LA Wildfires Impact Supply Chains
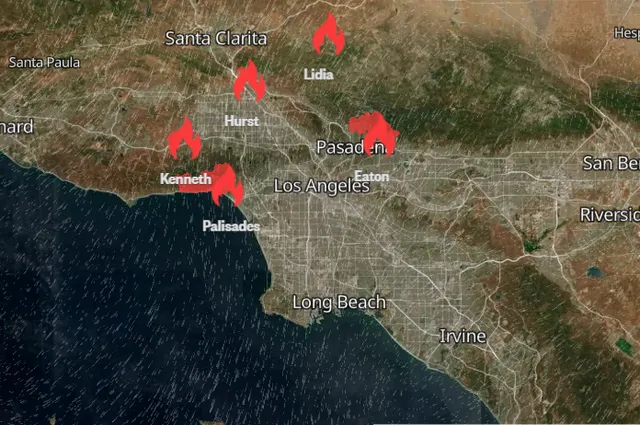
The Los Angeles wildfires have created a state of emergency, significantly highlighting the wildfires impact on supply chains and affecting industries across the region. Road closures and evacuations have halted transportation, while smoke and poor air quality have endangered outdoor workers. The trucking industry, a critical link in supply chains, has faced significant delays due to these challenges. Analysts estimate economic losses from the wildfire crisis could reach $135 billion, with damages impacting nearly 4% of California's annual GDP. The wildfires' impact extends beyond logistics, threatening livelihoods and communities. Addressing this crisis requires immediate action to mitigate further disruptions.
Overview of Los Angeles Wildfires

Scale and Frequency of California Wildfires
Increasing intensity due to climate change
California wildfires have grown more intense over the years, largely due to climate change. Rising temperatures and prolonged droughts have created ideal conditions for fires to ignite and spread. High winds further exacerbate the situation, making it harder to contain these blazes. The frequency of mega-fires, those burning over 100,000 acres, has surged. From 1900 to 1999, California recorded 45 mega-fires. However, since 2000, 35 such fires have occurred, highlighting a troubling trend.
Historical trends and recent wildfire events
The number of wildfires and the acreage burned have steadily increased over the decades. For example, between 1979 and 1988, 2,413 wildfires burned 3.37 million acres. By 2009-2018, this number rose to 3,356 wildfires, consuming 7.08 million acres. Recent events, such as the August Complex Fire in 2020, which burned over 1 million acres, underscore the growing scale of these disasters.
Causes of Los Angeles Wildfires
Natural factors like drought and heatwaves
Drought and heatwaves are significant contributors to wildfires in Los Angeles. Extended dry periods leave vegetation parched, turning it into fuel for fires. Heatwaves further dry out the landscape, creating a tinderbox effect. These natural factors, combined with strong winds, make fire outbreaks more likely.
Human activities and urban expansion
Human activities also play a critical role in the increasing frequency of wildfires. Urban expansion has pushed communities closer to fire-prone areas, such as chaparral ecosystems, which are highly flammable. The wildfire-urban interface in Southern California is particularly vulnerable. Higher population density in these regions increases ignition sources, complicating fire management efforts.
Immediate Regional Effects
Evacuations and property damage
Los Angeles wildfires have forced mass evacuations, with over 130,000 residents displaced in recent incidents. Mandatory evacuation orders disrupt lives and local economies. Thousands of homes and businesses have been destroyed, with economic losses projected to exceed $50 billion. High-value properties in affluent neighborhoods have suffered significant damage, adding to the financial toll.
Environmental consequences, including air quality
The environmental impact of wildfires is severe. Smoke from the fires contains harmful pollutants, degrading air quality in Los Angeles and surrounding areas. The Air Quality Index (AQI) often reaches hazardous levels, with readings exceeding 400 near active fires. Breathing this smoke can harm vulnerable populations, such as children and individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
Wildfires Impact on Supply Chains

Transportation and Logistics Disruptions
Road closures and detours
The LA fires have caused significant disruptions to transportation networks. Five separate fires, including those in Palisades and Pasadena, are burning on the outskirts of Los Angeles. These fires have led to road closures and detours, making it difficult for trucking operations to maintain supply chain continuity. High winds further complicate the situation by increasing the risk of broader disruptions. Transportation services face interruptions as fires threaten populated areas, delaying deliveries and straining logistics.
Rail and port delays in key hubs
Rail and port operations in Los Angeles have also been affected. Smoke from the wildfires reduces visibility, creating challenges for rail operators. Evacuations of over 110,000 residents have caused traffic congestion, further delaying freight movement. Ports, critical hubs for international trade, experience operational slowdowns as logistics strained by the fires struggle to adapt. These delays disrupt the efficiency of supply chains, increasing costs for carriers and shippers.
Air Quality and Worker Safety
Impact on outdoor labor and trucking operations
The wildfires impact outdoor laborers and trucking personnel significantly. Smoke exposure poses serious health risks, especially for truck drivers and first responders. Employers must implement safety measures, such as providing respiratory protection and adjusting work schedules. Without these precautions, workers face increased risks of cardiovascular and respiratory issues. Prolonged exposure to wildfire smoke has even been linked to long-term health problems, including dementia.
Delays in warehouse and distribution center activities
Warehouse and distribution center operations face delays due to infrastructure damage and power outages caused by the fires. In 2018, similar wildfires disrupted the distribution of essential goods like natural gas and coal. Proactive planning and communication are essential to mitigate these challenges. However, the current LA fires continue to strain logistics, leading to increased costs and operational inefficiencies.
Delays in Goods and Services
Disruptions in retail and e-commerce deliveries
The wildfires impact retail and e-commerce sectors by delaying deliveries. Road closures and detours slow down trucking routes, leaving customers waiting longer for their orders. High winds and smoke exacerbate these delays, making it harder for logistics providers to meet delivery timelines. This disruption affects both local businesses and large-scale e-commerce platforms.
Shortages of essential goods in affected areas
Shortages of essential goods have become a pressing issue in wildfire-affected regions. Damage to agricultural infrastructure reduces food supplies, while road closures delay the transportation of critical items. Energy disruptions further complicate logistics, impacting the availability of water and other necessities. The destruction of trees also limits the supply of wood products, driving up prices. These shortages highlight the urgent need for effective supply chain management during crises.
Broader Implications for Industries and Communities
Economic Ripple Effects
Rising costs of goods and services
The economic toll of wildfires in Los Angeles extends far beyond immediate damages. The destruction of infrastructure and supply chain disruptions has led to increased costs for goods and services. Transportation delays caused by road closures and detours have raised shipping expenses, which businesses often pass on to consumers. Additionally, rebuilding efforts require significant investment, further straining local economies. The economic impacts of these wildfires are among the costliest natural disasters in U.S. history, with losses projected to exceed $50 billion.
Strain on local businesses and communities
Local businesses in wildfire-affected areas face immense challenges. Many have been forced to close temporarily, while others have suffered permanent damage. This disruption has left workers without income and created a ripple effect in the job market. Tourism, a vital industry in Los Angeles, has also taken a hit as the region’s appeal diminishes due to smoke and destruction. Communities must now contend with rebuilding efforts, which require time, resources, and resilience.
Impact on Key Industries
Trucking and freight transportation
Trucking operations have been severely disrupted by the wildfires. Road closures and detours have delayed freight movement, while hazardous air quality has posed health risks to drivers. The trucking industry, a critical component of supply chains, has struggled to maintain efficiency under these conditions. Forced evacuations and traffic congestion have further complicated logistics, highlighting the vulnerability of this sector to natural disasters.
Retail, manufacturing, and agriculture
Retailers and manufacturers have faced delays in receiving raw materials and delivering finished goods. Agricultural production has also suffered. Reduced sunlight from smoke has stunted crop growth, while intense heat has damaged root systems. Farmworkers, unable to work in hazardous air conditions, have missed critical harvesting periods. These disruptions have led to reduced yields and higher prices for consumers, amplifying the economic impacts of the wildfires.
Environmental and Social Costs
Long-term damage to infrastructure
Wildfires have caused extensive damage to infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and power lines. The loss of vegetation has increased the risk of soil erosion, which could lead to landslides and further damage. Rebuilding efforts will require substantial investment, placing additional strain on local and state budgets. The fires have also released significant carbon emissions, contributing to climate change and increasing the likelihood of future disasters.
Health and safety concerns for residents
The health impact of wildfire smoke on residents cannot be overstated. Harmful pollutants in the air have triggered respiratory issues, particularly among vulnerable populations like children and older adults. Prolonged exposure to smoke has been linked to asthma attacks, heart problems, and other serious health conditions. Residents in affected areas face ongoing risks, as poor air quality persists long after the fires are extinguished.
Resilience Strategies and Solutions
Infrastructure Investments
Strengthening transportation networks
Investing in robust transportation networks can mitigate wildfire disruptions. Companies should monitor peak fire seasons to anticipate potential challenges. Geographic diversification of goods storage can reduce dependency on a single location, enhancing resilience. Partnering with logistics providers allows businesses to leverage expertise in managing supply chain disruptions. These measures ensure trucking operations remain functional during a crisis.
Enhancing warehouse and distribution center resilience
Warehouses and distribution centers play a critical role in efficient logistics systems. Strengthening these facilities against wildfires involves implementing fire-resistant designs and ensuring backup power systems. Proactive response strategies, such as relocating inventory to safer zones, can minimize losses. Businesses must also prioritize communication with carriers to maintain operational continuity during emergencies.
Climate Adaptation Measures
Reducing wildfire risks through land management
Effective land management practices can significantly reduce wildfire risks. Creating defensible spaces around structures by clearing vegetation and combustible materials slows fire spread. Controlled burns and fuel management practices lower wildfire intensity. Land use planning, including zoning regulations and building codes, ensures new developments incorporate wildfire resilience. These measures protect communities and critical infrastructure in wildfire-prone areas like Los Angeles.
Incorporating climate resilience into supply chain planning
Incorporating climate resilience into supply chain planning involves preparedness, risk assessment, and mitigation. Real-time monitoring and early warning systems enable businesses to respond swiftly to disruptions. Mapping supply chains helps identify vulnerabilities and critical nodes. Proactive investments, such as reinforcing infrastructure near supplier facilities, enhance overall resilience. These strategies ensure supply chains remain operational during emergencies.
Emergency Response Improvements
Faster response to road closures and logistics disruptions
A swift response to road closures and logistics disruptions is essential during wildfires. Companies must implement contingency plans for alternative routes and supply lines. Real-time updates on road conditions help trucking operations adapt quickly. Collaboration with local authorities ensures timely access to critical information, reducing delays and maintaining supply chain efficiency.
Collaboration between public and private sectors
Public and private sector collaboration strengthens wildfire response efforts. Partnerships among utilities, insurers, fire suppression agencies, and local governments foster innovative solutions. The Wildland Fire Mitigation and Management Commission exemplifies this approach by uniting stakeholders to develop proactive strategies. These efforts build sustainable solutions and resilient communities, ensuring a coordinated response to future crises.
Role of Companies Like Translogistics
Proactive communication and monitoring
Proactive communication plays a vital role in helping companies like Translogistics navigate wildfire disruptions. By keeping clients informed about potential delays and operational changes, they ensure all parties remain aware of the evolving situation. This approach supports effective decision-making and minimizes disruptions. During a wildfire emergency, timely updates about road closures, detours, and alternative routes become essential. Translogistics excels in this area by maintaining open lines of communication with shippers and carriers.
Monitoring wildfire activity in real time allows companies to anticipate challenges and adjust operations accordingly. Translogistics uses advanced tracking systems to stay updated on conditions in affected areas, such as Los Angeles. This enables them to reroute shipments and avoid high-risk zones, ensuring the safety of goods and personnel. Their commitment to proactive communication and monitoring helps streamline operations during a crisis, reducing inefficiencies and delays.
Maintaining operational resilience during crises
Operational resilience is critical for logistics companies during emergencies like wildfires. Translogistics develops comprehensive plans to address disruptions caused by these events. These plans include identifying alternative routes, coordinating with local authorities, and ensuring the availability of backup resources. By preparing for potential challenges, they maintain continuity in their services.
Building strong relationships with shippers and carriers further enhances resilience. Effective communication fosters trust and collaboration, enabling smoother logistics even during a crisis. Translogistics prioritizes these relationships to mitigate risks and maintain efficiency. Their ability to adapt quickly to changing conditions ensures that supply chains remain functional, even in the face of emergencies.
Companies like Translogistics demonstrate the importance of preparation and adaptability during wildfire crises. Their proactive strategies and commitment to operational resilience set a standard for the logistics industry, ensuring reliable service in challenging times.
The Los Angeles wildfires have caused widespread disruptions to supply chains, affecting transportation, logistics, and essential goods availability. These challenges underscore the importance of proactive planning and collaboration. Lessons from past events reveal that strategies like geographic diversification and effective communication with shippers can minimize disruptions. Companies must also adapt quickly to changing conditions, ensuring supply chain resilience.
Collaboration between industries and communities plays a vital role in reducing wildfire impacts. Enhanced communication, resource sharing, and modern technologies like predictive modeling strengthen preparedness. Companies like Translogistics exemplify this approach by maintaining operational resilience and providing timely updates during crises. Their proactive strategies ensure supply chains remain functional, even in the face of natural disasters.
See Also
Understanding Inflation: Managing Supply Chain Challenges Effectively
Stay Ready: JUSDA's Approach to Robust Supply Chain Risk
Analyzing Logistics Risks: Current Trends and Their Effects
Transforming Industries: The Role of Cloud Supply Chain Solutions
