How Supply Chains Manage Geopolitical Risk

Geopolitical risk can disrupt supply chains overnight. Recent events, such as pandemic-driven shutdowns in China and export restrictions in Europe, have shown that companies with resilient, technology-enabled supply chains adapt faster. For example, European firms that invested in innovation and preparedness faced fewer trade interruptions during COVID-19. Data also shows that production flexibility improves resilience by 30%. These facts highlight why proactive strategies and real-time visibility matter in protecting supply chains from global uncertainty.
Key Takeaways
Geopolitical risks like wars and trade disputes can disrupt supply chains and cause delays, higher costs, and lost sales.
Companies that identify risks early using mapping, AI, and real-time data can prepare better and avoid major problems.
Diversifying suppliers and transportation routes reduces vulnerability and helps companies stay strong during global uncertainty.
Working closely with suppliers and sharing data improves response speed and builds more resilient supply chains.
Technology solutions like JUSDA’s JusLink platform provide real-time visibility and predictive analytics to help companies manage risks effectively.
Why Geopolitical Risk Matters
Supply Chain Impacts
Geopolitical risk can change the way goods move around the world. When countries face conflict, trade wars, or new rules, supply chains often slow down or stop. Many supply chain leaders worry about these risks.
95% of Chief Procurement Officers feel concerned about geopolitical risk.
64% worry about tariffs, trade wars, and sanctions.
91% of supply chain leaders feel uneasy about changing regulations.
88% worry about the financial health of their suppliers.
A table below shows how these risks affect trade and shipping:
Statistic Description | Impact/Value |
|---|---|
Reduces trade flows by 2-3% | |
Brexit-related supply chain revenue loss | 15-19% |
Companies with late goods arrivals | 60-65% suffer reputational damage |
Air shipments from Vietnam to Europe (2024) | 62% increase |
Oil prices after war | Over $90 per barrel, raising costs |
When a conflict happens, like the Russia-Ukraine war, the Global Supply Chain Pressure Index shows that many sectors lose value. Utilities and telecommunications often see the biggest drops. These events prove that geopolitical risk can cause real problems for supply chains.
Business Consequences
Businesses feel the effects of geopolitical risk in many ways. They may lose money, face higher costs, or damage their reputation.
Over 80% of supply chain executives expect disruptions to continue or get worse.
Companies with strong risk management turn uncertainty into growth opportunities.
Firms that map their supply chains and use scenario modeling can spot weak points and plan better.
A table below shows some business risks:
Metric Category | Specific Metrics / Indicators | Description / Impact |
|---|---|---|
Reputational Risk | Reputation is 81% of market value; market cap can drop 1-3% in a day | Loss of trust leads to customer loss and investor worry. |
Strategic Risk | 45% of value lost in downturns; 8% lower shareholder return | Bad decisions hurt profits and company strength. |
Market Risk | Equity benchmarks can drop 5% in a day; currency moves cut margins | Price changes can quickly hurt business value. |
Credit Risk | Default risk rises; funding costs go up | Borrowers may default, raising costs and stress. |
Liquidity Risk | 40% of bankruptcies from cash-flow problems | Lack of cash can stop business operations. |
Unmanaged geopolitical risk can lead to lost sales, higher costs, and even bankruptcy. Companies that invest in technology, diversify suppliers, and work closely with partners can better handle these challenges.
Geopolitical Risk Assessment

Risk Identification
Supply chains must identify risks early to stay resilient. Companies use several methods to spot threats. Supply chain mapping helps visualize where problems might occur. Teams use risk matrices and scenario analysis to rate the likelihood and impact of each risk. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) breaks down each step in the supply chain to find weak spots. Many organizations now use AI and predictive analytics for continuous monitoring. For example, JUSDA’s JusLink platform uses real-time data and AI to track changes in political climates, trade policies, and supplier health. This approach gives early warnings so teams can act before disruptions grow.
Risk assessment techniques like risk matrices and FMEA
Continuous monitoring with AI and predictive analytics
Real-time tracking with IoT sensors
Vulnerability Mapping
Mapping vulnerabilities means finding weak points in the supply chain. Companies use digital tools to create maps of all suppliers, including those beyond the first tier. AI-driven platforms, such as JusLink, automate this process and reveal hidden risks. Weighted ranking systems score each supplier based on risk factors like location or financial health. Value at Risk (VaR) models estimate possible losses if a disruption occurs. These methods help companies compare risks and focus on the most critical areas.
Weighted ranking to score supplier risk
Value at Risk (VaR) to measure potential financial exposure
Bitsight Discover and IBM use AI to map digital supply chains and uncover single points of failure. This level of detail supports better decision-making.
Impact Evaluation
After mapping risks, companies must evaluate how disruptions could affect their operations. Many use numerical models to measure impact. Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) helps rank suppliers in risky environments. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) analyzes relationships between supply chain nodes. Probabilistic models, like Bayesian networks, study how risks spread. Fuzzy models rank risk factors and products. The TVP-SV-VAR model tracks how geopolitical risk changes over time and affects supply chain pressure.
Model Type | Description and Application | Frequency in Studies |
|---|---|---|
Multi-Criteria Decision Making | Used for supplier selection and risk ranking in disruptive environments, including risk and resilience profiles. | 13 out of 51 papers |
Structural Equation Modeling | Applied for empirical risk and resilience assessment, analyzing relationships among variables/nodes. | 12 out of 51 papers |
Probabilistic Models (Bayesian) | Used for risk and resilience management by studying variable relationships and network nodes. | 4 out of 51 papers |
Fuzzy Models | Employed for risk identification, assessment, and ranking of risk factors and products; includes dynamic fuzzy approaches for risk propagation. | 4 out of 51 papers |
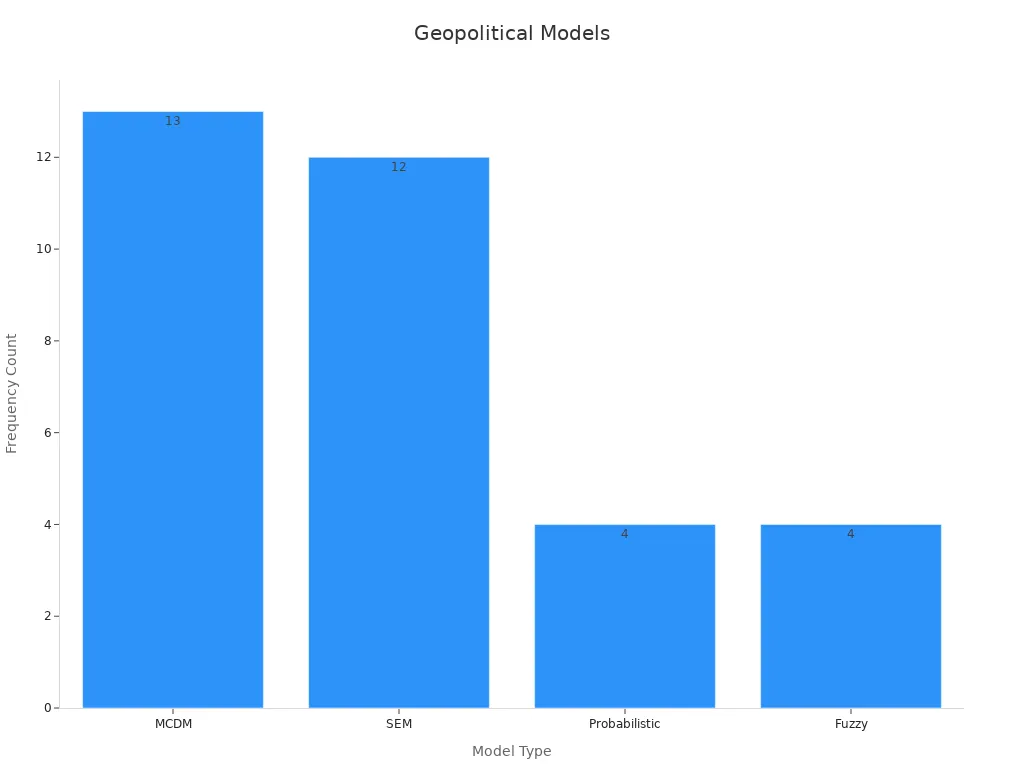
JUSDA’s JusLink platform uses these models and predictive analytics to give companies a clear view of how geopolitical risk can impact their supply chain. This helps leaders make informed decisions and build stronger, more resilient operations.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Diversification
Diversification helps companies reduce risk by spreading their supply chain across different suppliers, regions, and transportation modes. When a company relies on only one supplier or country, it becomes more vulnerable to disruptions. Studies show that higher supply chain concentration increases vulnerability to geopolitical risk. Firms with more diverse supply chains perform better during global uncertainty. For example, Ecuador’s cut-flower industry grew into a world leader by diversifying its suppliers and markets. This strategy helped the industry stay strong even when trade tensions rose. Companies that keep a diversified supply chain often see better financial results and greater resilience.
Tip: Diversification is not just about having more suppliers. It also means choosing suppliers in different countries and using various shipping routes.
Contingency Planning
Contingency planning prepares companies for unexpected events. This process includes mapping the supply chain, assessing supplier risks, and creating backup plans. The PPRR model—Prevention, Preparedness, Response, Recovery—gives a clear structure for managing risks. Scenario planning and simulation help companies predict possible problems and test their responses.
Companies use risk assessment tools like predictive analytics to spot risks early.
Real-time supply chain visibility allows quick action when disruptions happen.
Monitoring supplier performance helps identify issues before they grow.
Diversifying suppliers reduces dependency on one source.
Good communication strategies improve response times and reduce delays.
Technologies like IoT and cloud computing make tracking and data sharing easier.
A manufacturing company in 2020 kept its production running during a global crisis by using a contingency plan with backup suppliers and AI-powered early warning systems. This approach allowed the company to act quickly and avoid major disruptions. Regular training and updating of plans also help companies stay ready for new risks.
Supplier Collaboration
Working closely with suppliers builds stronger supply chains. Supplier collaboration means sharing data, planning together, and solving problems as a team. Companies that use Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) platforms can monitor supplier risks and performance in real time. These platforms send alerts and use predictive analytics to help companies act fast.
Metric | Description | Impact During Disruptions |
|---|---|---|
Time from order to delivery | Shorter times mean faster response to shocks | |
Cash-to-Cash Cycle Time | Time to turn inventory into cash | Shorter cycles help keep cash flowing during disruptions |
Backorder Rate | Frequency of delayed orders | Lower rates mean better inventory management |
Speed of supplier reactions to changes | Quick responses prevent downtime | |
Supplier Adaptability | Ability to adjust to new demands or conditions | Flexible suppliers help avoid supply chain shocks |
Contribution to Innovation | Supplier-driven improvements | New ideas boost resilience and competitiveness |
Sustainability Practices | Alignment with ESG standards | Sustainable suppliers reduce risk and meet regulations |
Supplier collaboration also brings other benefits:
Enhanced visibility through shared data
Faster response to demand changes
Better risk mitigation with real-time analytics
Lower costs from improved transparency
Stronger sustainability and compliance
A Gartner survey found that 39% of industrial manufacturers credited supplier collaboration as a key factor in handling network challenges during geopolitical uncertainty. Companies that work closely with suppliers can quickly find alternatives and keep operations running smoothly.
Technology Solutions by JUSDA
JUSDA uses advanced technology to help companies manage risk and build resilient supply chains. The JusLink AI Solution offers predictive analytics, risk control, and real-time supply chain visibility. JusLink analyzes trends, predicts freight rates, and forecasts demand. The platform’s Risk Control Tower monitors risks and sends early warnings. JusElsa, an intelligent assistant, helps users interact with the system and make better decisions.

JUSDA Solutions
To provide you with professional solutions and quotations.
JUSDA’s technology supports:
Supply chain trend analysis
Freight rate prediction
Sales demand forecasting
Automated replenishment strategies
Real-time risk monitoring
A leading Chinese manufacturer used JUSDA’s Supply Chain Management Collaboration Platform to handle complex global operations. The platform improved transparency, reduced manual work, and standardized processes. As a result, the company expanded globally with lower costs and higher efficiency.
Note: JUSDA’s JusLink platform integrates IoT, cloud computing, and big data. This combination gives companies a clear view of their supply chain and helps them respond quickly to geopolitical risk.
Building Resilience

Training and Awareness
Companies build resilience by investing in training and raising awareness among employees. Staff learn how to spot risks and respond quickly to disruptions. Regular workshops and drills help teams practice real-life scenarios. Many organizations teach employees about the importance of supply chain visibility and proactive communication. These efforts create a risk-aware culture, where everyone knows their role during a crisis.
Industry experts note that long-term partnerships with suppliers and carriers, along with real-time visibility tools, help companies adapt to sudden changes. Companies like Honda and Toyota invest in supplier reliability and recovery skills. They also use flexible contracts and keep inventory reserves to shorten response times. These actions show that proactive risk management leads to faster recovery and stronger supply chains.
Companies that train their teams and build strong relationships recover faster from disruptions and maintain steady operations.
Cross-Functional Teams
Cross-functional teams (CFTs) bring together people from different departments, such as supply chain, legal, and marketing. These teams work together to solve problems and respond to geopolitical risks. CFTs improve alignment between strategy and daily operations. They help companies act quickly when facing new challenges.
CFTs foster adaptability and resilience by enabling rapid responses.
They promote collaboration and continuous learning.
Clear roles and diverse expertise lead to better decisions.
Agile practices support flexibility in risk management.
A consumer goods company formed a cross-functional task force to handle new regulations. The team developed strategies that kept the company compliant and active in the market. This example shows how CFTs improve agility and teamwork during uncertain times.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement means companies always look for ways to get better at managing risks. They use different methods to track progress and make changes when needed.
Practice | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Ongoing checks for new and changing risks | Keeps strategies current and effective | |
Scenario Planning | Creating plans for possible future events | Improves readiness and decision-making |
Employee Training | Teaching staff about risk and response | Builds a risk-aware culture |
Leveraging Technology | Using software for real-time data and analytics | Faster detection and response |
Compliance Audits | Checking processes for rules and improvement opportunities | Ensures adherence and growth |
Over 60% of supply chain leaders now focus on resilience instead of just speed. More than half of manufacturing businesses see better visibility as a top goal. These trends show that companies who invest in continuous improvement become more agile and efficient, ready to face any challenge.
Proactive risk management protects supply chains from costly disruptions. The financial impact of global instability can reach $1 trillion, making resilience essential. Companies use scenario planning, supplier diversification, and real-time monitoring to stay prepared. Technology-driven solutions like JUSDA’s JusLink help leaders make fast, informed decisions.
Statistic Description | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|
Organizations with at least one disruption in the past year | ~80% | BCI |
U.S. CEOs planning supply chain changes | 71% | Deloitte |
Executives taking steps to address disruptions | 85% | BCG |
Companies should review their supply chain risks and explore intelligent solutions to build lasting resilience.
FAQ
What is geopolitical risk in supply chains?
Geopolitical risk means events like wars, trade disputes, or new laws that can disrupt how goods move. These risks can slow shipments, raise costs, or stop production. Companies must watch for these risks to keep their supply chains strong.
How does JUSDA help companies manage geopolitical risk?
JUSDA uses technology like JusLink’s AI Solution. This platform gives real-time updates, predicts risks, and helps companies act fast. JusLink also tracks trends and sends early warnings, so leaders can make smart decisions.
Why is supply chain visibility important during global disruptions?
Supply chain visibility lets companies see every step of their process. With clear data, they can spot problems early and fix them quickly. This helps prevent delays and keeps products moving, even when disruptions happen.
Can technology really make supply chains more resilient?
Yes. Technology like AI, IoT, and cloud computing gives companies better data and faster alerts. These tools help teams respond to risks, plan ahead, and recover faster. JUSDA’s JusLink platform uses these technologies to build stronger supply chains.
See Also
Managing Risks To Secure Your Supply Chain Effectively
The Importance Of Supply Chains In Global Trade Success
Don’t Overlook Supply Chain Threats To Shield Your Business
JUSDA Strategies For Building Strong And Resilient Supply Chains
