2025 Mid-Year Reviews:Major Events in the Global Logistics and Supply Chain Industry

Staying updated on Major Events in the logistics and supply chain industry shapes how companies respond to change. Recent disruptions and rapid technology shifts create new challenges and opportunities. Industry conferences provide fresh insights and help professionals build strong networks. Leaders who track these changes can better manage risks and improve performance. They should consider how each new development might affect their own operations, costs, and long-term planning.
Key Takeaways
Major disruptions like natural disasters and labor strikes cause high costs, long recovery times, and lower sales growth in supply chains.
Mergers and acquisitions help companies expand, improve efficiency, and adapt to changing market conditions.
Attending industry conferences offers valuable learning, networking, and insights into new technologies and trends.
AI and automation boost logistics by cutting errors, reducing costs, and speeding up deliveries and warehouse operations.
Building supply chain resilience through risk management, inventory strategies, and technology helps companies recover faster and reduce losses.
Major Events Overview
Recent Disruptions
The global logistics and supply chain industry has faced a series of Major Events that have tested its resilience. Disruptions such as the Red Sea Crisis, the Baltimore Bridge Collapse, the Taiwan earthquake, and widespread labor strikes have caused significant operational challenges. Trade policy changes, like the removal of the $800 de minimis exemption for imports from China and Hong Kong, have further complicated cross-border trade and increased costs for many companies.
A study of 470 French firms confirmed that disruptions, These disruptions make it harder for companies to identify, assess, and control risks. The research also highlights that strong risk management practices help companies recover and build resilience after such Major Events.
Note: Companies with dynamic risk management adapt faster and recover more quickly from disruptions.
The frequency and financial impact of these disruptions continue to rise. The table below shows key data on natural disasters and their effects on supply chains:
Aspect | Numerical Data | Description |
|---|---|---|
Number of natural disasters in the U.S. since 1980 | Resulting in approximately $1.2 trillion in damage | |
Average annual disasters in the U.S. by decade | 1980s: 2.7; 1990s: 4.6; 2000s: 5.4; 2010s: 10.5 | Shows increasing frequency over decades |
Global disaster frequency | <200 per year in 1980s; >300 per year in 2010s | Indicates global increase in disasters |
Small businesses never reopening after disaster | 40–60% | Illustrates severe business impact post-disaster |
Profitability drop due to supply chain disruptions | 107% average drop in operating income | Empirical research on financial impact |
Sales growth impact | 7% lower sales growth | Due to disruptions |
Cost growth impact | 11% increase in costs | Due to disruptions |
Recovery time after disruption | Up to 50 trading days | Time to restart production |
Duration of lower performance post-disruption | Up to 2 years | Sustained negative effect on firms |
Stock market reaction to disruption announcements | 1990s: >10% drop; 2000s: ~2% drop | Shows reduced but still significant financial market impact |
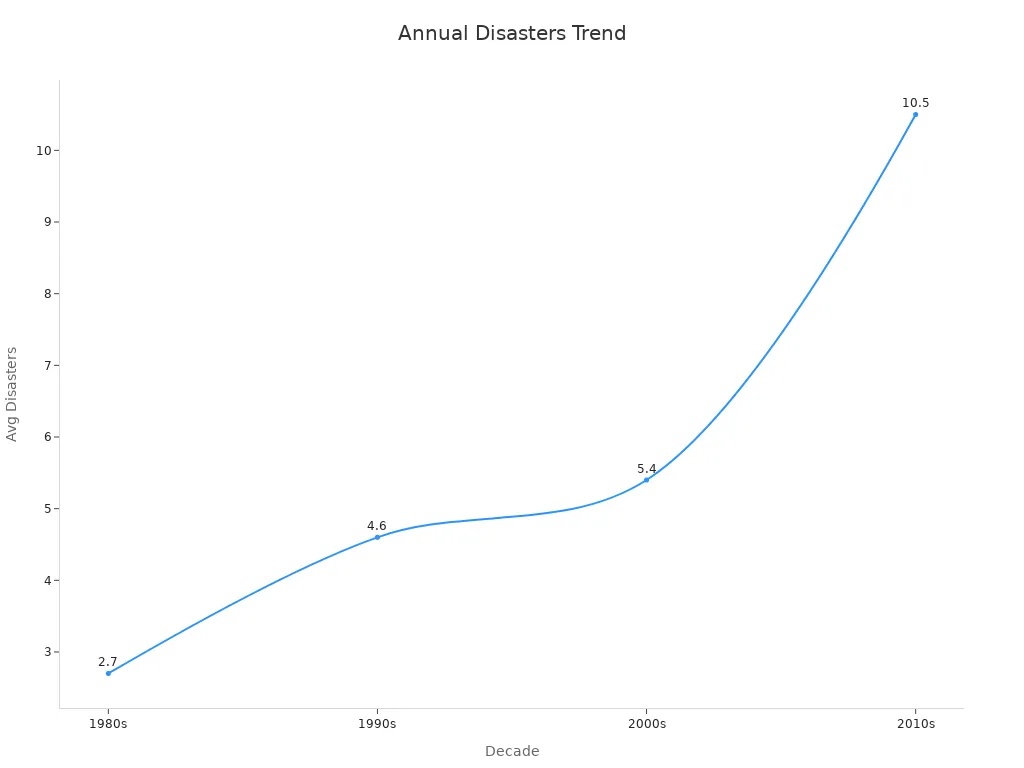
These numbers show that Major Events like natural disasters and labor strikes not only disrupt operations but also lead to higher costs, lower sales growth, and long recovery times. For example, companies often need up to 50 trading days to restart production after a disruption, and the negative effects can last for up to two years. The stock market also reacts strongly to news of disruptions, with significant drops in company value.
Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) have become another set of Major Events shaping the logistics landscape. In 2025, deals like Blackstone Group’s $22.8 billion acquisition of CK Hutchison’s global port business and UPS’s $1.6 billion purchase of Andlauer Healthcare Group signal a push for strategic expansion and technological advancement. These transactions allow companies to expand their geographic reach, enter new markets, and improve operational efficiency.
M&As in global freight transportation, including ocean shipping, rail, and trucking, generate average synergistic gains of 3.3%.
Vertical mergers, which combine different supply chain modes, create greater value than horizontal mergers within the same mode.
Most of the gains from these deals go to the shareholders of the target companies, but bidders also benefit, especially in friendly mergers.
Regulatory changes, such as the US Staggers Act and the Ocean Shipping Reform Act, have influenced M&A activity and market integration.
M&As help integrate supply chain services, improve operational efficiency, and increase market share.
Efficiency gains from M&A activity are not limited to one region. For example, in China’s railway sector, geographically meaningful mergers have led to better efficiency due to network economics. These deals can increase market share, improve service quality, and generate cost savings, although sometimes at the expense of scale efficiency. In the US, long-term effects on prices and consumer welfare have been mixed, but most research shows that M&As in freight transportation maximize value for shareholders.
Shareholders of both acquirers and targets in shipping M&As see average abnormal gains, with targets gaining 3.3% and acquirers 1.2%. Cross-border and diversifying deals tend to deliver higher returns. Regulatory interventions in regions like the EU and US also play a key role in shaping the outcomes of these Major Events.
Tip: Companies should monitor M&A activity closely, as these Major Events can change competitive dynamics, open new opportunities, and require adjustments in supply chain strategy.
Industry Conferences

Trends and Innovations
AI and Automation
Artificial intelligence and automation have transformed logistics and supply chain operations. Companies now use AI for predictive logistics, route optimization, and warehouse automation. These technologies help reduce errors, cut costs, and improve speed. The smart warehousing market is growing fast, expected to double from $20.4 billion in 2023 to $40.5 billion by 2028. This growth comes from the rise of e-commerce and investments in intelligent automation.
Metric | Improvement/Impact |
|---|---|
Forecasting error reduction | |
Route optimization | Delivery times cut by 25% or more |
Inventory optimization | Inventory levels reduced by 35% |
Warehouse automation | Throughput increased by 40-50% |
Labor cost reduction in warehouses | Up to 40% reduction |
Predictive maintenance | Maintenance costs lowered by 10-40% |
Fuel reduction | 10-15% fuel savings |
Overall logistics cost reduction | Around 15% for early adopters |
AI also improves decision-making and risk management. Real-time analytics help companies respond quickly to disruptions. Automation in warehouses and delivery reduces labor costs and increases accuracy. Companies like DHL use AI to optimize routes, saving fuel and speeding up deliveries.

Regionalization
Many companies now shift from global to regional supply chains. Rising transportation and fuel costs make regional networks more cost-effective. Regionalization helps contain disruptions within a region, reducing risk and improving resilience. For example, Procter & Gamble and Diageo moved to regional models to lower costs and respond faster to market changes.
Regional supply chains reduce shipping distances and costs.
Companies detect and respond to disruptions faster due to proximity.
Nearshoring improves agility and reduces exposure to geopolitical risks.
Advances in automation make regional manufacturing more competitive.
This trend supports faster delivery, better risk management, and cost control.
Sustainability
Sustainability has become a top priority in logistics. Companies invest in green logistics and ESG initiatives to reduce their carbon footprint and meet customer expectations. Deutsche Post DHL achieved a 30% reduction in carbon emissions and saved €1.6 billion over five years through sustainability efforts. Unilever reduced empty miles by 18% and cut CO₂ emissions by 40% compared to its 2010 baseline.
Indicator / Metric | Numerical Value / Impact |
|---|---|
Carbon Emissions Reduction | 30% (Deutsche Post DHL) |
Fuel Consumption Savings | 10-15% (route optimization) |
Financial Savings | €1.6 billion (DHL, 5 years) |
CO₂ Emissions Reduction (Unilever) | 40% vs. 2010 baseline |
Renewable Grid Electricity Usage | 100% (Unilever) |
Climate Footprint Reduction (IKEA) | 17.3% |
Sustainable supply chains not only help the environment but also improve efficiency and brand value. Companies that lead in green logistics often see higher customer loyalty and financial savings.
Actionable Insights
Building Resilience
Supply chain professionals can strengthen resilience by adopting proven strategies and monitoring key performance indicators. Companies face an average annual cost of $184 million from supply chain disruptions. Tariffs can erode EBITDA by 5-10%, and every 10% tariff increase may reduce profit margins by 2-5%. The table below summarizes these quantified outcomes:
Quantified Outcome | Value/Percentage | Description/Context |
|---|---|---|
Average annual cost of supply chain disruptions | $184 million | Estimated financial loss due to disruptions |
EBITDA erosion due to tariffs | 5-10% | Loss from tariff impacts |
Margin loss per 10% tariff increase | 2-5% | Profit margin reduction linked to tariff increases |
Many organizations now hold more inventory and diversify sourcing to buffer against disruptions. Nearly half of surveyed companies plan to increase inventory, while 58% intend to diversify suppliers. Pre-positioning emergency supplies and using virtual inventory help maintain service during demand surges. Companies also use technology like AI and warehouse management systems to improve visibility and agility. Setting measurable KPIs, such as cycle time and order accuracy, allows teams to track progress and adjust strategies. These steps help companies recover faster from Major Events and minimize financial losses.
Tip: Collaborative inventory management and scenario planning can further reduce risk and improve service continuity.
Leveraging Events
Industry events and real-time data offer valuable opportunities for operational improvement. Professionals who attend conferences gain insights into the latest trends and technologies. Networking at these events helps build relationships with partners and suppliers. Real-time data from events and operations enables route optimization, reduces costs, and speeds up deliveries. Companies use customer data to personalize services and improve satisfaction. Monitoring event data, such as attendee engagement and feedback, supports better planning and execution.
Real-time shipment tracking improves delivery reliability.
Data analytics help forecast inventory needs and prevent stockouts.
Monitoring driver behavior enhances safety and reduces risk.
Analytics support sustainability by tracking emissions and fuel use.
Aligning event data strategies with business goals boosts sales, increases brand awareness, and improves efficiency. By learning from Major Events and industry gatherings, companies can adapt quickly and stay competitive.
Tracking Major Events and trends in logistics and supply chain helps companies stay ahead. Data-driven decisions can lead to a 22% reduction in processing times and a 30% drop in bottlenecks, as shown below:
Evidence Type | Description | Numerical Details |
|---|---|---|
Statistical Insights | Data-driven decisions improve logistics operations | 22% faster processing; 30% fewer bottlenecks |
Companies like Walmart and Toyota show that proactive planning, supplier diversification, and new technologies build resilience. Regular updates and strong partnerships help organizations adapt and grow. Staying connected with industry updates and events supports long-term success.
FAQ
What are the biggest risks in global supply chains today?
Geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and labor shortages top the list. Companies also face risks from cyberattacks and trade policy changes. Leaders must monitor these threats and update risk management plans often.
How does AI improve logistics operations?
AI helps companies predict demand, optimize routes, and manage inventory. Real-time data allows faster decisions. Many firms see lower costs and fewer errors after using AI tools.
Why do companies attend logistics conferences?
Professionals attend to learn about new trends, network with peers, and find solutions for their challenges. Conferences offer workshops, expert talks, and hands-on demos.
How can companies make their supply chains more sustainable?
Firms use electric vehicles, optimize routes, and track emissions. Many set clear sustainability goals and report progress. Green logistics improves brand value and saves money.
What is supply chain regionalization?
Regionalization means companies build supply networks closer to their main markets. This approach reduces shipping time, lowers costs, and helps firms respond quickly to disruptions.
See Also
Top Five Essential Events For Supply Chain Professionals
How Innovations Are Transforming The Future Of Logistics
Comprehensive Insights Into Leading Global Logistics Firms
