A Lifecycle Approach to Transforming Supply Chain Ecosystems

Industrial-supply chain ecosystems face unprecedented challenges, driven by rising costs, inefficiencies, and disruptions. Recent data reveals that 84.6% of businesses report increased operational expenses due to supply chain disruptions, while 55% prioritize visibility improvements to mitigate these issues. The lifecycle framework offers a strategic pathway for innovation, enabling businesses to adopt end-to-end supply chain solutions that enhance adaptability and efficiency. By embracing digital transformation and personalization, organizations can foster resilience and sustainability. This approach not only aligns with the ongoing technology revolution but also ensures impactful content delivery across omnichannel ecosystems, meeting the evolving demands of customers.
Core Components of the Lifecycle Framework
Digital Connectivity in Supply Chains
Real-Time Data Sharing
Digital connectivity has revolutionized supply chain ecosystems by enabling real-time data sharing. Companies leveraging advanced analytics can identify patterns in large datasets, improving demand forecasting and optimizing sourcing, inventory, and logistics planning. Digitized processes also reveal trends and insights that foster innovation, enhancing the overall efficiency of the content supply chain. Factories capturing real-time data have reported a 12% increase in efficiency and a 15% reduction in downtime. These advancements ensure that businesses remain agile and responsive to market demands, strengthening their lifecycle approach.
Enhancing Communication Across Ecosystems
Effective communication is critical for a robust content supply chain. Digital tools, such as IoT-enabled equipment and automated reporting systems, streamline information flow across the ecosystem. Manufacturers using IoT-enabled devices for continuous monitoring have achieved up to a 30% improvement in operational efficiency. Additionally, automated reporting tools have reduced manual reporting efforts by 40%, allowing teams to focus on strategic tasks. These technologies not only enhance collaboration but also ensure the delivery of quality content across the supply chain lifecycle.
Building Resilience in Supply Chains
Adaptive and Flexible Strategies
Resilience in supply chains depends on adaptive and flexible strategies. Predictive analytics, for instance, has enabled retailers to reduce lead times by 25%, preventing stockouts and cutting warehousing costs by 15%. Logistics firms employing IoT-enabled tracking have achieved a 98% on-time delivery rate, boosting customer satisfaction by 20%. These strategies empower businesses to respond swiftly to disruptions, ensuring the seamless flow of goods and services within the content ecosystem.
Risk Mitigation and Disruption Management
Proactive risk mitigation techniques are essential for managing supply chain disruptions. Recent statistics reveal that 85% of global supply chains experienced disruptions within 12 months, with 73% of companies facing detrimental impacts during the COVID-19 pandemic. Companies adopting proactive measures have managed supplier disruptions at 50% lower costs compared to reactive counterparts. By integrating these strategies, businesses can safeguard their operations and maintain resilience throughout the content lifecycle.
Sustainability as a Pillar of Transformation
Reducing Environmental Footprints
Sustainability is a cornerstone of modern supply chain strategies. A German chemical company implemented a return and refill system for glycerin containers, reducing packaging by 86% and cutting its carbon footprint by 68%. Similarly, Cisco has encouraged suppliers to disclose greenhouse gas emissions, promoting transparency and accountability. These initiatives highlight the importance of reducing environmental footprints while maintaining the quality content supply chain.
Promoting Social and Economic Responsibility
Sustainability extends beyond environmental concerns to include social and economic responsibility. Intertek's partnership with a Chinese steel manufacturer to certify products under the Green Leaf Mark demonstrates this commitment. By verifying 30 products across 10 categories, the initiative showcases how businesses can align their operations with sustainability goals. Such efforts not only enhance the content ecosystem but also build trust among stakeholders, ensuring long-term success.
Practical Applications of the Lifecycle Framework
Circular Economy in Manufacturing
The circular economy model transforms traditional manufacturing by prioritizing resource efficiency and waste reduction. This approach emphasizes reusing, recycling, and refurbishing materials to extend their lifecycle. For example, manufacturers adopting closed-loop systems have significantly reduced raw material consumption. These systems enable companies to recover valuable materials from end-of-life products, minimizing environmental impact and lowering production costs.
Organizations implementing circular practices often experience enhanced operational efficiency. By designing products with modular components, manufacturers simplify repairs and upgrades, reducing waste. Additionally, partnerships with recycling facilities ensure that discarded materials re-enter the production cycle. This strategy not only conserves resources but also aligns with consumer demand for sustainable products. The circular economy fosters innovation, enabling businesses to remain competitive while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Sustainable Logistics Practices
Sustainable logistics practices play a critical role in reducing the environmental footprint of supply chains. Companies adopting these practices achieve measurable outcomes, such as decreased carbon emissions and waste production. For instance:
Intertek's Green Leaf Mark certifies products that meet environmental regulations, showcasing the effectiveness of sustainable practices.
The Zero Discharge of Hazardous Chemicals (ZDHC) Programme promotes best practices in the textile, leather, and footwear industries, protecting the environment.
Mahindra Group's Zero Waste to Landfill certification highlights its commitment to waste reduction and operational efficiency.
Sustainable logistics also deliver financial and reputational benefits. Energy-efficient transportation methods reduce fuel consumption, leading to cost savings. Furthermore, environmentally friendly practices enhance market share and consumer loyalty. Strong sustainability leadership improves supplier and stakeholder engagement, fostering collaboration across the lifecycle. These efforts demonstrate how logistics can drive both environmental and economic value, ensuring long-term success.
Emerging Technologies Driving Supply Chain Innovation

Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Supply Chains
Predictive Analytics for Optimization
Artificial intelligence has become a cornerstone of supply chain innovation, with 85% of industry leaders adopting it to enhance operations. Predictive analytics, powered by AI, enables businesses to forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and improve delivery times. For instance, companies using AI have reported a 30% reduction in inventory levels and a 25% improvement in delivery times. These advancements not only streamline operations but also reduce costs, with 35% of businesses achieving significant cost savings. AI-driven predictive analytics ensures supply chains remain agile and responsive to market fluctuations.
Process Automation for Efficiency
AI also drives process automation, significantly improving operational efficiency. Automated systems powered by AI reduce errors, enhance turnover rates, and boost overall satisfaction. For example, businesses integrating AI have experienced a 70% reduction in errors and a 15% increase in turnover. These improvements highlight the transformative potential of AI in automating repetitive tasks, allowing teams to focus on strategic initiatives. Generative AI further enhances these capabilities by creating innovative solutions for complex supply chain challenges, ensuring sustained growth and competitiveness.
Internet of Things (IoT) for Visibility
Smart Sensors and Monitoring
The Internet of Things revolutionizes supply chain visibility through smart sensors and monitoring technologies. IoT sensors provide real-time tracking of goods, offering end-to-end transparency across the supply chain. These sensors also deliver real-time inventory updates, optimizing stock levels and reducing carrying costs. For example, businesses using IoT for inventory management have achieved significant cost reductions and improved demand planning. This technology ensures accurate data collection, enabling informed decision-making and enhancing overall supply chain transparency.
Proactive Maintenance and Operations
IoT also supports proactive maintenance, reducing system downtime and improving operational efficiency. In manufacturing, IoT sensors monitor machinery in real time, preventing unexpected breakdowns and increasing productivity. For instance, a manufacturing company using IoT reduced machine downtime and maintenance costs while boosting output. Similarly, in retail, IoT devices monitor refrigeration units, minimizing food spoilage and saving costs. These applications demonstrate how IoT enhances operational reliability and ensures seamless supply chain operations.
Blockchain for Transparency
Ensuring Traceability Across the Lifecycle
Blockchain technology enhances transparency by providing a tamper-evident ledger for recording transactions. This technology enables businesses to track products throughout their lifecycle, ensuring traceability and accountability. Companies can monitor environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, improving supply chain visibility. Blockchain also helps detect and mitigate risks, fostering trust among stakeholders and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Strengthening Stakeholder Trust
Blockchain strengthens stakeholder trust by offering unparalleled transparency. By recording every transaction on a shared ledger, businesses can verify the authenticity of products and processes. This capability builds confidence among consumers, suppliers, and partners, ensuring long-term relationships. Blockchain's ability to enhance transparency and traceability makes it an indispensable tool for modern supply chain ecosystems.
Collaboration for Ecosystem Transformation

Business Leadership in Lifecycle Integration
Investing in Innovation and Technology
Business leaders play a pivotal role in driving transformation within industrial-supply chain ecosystems. Investments in innovation and technology yield measurable outcomes, such as reduced environmental footprints and cost savings. For instance, companies adopting sustainable practices report significant reductions in material usage and energy consumption. A focus on eco-friendly products not only enhances market share but also fosters consumer loyalty.
Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
Reduction in Environmental Footprint | Decrease in carbon emissions, water usage, and waste production during the product lifecycle. |
Cost Savings through Sustainable Practices | Significant savings from reduced material use and energy-efficient production methods. |
Increase in Market Share and Consumer Loyalty | Eco-friendly products resonate with consumers, leading to increased loyalty and market share. |
Leadership initiatives that prioritize sustainability also improve supplier engagement and employee satisfaction. These efforts align operations with lifecycle goals, ensuring long-term success.
Aligning Operations with Lifecycle Goals
Aligning operations with lifecycle integration goals enhances organizational performance. Information-driven companies are 23 times more likely to acquire customers and 19 times more likely to achieve profitability. Businesses that synchronize their innovation strategies with operational goals experience a 74% increase in revenue from new products. This alignment fosters a cohesive content ecosystem, ensuring seamless collaboration across all stakeholders.
Government's Role in Supporting Transformation
Policies for Sustainable Practices
Governments play a critical role in advancing sustainability within industrial-supply chain ecosystems. Policies such as the US General Services Administration's green practices and Executive Order 14017 promote sustainable supply chain management. These initiatives encourage businesses to adopt environmentally responsible practices, setting new industry standards.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
The US General Services Administration collaborates with industry partners to create best practices for supply chain management, expecting contractors to follow green practices. | |
Executive Order 14017 | Signed in 2021, this order aims to revitalize American manufacturing and secure sustainable supply chains, with a focus on environmental impact. |
Incentives for Lifecycle-Oriented Initiatives
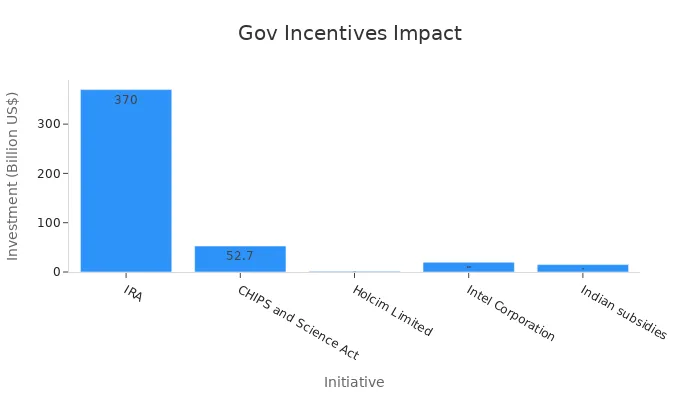
Government incentives further accelerate transformation by supporting lifecycle-oriented initiatives. Programs like the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and CHIPS and Science Act provide substantial investments in clean technology and semiconductor production. These initiatives drive innovation and strengthen partnerships within the content ecosystem.
Initiative | Investment Amount | Impact |
|---|---|---|
IRA | Advances in clean technology manufacturing | |
CHIPS and Science Act | US$52.7 billion | Domestic chip production and semiconductor R&D |
Consumer Engagement in Supply Chain Ecosystems
Educating on Sustainable Choices
Consumer engagement is essential for fostering a sustainable content supply chain. Companies that educate customers about sustainable choices gain valuable insights into their environmental priorities. This understanding helps businesses create products that align with consumer values, enhancing the overall content ecosystem.
Encouraging Participation in Circular Models
Encouraging customers to participate in circular models strengthens the content supply chain. Oracle's response to consumer pressure led to the introduction of services promoting ethical and environmentally friendly practices. Businesses that prioritize environmentally conscious product development build a legacy of sustainability, resonating with evolving consumer expectations.
The lifecycle framework has significantly transformed supply chain ecosystems by fostering resilience, sustainability, and efficiency. Its impact is evident in the seamless integration of technology, sustainable practices, and collaborative efforts. Organizations adopting this approach experience enhanced operational performance and stakeholder trust.
To drive transformation, businesses should:
Develop shared KPIs to align goals and encourage collaboration.
Utilize predictive analytics to optimize inventory and reduce risks.
Integrate cloud-based platforms and IoT devices for real-time data sharing and visibility.
These actionable steps ensure long-term success while addressing the evolving demands of modern supply chains.
