Analyzing the Implications of Reciprocal Tariffs on Global Supply Chains

Reciprocal tariffs happen when countries charge equal taxes on goods. These taxes change global trade and make products cost more. For example, the U.S. added a 125% tax on goods from China. This made companies look for new suppliers. Knowing these changes shows how they affect buyers, businesses, and economies.
Key Takeaways
Reciprocal tariffs make production more expensive, raising prices for buyers.
They disturb global trade, causing delays and forcing new suppliers.
Tools like JUSDA’s platform and China-Europe Rail help cut costs.
The Impact of Tariffs on Industries

Rising Costs and Production Challenges
Tariffs make imported materials more expensive for factories. This raises production costs for many industries. When countries add reciprocal tariffs, businesses face even higher expenses. In March, U.S. manufacturing costs rose the most worldwide, according to S&P Global. About one-third of manufacturers said tariffs caused these higher costs.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Input Cost Inflation | U.S. manufacturing costs were the highest in the world. |
Sector Impact | One-third of producers blamed tariffs for rising costs. |
Historical Context | Factory costs peaked since April 2018 due to tariffs. |
Industries like metal products, taxed over 30%, feel the most pressure. These costs often lead to fewer jobs in areas hit hardest by tariffs. Companies must either pay these costs themselves or charge customers more. Both options make it harder to stay competitive.
Disruption in Trade Flows and Logistics
Tariffs change how goods move around the world. They cause delays, rerouting problems, and higher costs for industries relying on global suppliers. For example, U.S. carmakers like Ford and Tesla saw stock prices drop after tariff news. This shows how quickly markets react to supply chain issues.
Industry | Tariff Rate |
|---|---|
Automotive | 25% |
Steel and Aluminum | 25% |
Consumer Goods | 20%+ duties |
Pharmaceutical | ~25% |
Supply chains often cross many countries, making them fragile. Tariffs cause problems like finding new suppliers, material shortages, and shipping delays. On average, industries face a 29% tariff, with some as high as 40%. Chinese imports may face up to 104% tariffs, making trade even harder.
Effects on Export-Dependent Sectors
Industries that depend on exports are hit hardest by tariffs. Sectors like electronics, auto parts, and home appliances struggle because they rely on global markets. For instance, electronics make up 20% of China’s exports to the U.S., making them very vulnerable to tariffs.
Industry Sector | Impact of Tariffs |
|---|---|
Traditional Labor-Intensive Sectors | Have trouble adjusting to higher costs from tariffs. |
Electronics Industry | Tariffs affect 20% of U.S.-bound exports, causing big problems. |
Auto Parts and Home Appliances | Heavy reliance on U.S. markets leads to major challenges. |
New Energy Companies | Move operations to nearby countries to lower costs. |
Some industries, like pharmaceuticals, avoid tariffs, but others, like solar panels, face too much supply and higher costs. By 2030, a 54% tariff could end most U.S.–China trade, changing jobs and global supply chains.
JUSDA’s Role in Mitigating Industry Challenges
JUSDA helps industries deal with tariff problems. Its Supply Chain Management Platform uses AI and blockchain to improve operations. It helps with planning, shipping, and customs tracking, keeping trade smoother despite tariffs.
JUSDA’s China-Europe Express Rail is another helpful service. It’s cheaper and faster than air or sea shipping, taking only 15–20 days. This service helps businesses save money and stay efficient. With JUSDA’s support, industries can adjust to new trade rules and reduce tariff impacts.
Economic Consequences of Reciprocal Tariffs
Changes in Global Trade Patterns
Reciprocal tariffs have changed how countries trade goods. When nations tax each other’s products, it disrupts trade systems. For example, the U.S.-China trade war showed how fast problems can grow. These taxes made businesses change suppliers and shipping routes.
While tariffs aim to balance trade, they often cause problems. Countries may gain better deals, but trade wars can start. This creates confusion for businesses and harms the global economy.
Key examples include:
The U.S.-China trade war raised costs and hurt supply chains.
Tensions between the U.S. and EU made trade harder.
Trade deals often cause short-term problems before helping.
These changes show how fragile global trade is. Companies must adjust quickly to new rules, which costs money. This creates a less connected trade system, where businesses focus on being strong instead of fast.
Winners and Losers in the World Economy
Tariffs create both winners and losers. Some countries grow their local industries, while others lose trade chances. Between 2018 and 2019, global trade shrank by 0.9% each year. This was much lower than the 3.3% yearly growth from 2002 to 2017. Tariffs clearly hurt the economy.
Here’s how regions were affected:
The U.S. grew slightly, with a 0.6% boost above past trends.
Europe’s economy dropped by 0.1% due to trade reliance.
Non-G10 countries, needing free trade, faced the worst problems.
A 10% tariff increase could cut global trade by 1.2% yearly. It would also slow Europe’s GDP by 0.3% and the U.S.’s by 0.1%. The table below shows how tariffs impact economies based on studies:
Study | Model Type | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|
Felbermayr and Steininger | Comparative static model | -0.14% |
Balistreri et al. | Monopolistic competition model | -0.34% |
Freund et al. | Various | -0.4% (higher service costs) |
Itakura | Various | -1.4% (lower productivity) |
Walsmley and Minor | Various | -1.3% (car tariffs) |
Freund et al. | Various | -1.6% (less investment) |
WTO study | Various | -1.15% to -1.66% (uncertainty effects) |
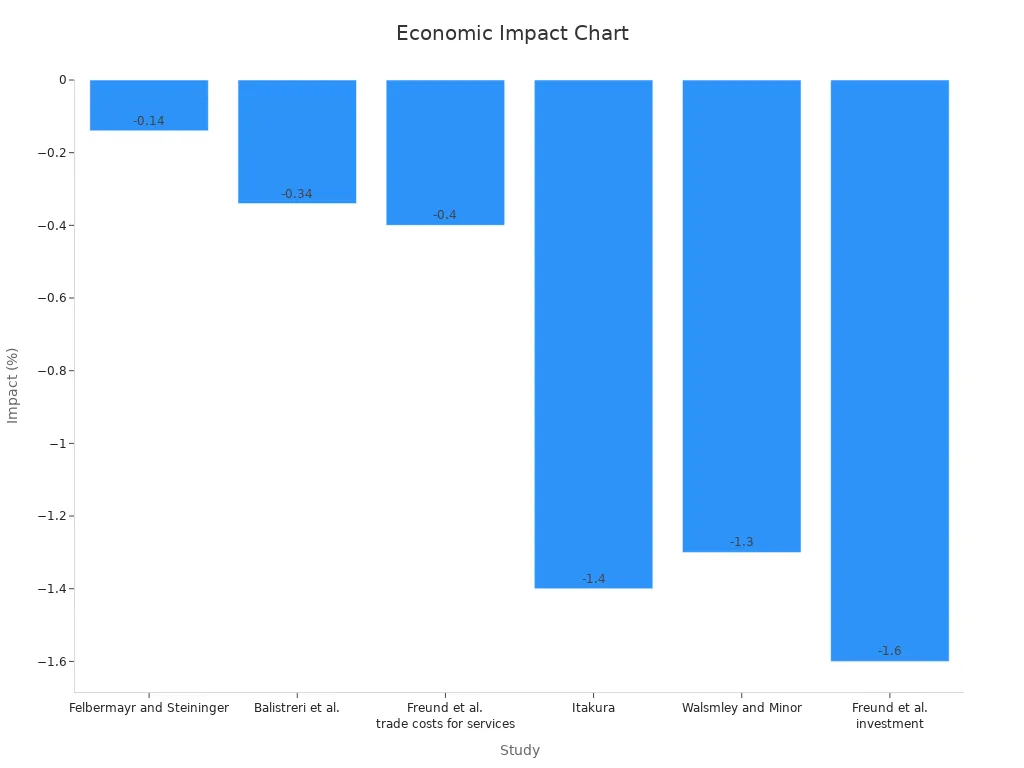
Non-G10 countries, which relied on free trade, now face higher costs and fewer exports. These differences show how unevenly tariffs affect the world economy.
How China-Europe Express Rail Helps with Trade Changes
The China-Europe Express Rail is helping businesses deal with tariffs. This rail service is faster and cheaper than shipping by sea. It takes only 15–20 days, making it a good choice for companies.
The rail system is growing fast, moving containers at a 29% yearly rate. Even if subsidies drop, the rail stays strong because it’s efficient and quick. Reasons for its success include:
Special subsidies for certain goods and routes.
Fewer delays compared to sea shipping.
Better connections for goods from Southeast Asia to Europe.
Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
Penalty factor (γ) | 20 |
Sensitivity factor (δ) | 0.5 |
45 days |
The rail also helps industries like electronics and medical supplies, which are hurt by tariffs. By offering reliable shipping, it helps businesses stay competitive.
The rail service shows how smart logistics can reduce tariff problems. It cuts costs and ensures goods arrive on time, helping businesses adjust to new trade rules.
Consumer Impacts of Tariffs

Changes in Product Availability
Tariffs can mean fewer choices for shoppers like you. When tariffs raise costs, businesses may stop importing some goods. This leads to shortages and forces people to find other options. For example, spending on Chinese goods has dropped a lot. Many now buy local products to avoid high prices.
Findings | What It Means |
|---|---|
Spending on Chinese goods fell | People now prefer local items to save money. |
A 25% tariff on Canadian and Mexican goods could raise prices by 1.63% | Tariffs make products cost more and harder to find. |
In places like Africa, trade limits make shortages worse. In 2000, only 7.6% of African trade was within the continent. This shows heavy reliance on outside markets. Tariffs disrupt trade, increasing risks of shortages.
MBM says tariffs will still trouble distributors in 2025.
The Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta predicts tariffs will keep raising prices.
Rising Costs for Everyday Goods
You might notice everyday items costing more now. Tariffs raise import prices, and businesses pass these costs to you. For instance, food prices went up 0.4% in March. Eggs rose by 60.4% over the past year. Personal care items also cost 1% more in March. These increases make basic needs harder to afford.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose 2.8% last year. Shelter costs went up 4%. Tariffs on key goods may cause inflation to rise again. This makes it harder for families to manage their budgets. Tariffs affect your daily life, from food to housing.
Long-Term Effects on Consumer Behavior
Over time, tariffs change how people shop. Higher prices and fewer choices push many to buy local or cheaper items. This reduces reliance on imports but limits access to special or high-quality goods.
Tariffs also make companies move production closer to home. This could lower costs for you in the future. But this takes time and won’t fix problems right away. As tariffs change trade, your shopping habits will keep adjusting.
Ways to Handle Tariff Problems
Spreading Out Supply Chains
Spreading out supply chains helps lower risks from tariffs. Getting materials from different countries avoids relying on high-tariff areas. For example:
U.S. companies now buy from places with fewer tariffs.
Businesses change product designs to fit lower tariff rules.
Using smaller packaging or new materials can also save money.
Plan | What It Does |
|---|---|
Spreading Suppliers | Lowers risks from trade issues and policy changes. |
Fewer Main Suppliers | Reduces risks but may cause quality or teamwork problems. |
These ideas cut costs and make supply chains stronger. But without good policies, tariffs can still cause problems and raise prices.
Using JUSDA’s Supply Chain Tools
JUSDA gives smart tools to handle tariff problems. Its Supply Chain Platform uses AI and blockchain to work better. It helps with planning, shipping, and tracking customs. Real-time data helps manage stock and avoid risks.
For example, JUSDA helped Sharp lower shipping costs by 20%. By improving systems, it keeps supply chains running smoothly during trade troubles. JUSDA’s tools help you adjust to tariffs while staying efficient.
Benefits of the China-Europe Express Rail
The China-Europe Express Rail is a fast and cheap shipping option. It delivers goods in 15–20 days, quicker than sea and cheaper than air. Since 2011, it has grown with more trains and cargo.
The rail boosts city logistics by 4.55% on average.
Big cities and inland areas gain the most from it.
It connects China and Europe, making trade easier.
Long-Term Benefits | Study Source | What It Shows |
|---|---|---|
Lower Costs | Yang et al., 2020 | Companies using the Qianhai platform saved a lot on shipping. |
Better Efficiency | Ma et al., 2019 | Faster customs and organized shipping improved supply chain work. |
Stronger Connections | Liu & Chen, 2023 | The CR Express links transport types, making goods move smoothly. |
Using this rail service saves money, speeds up deliveries, and keeps you competitive in changing trade times.

JUSDA Solutions
To provide you with professional solutions and quotations.
Reciprocal tariffs raise costs and disrupt trade for everyone. They also make some products harder to find in stores. Global supply chains link businesses and markets worldwide. Tools like JUSDA’s China-Europe Express Rail help fix these problems. These solutions save money and keep businesses strong during trade changes.
See Also
Exploring How Global Trade Policies Shape Economic Landscapes
Addressing Challenges of Supply Chain Growth in Global Markets
Understanding the Importance of Supply Chains in Global Trade
Examining Jusda Supply Chains and Worldwide Consumer Expectations
Enhancing Strategies to Tackle Supply Chain Problems in Tech
