The Logistics Landscape in 2025

The logistics landscape in 2025 describes a dynamic network that moves goods efficiently across the globe. Companies face rising complexity as they adapt to new technologies and shifting supply chains.
Container shipping emissions hit a record high, reaching 199.7 million tons of CO2 in early 2024.
Nearly 25% of logistics KPIs are expected to use generative AI by 2028.
Six in ten businesses have changed their freight strategies in 2025.
Key Takeaways
Logistics in 2025 is shaped by new technologies like AI and automation that improve efficiency, reduce costs, and support sustainability.
Companies face challenges from trade policies, geopolitical risks, and labor shortages, requiring flexible strategies and quick adaptation.
Regionalization and nearshoring help businesses build more resilient supply chains by bringing production closer to key markets.
Real-time visibility and data-driven decision making enable better tracking, faster problem solving, and improved customer satisfaction.
Strong performance measurement and customer focus help logistics firms stay competitive and prepare for future growth.
Logistics Landscape Overview

2025 Trends
M&A Activity
The logistics sector in 2025 continues to see strong merger and acquisition (M&A) activity, even as global uncertainties shape investment decisions. Companies focus on strategic integration to build resilience and expand technological capabilities. In March 2025, there were 28 global logistics M&A transactions. North America led with 13 deals, followed by Europe with 9 and Asia with 6. The largest deal involved the MSC Consortium acquiring an 80% stake in 43 ports from Hutchison Ports for $22.8 billion. Technology-driven deals remain a bright spot, with companies like WiseTech Global and Descartes Systems Group making significant acquisitions.
Despite a slight slowdown in April, investor interest remains high in infrastructure assets like ports and airports. Companies realign portfolios, focusing on specialized logistics such as cold chain and healthcare. Technology and supply chain modernization drive many deals, even as tariff uncertainty and geopolitical tensions create caution. The logistics landscape reflects these shifts, with M&A activity supporting growth and innovation.
Regionalization
Regionalization shapes the logistics landscape in 2025 as companies move supply chains closer to home. Nearly 75% of small and medium-sized businesses see tariffs from China as a major threat, pushing them to nearshore operations for greater stability. This trend leads to increased investment in local and regional supply networks.
Region | Supporting Data / Trend | Description |
|---|---|---|
North America | Nearshoring boom bringing production closer to U.S. markets to balance resilience and efficiency. | |
Europe | 62% of companies have at least two suppliers for critical components | Strategy to maintain global suppliers while adding regional alternatives for redundancy. |
Asia Pacific | China's "dual circulation" strategy fostering stronger intra-Asian supply networks | Building regional supply networks alongside global connections, combining regionalization with globalization. |
Industries | Reshoring in semiconductors and EV batteries | Driving regionalized freight networks, further supporting localized logistics. |
Companies in North America boost manufacturing in Mexico by 32%, while European firms diversify suppliers to reduce risk. Asia Pacific strengthens intra-regional supply networks, blending regionalization with global trade. Industries like semiconductors and electric vehicle batteries lead the way in reshoring, creating more localized freight networks.
AI in Logistics
Artificial intelligence (AI) transforms logistics operations in 2025. Companies use AI to optimize routes, forecast demand, and manage inventory. The AI market in supply chains is projected to reach over $10 billion by the end of the year. AI-driven solutions deliver measurable improvements across logistics functions.
Performance Metric | Improvement/Impact |
|---|---|
Route optimization improvement | 27% |
Fuel consumption reduction | 19% |
Cost reductions | Up to 30% |
Forecast accuracy | Exceeding 90% |
Cost reduction through waste minimization | 15% |
Inventory optimization | 35% |
Service level improvements | 65% |
Reduction in customer service call transfers | 20% |
Potential logistics cost reduction | 15% |
Economic value generated annually (next 20 years) | $1.3T to $2T |
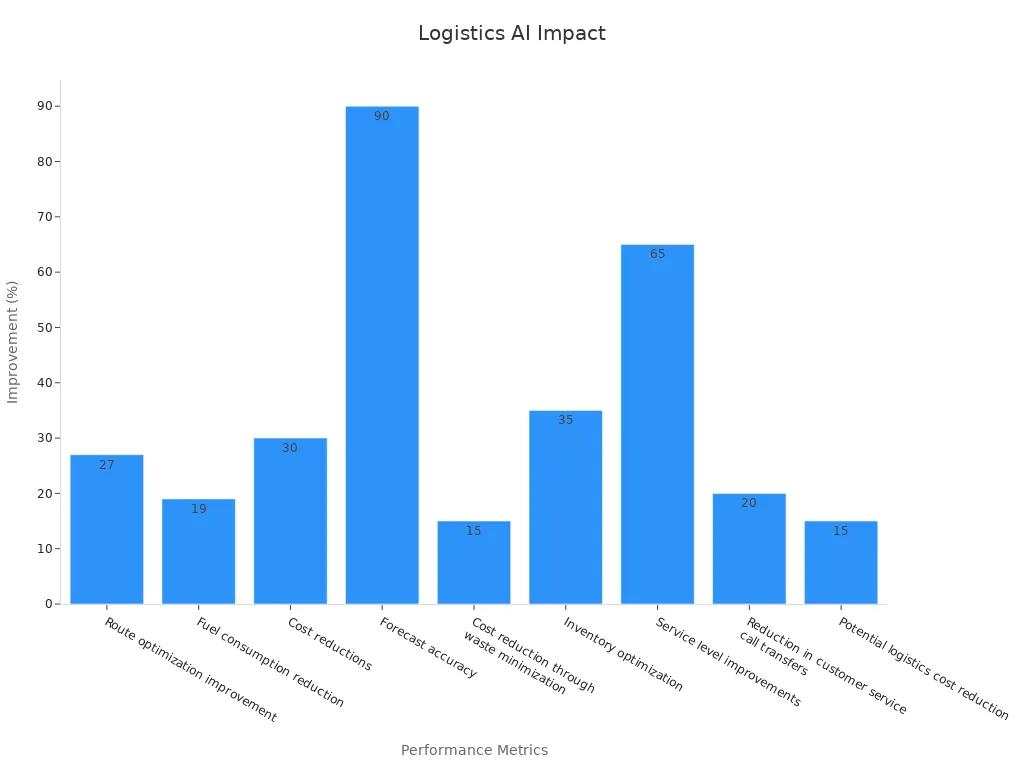
For example, SPAR Austria improved demand forecasting accuracy to over 90% using AI, cutting costs by 15% through waste reduction. Decathlon, a global sports retailer, reduced customer service call transfers by 20% with AI automation. Companies like UPS and Maersk save millions in fuel costs and reduce emissions through AI-powered route planning. These advances make logistics more efficient, sustainable, and responsive.
Trade Policy
Trade policy changes in 2025 have a major impact on global logistics. New tariffs and regulatory shifts increase costs and disrupt supply chains. The World Trade Organization estimates that tariffs introduced in early 2025 caused a 3% drop in global real goods exports. US reciprocal tariffs alone are expected to reduce global trade growth by 0.6 percentage points, while US-China tariff escalations subtract another 0.8 points.
25 tariff announcements occurred between January and April 2025, averaging one every 3.6 days.
Over half of these tariffs were reversed or paused soon after implementation.
A universal 10% tariff announcement caused a $6.6 trillion loss in global stock markets within 48 hours.
Tariffs affected over 57,000 product categories, impacting nearly every sector of global trade.
China’s import duties reached record highs of up to 125%.
The US imposed tariffs averaging between 9% and 11.4%, with some rates near 30%.
These rapid changes create operational chaos for logistics providers. Companies must adapt quickly, finding new suppliers or shifting production to avoid delays and higher costs. Regulatory changes also require compliance with new transportation laws, environmental standards, and security rules. The logistics landscape in 2025 demands flexibility and strategic planning to manage these challenges.
Market Dynamics
Growth Outlook
The logistics sector continues to expand at a steady pace. Market analysts project the global logistics market will reach nearly $6 trillion by 2030, up from $3.8 trillion in 2023. This growth comes from rising e-commerce, better infrastructure, and the need for faster delivery. Asia Pacific leads the market, with China holding the largest share. Europe shows the fastest growth rate. Transportation services and retail remain the top segments, driving most of the revenue.
Metric/Segment | Value/Projection |
|---|---|
Global Market Size 2023 | |
Projected Market Size 2030 | USD 5,951.0 billion |
CAGR (2024-2030) | 7.2% |
Largest Regional Market (2023) | Asia Pacific (35.0% revenue share) |
Largest Market Share in Asia | China (26.1%) |
Largest Service Segment | Transportation services (29.5% revenue) |
Leading End-Use Segment | Retail & e-commerce (29.5% market share) |
Dominant Category Segment | Conventional logistics (73.9% revenue) |
Fastest Growing Region | Europe |
Several factors shape this outlook:
Freight tonnage and pricing trends show how demand and inflation affect the market.
GDP growth links closely to logistics demand.
Inflation raises costs for fuel, wages, and maintenance.
Good infrastructure boosts efficiency and growth.
Freight Volatility
Freight volumes and costs often change quickly. Data from the Bureau of Transportation Statistics shows that spot ocean freight rates, inventory-to-sales ratios, and diesel prices all impact the market. For example, in 2021, freight volumes jumped by over 35% during the pandemic recovery, but then slowed as capacity tightened and costs rose. By 2023, volumes dropped and rates declined, showing how quickly the market can shift.
In 2025, ocean freight rates on Asia-US and Asia-Europe routes increased by 1-3% due to higher demand and fewer available ships. Port congestion and changing trade routes also affect growth. Air freight faces lower e-commerce volumes and less capacity, but spot rates remain stable. These shifts show that logistics companies must stay alert and flexible.
Labor and Resilience
The logistics labor market shows strong resilience, even during tough times. Firms that respond quickly to changes in supply chains tend to recover faster from disruptions. Studies show that supply chain responsiveness has a positive effect on resilience, especially when companies manage logistics in-house. However, when firms outsource too much, their ability to bounce back weakens.
Larger firms often outsource more and operate in many locations, but size alone does not guarantee better resilience.
Quick responses to supply chain changes help firms stay strong during crises like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Too much outsourcing can reduce a company’s ability to adapt when disruptions occur.
Note: Companies that balance in-house logistics with some outsourcing often achieve the best results in resilience and flexibility.
Technology Impact

Automation
Automation transforms logistics by streamlining operations and reducing manual work. Companies deploy automated guided vehicles, robotic arms, and advanced sorting systems to speed up order fulfillment and boost productivity. These technologies help logistics teams process more orders with fewer errors. Automated systems also improve safety by minimizing workplace hazards and protecting employees.
Improved accuracy in tracking and inventory management
Lower labor costs and fewer mistakes
Enhanced customer service through real-time shipment tracking
Better inventory control, reducing holding costs
Data-driven decision making with real-time analytics
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Measures volume of work processed per unit time, showing efficiency gains from automation. | |
Labor Savings | Tracks reduction in human labor costs and effort. |
ROI | Evaluates financial benefits from automation investments. |
Accuracy | Reflects fewer errors and better precision in logistics tasks. |
Consistency | Measures reliability and uniformity of operations over time. |
Automation in warehousing directly impacts fill rate and on-time delivery. Companies that balance technology with human decision-making achieve the best results.
Real-Time Visibility
Real-time visibility technologies give logistics teams instant updates on shipments and assets. These systems use sensors, cloud platforms, and AI to track inventory and vehicles at every stage. Companies can spot problems early and act quickly to avoid delays.
Reduces dwell time and improves throughput
Enhances asset utilization and dock scheduling
Cuts costs by minimizing detention fees and fuel use
Improves security with automated gate access
Enables proactive decisions with real-time data
Research shows that almost 93% of customers want to track their goods during delivery. Real-time visibility helps companies deliver on time and keep customers satisfied. It also supports operational resilience by allowing quick responses to disruptions.
Sustainability
Sustainability has become a top priority in logistics. Over 92% of logistics companies now have sustainability policies. Many invest in green technologies like electric fleets, wind-assisted propulsion, and hydrogen-powered trucks. Companies also use AI and IoT to optimize routes, reduce emissions, and prevent losses.
80% of companies plan to adopt automated transportation to digitize workflows and cut errors
AI adoption leads to 15% cost reduction and 35% inventory optimization
66% of consumers prefer eco-conscious brands
40% of logistics providers win business due to green initiatives
Industry leaders focus on decarbonizing logistics energy infrastructure and building partnerships for green technology. These efforts help companies meet customer expectations and support a cleaner future.
Shaping the Logistics Landscape
Industry Collaboration
Industry collaboration shapes the Logistics Landscape by bringing together logistics providers, technology companies, and manufacturers. These partnerships help companies solve complex problems and drive innovation. For example, logistics leaders work with technology partners to use AI for route optimization, blockchain for transparency, and IoT for real-time tracking. Open innovation allows companies to move faster and adapt to market changes.
The table below shows how collaboration leads to real results:
Company | Collaboration Focus | Innovation Type | Measurable Outcome / Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
DHL | AR Vision Picking project | Augmented Reality in warehouse | 25% increase in picking efficiency, reduced errors |
Amazon | Climate Pledge with Rivian | Electric vehicle deployment | Advancement in sustainable logistics fleet |
CJ Logistics | Partnership with Moorim Paper | Sustainable packaging | Reduced plastic use, eco-friendly materials |
Torc Robotics | Partnership with Daimler Trucks | Autonomous driving systems | Commercial ADS for Freightliner trucks by 2027 |
ISEE | Autonomous yard truck solutions | Autonomous vehicle deployment | Improved efficiency and safety in distribution centers |
These examples show that collaboration leads to better efficiency, sustainability, and safety in logistics.
Innovation Drivers
Innovation drivers transform logistics by improving accuracy, reducing waste, and supporting sustainability. Companies use new technologies to stay ahead and meet customer needs.
Delivery accuracy rises to over 98% with AI adoption.
AI-driven management reduces inventory errors.
Route optimization saves fuel and lowers vehicle maintenance costs.
AI-enabled sustainability efforts cut CO2 emissions by up to 30%.
Advanced algorithms predict seasonal demand, helping companies plan storage and transportation.
AI-powered demand forecasting reduces stockouts by 30% and lowers inventory holding costs by 15%.
IoT sensors in cold storage monitor temperature and humidity, reducing waste and protecting product quality.
Companies in the Logistics Landscape adapt quickly to new challenges by using these innovation drivers. They invest in training and tailored solutions to overcome barriers like high initial costs and system integration.
Challenges Ahead
Geopolitical Risks
Geopolitical risks create major challenges for logistics companies. Conflicts, trade wars, and sanctions disrupt supply chains and force companies to change their operations quickly. The Russia-Ukraine war led to sanctions that limited Russia’s exports of oil, gas, and metals. Companies had to find new suppliers and reroute shipments, which increased costs. The US-China trade war caused export controls and trade bans, especially on rare earth metals. These metals are essential for electronics and semiconductors. As a result, companies faced shortages and higher production costs.
Geopolitical tensions also affect key indicators in logistics. Currency values can drop by 12% in just two weeks, making trade more expensive. Stock markets may fall by 28% in a month, reducing investment in logistics infrastructure. Trade volumes can decrease by 31% in two months, showing how quickly disruptions spread.
Researchers use the Geopolitical Risk Index and the Global Supply Chain Pressure Index to measure these effects. When geopolitical risk rises, supply chains face more disruptions, including labor shortages and damaged infrastructure. These risks require companies to stay alert and adapt quickly.
Environmental Concerns
Environmental concerns have become a top priority for logistics companies. They must measure and reduce their carbon footprints to meet new standards and customer expectations. Companies track emissions from vehicle fleets, energy use, and waste. They set targets to lower emissions and use waste audits to find ways to recycle more and waste less. Many firms invest in green transportation, eco-friendly warehouses, and waste reduction programs.
Researchers use life cycle assessments and vehicle routing models to find ways to cut greenhouse gas emissions. These models help companies plan routes that use less fuel and produce fewer emissions. Real-time data on waste and traffic helps improve efficiency. Some companies use advanced software to measure annual emissions. For example, switching to bio-LNG fuel and green electricity can reduce emissions from 7,100 tons of CO2 equivalent to as low as −4,300 tons. This shows that smart choices can make a big difference.
A study of 149 UK food manufacturers found that companies using environmental logistics practices improved both cost efficiency and environmental performance. When companies involve customers in these efforts, the benefits grow even more. These results show that green logistics is not just good for the planet—it also helps companies save money and build stronger relationships with customers.
Companies that invest in sustainable logistics gain a competitive edge and meet growing demands for environmental responsibility.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes shape the logistics landscape every year. In 2025, the National Motor Freight Traffic Association (NMFTA) will update the National Motor Freight Classification (NMFC) system. The new system uses a standardized density scale for less-than-truckload freight. It assigns unique codes for shipments that need special handling or have liability concerns. The update also condenses commodity listings and improves the ClassIT tool for easier use. These changes aim to simplify freight classification, reduce disputes, and make pricing clearer.
The NMFC update marks the first major revision in decades, addressing outdated and complex rules.
Most freight classifications will now depend on density, not just handling or liability.
The changes will impact how shippers and carriers negotiate rates and manage shipments.
Other regulations also affect logistics operations:
Companies must manage contracts and comply with service-level agreements to avoid penalties and legal issues.
Environmental regulations, especially those tied to ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) standards, require companies to meet strict environmental goals.
Non-compliance increases legal and financial risks, making it essential for companies to stay updated on new rules.
Regulatory changes can reduce cross-border investments by 41%, slowing network expansion.
Staying ahead of regulatory changes helps logistics companies avoid costly mistakes and maintain smooth operations.
Future Outlook
Opportunities
The logistics sector stands on the edge of significant growth. Market forecasts show the global logistics market will rise from $9.28 billion in 2024 to $15.58 billion by 2034, with a steady CAGR of 5.32%. This expansion comes from several key drivers:
Metric/Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Market Size 2024 | USD 9.28 billion |
Market Size 2034 | USD 15.58 billion |
CAGR (2024-2034) | 5.32% |
Key Growth Drivers | Infrastructure projects, tech advancements (blockchain, IoT), sustainability, manufacturing growth |
Regional Growth | Asia-Pacific leads in share and CAGR |
Emerging Opportunities | Blockchain, IoT, sustainable logistics |
Challenges | Geopolitical risk, rising costs, labor shortages |
Market Outlook | Positive, with opportunities across transport modes and sectors |
Governments invest in smart warehousing and automation, such as South Korea’s $200 million AI-automated warehouse project. Major logistics companies like Maersk, DHL, and FedEx focus on green logistics, AI-driven maintenance, and autonomous shipping. Public-private partnerships and regulatory incentives, including the EU’s Digital Europe Programme, support digitalization and sustainability. These trends create new opportunities for efficiency, transparency, and environmental responsibility.
The logistics market outlook remains positive, with robust growth prospects supported by technology and sustainability initiatives.
Strategic Recommendations
Logistics leaders can secure future success by focusing on clear performance metrics and customer experience. The following strategies help companies stay ahead:
Align logistics KPIs with business goals, such as efficiency, driver behavior, and cost management.
Track last-mile delivery metrics, including on-time rates, deliveries per hour, and driver-specific performance.
Prioritize customer-centric measures like Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), Net Promoter Score (NPS), and repeat customer rate.
Monitor financial indicators, such as cost per delivery and fuel expenses, to guide smart decisions.
Maintain consistent measurement over time for reliable performance evaluation.
Benchmark against internal data and customer expectations, not just competitors.
Long-term research shows that top firms invest in comprehensive measurement programs. These programs improve operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and financial results. By focusing on data-driven strategies, logistics companies can adapt quickly, create value, and lead in a changing market.
Consistent performance tracking and a customer-first mindset position logistics firms for growth and resilience in the years ahead.
The Logistics Landscape in 2025 shows rapid change. Key trends include automation, AI, and last-mile delivery innovations like drones and autonomous vehicles. Companies focus on data analytics, sustainability, and ecosystem integration to boost efficiency and resilience.
Invest in automation and real-time tracking to address labor shortages and rising costs.
Build strong partnerships and use advanced technologies for better supply chain visibility.
Businesses that embrace innovation and adapt quickly will lead the way in a resilient and sustainable future.
FAQ
What is the logistics landscape?
The logistics landscape describes how companies move goods from suppliers to customers. It includes transportation, warehousing, technology, and regulations. This network changes quickly as new trends and challenges appear.
How does AI improve logistics?
AI helps companies plan better routes, predict demand, and manage inventory. It reduces costs and errors. Many logistics firms use AI to make faster decisions and improve customer service.
Why do companies focus on sustainability in logistics?
Sustainability lowers emissions and saves money. Companies use green vehicles, smart route planning, and eco-friendly packaging. Customers prefer brands that protect the environment.
Note: Sustainable logistics also helps companies meet new government rules.
What risks affect global logistics in 2025?
Geopolitical tensions, trade policy changes, and extreme weather events create risks. Companies must adapt quickly to keep goods moving and avoid delays.
Common risks include:
Tariffs
Labor shortages
Supply chain disruptions
See Also
Exploring Cutting-Edge Innovations Shaping Logistics Technology
How Artificial Intelligence Transforms Future Supply Chains
Mastering Lean Strategies To Boost Advanced Manufacturing Logistics
Transforming Logistics Through Breakthroughs In Supply Chain
