests in big data analysis, cloud platforms, and IoT systems. These technologies enhance supply chain management. JUSDA's focus on innovation positions it as a leader in the future of manufacturing technology. The company continually seeks new ways to improve its services.
Future manufacturing technologies hold transformative potential. Businesses must stay informed and adaptable to leverage these advancements. Embracing innovation ensures a competitive edge in the evolving market. Technologies like automation, AI, and IoT drive efficiency and precision. Companies like JUSDA lead this transformation with advanced supply chain solutions. The JusLink platform exemplifies how technology can enhance operations. By adopting these innovations, manufacturers can achieve sustainable growth and operational excellence.
See Also
Maximizing Manufacturing Success in 2024 Through Supply Chain Tactics
Automated Tomorrow: Benefits of High-Tech Manufacturing Warehouses
Unlocking Triumph: Demystifying High-Tech Manufacturing Consulting
Collaborative Innovation: Strengthening Supplier Bonds in High-Tech Manufacturing
Journeying Through Lean Logistics for High-Tech Manufacturing Triumph
