Semiconductors Flicker Back to Life: Global Supply Chain Stabilizes After Years of Disruption and Shortage

The global semiconductor supply chain is stabilizing after years of disruption. Recent data from Avnet Silica’s Trendliner Q3 2025 report highlights this shift:
Lead times for many standard components now range from 9 to 16 weeks, signaling a return to normal conditions.
The EU’s Purchasing Managers’ Index rose to 49.5 in June 2025, the highest since June 2022.
Supply chain resilience has become vital for manufacturers, consumers, and global trade. Digital collaboration and global partnerships drive this new era, transforming supply chain management through innovation and shared visibility.
Key Takeaways
The semiconductor supply chain is stabilizing, with lead times for many components reduced to 9-16 weeks, a significant improvement from previous shortages.
Investments in AI chip development are projected to exceed $250 billion in 2025, driving growth in the semiconductor industry and enhancing production capabilities.
JUSDA's advanced warehouse solutions and digital platforms like JusLink provide real-time tracking and transparency, helping companies respond quickly to market changes.
Collaboration between manufacturers, logistics providers, and government initiatives is crucial for building a resilient supply chain and ensuring future stability.
Semiconductor Supply Chain: Signs of Stabilization

Market Recovery and Lead Time Improvements
The semiconductor industry is showing clear signs of recovery. Recent data from Avnet Silica’s Trendliner Q3 2025 report highlights a return to more predictable supply chain conditions. Lead times for many components have dropped significantly compared to the peak of the shortage in 2022. For example, DDR3 and LPDDR3 memory modules, which once had lead times of up to 30 weeks, now average between 9 and 16 weeks—a reduction of nearly 60%. Automotive microcontrollers, which faced lead times of over 50 weeks, now range from 20 to 30 weeks. Some 8-bit and 32-bit MCUs from major manufacturers are quoted at 10 to 26 weeks by mid-2025.
Component Type | Lead Time Peak (2022) | Lead Time 2024 | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
DDR3/LPDDR3 | 22-30 weeks | 9-16 weeks | -59% (low end) |
DDR4/LPDDR4 | 20-30 weeks | 9-16 weeks | -55% (low end) |
Flash-NAND | 22-26 weeks | 10-15 weeks | -54% (low end) |
SSD | 9-13 weeks | 9-13 weeks | No change |
Advanced Analog | 28-36 weeks | 23-41 weeks | -18% (low end) |
Passives | 20-35 weeks | 19-37 weeks | -5% (low end) |
Interconnect | 16-22 weeks | 15-20 weeks | -6% (low end) |
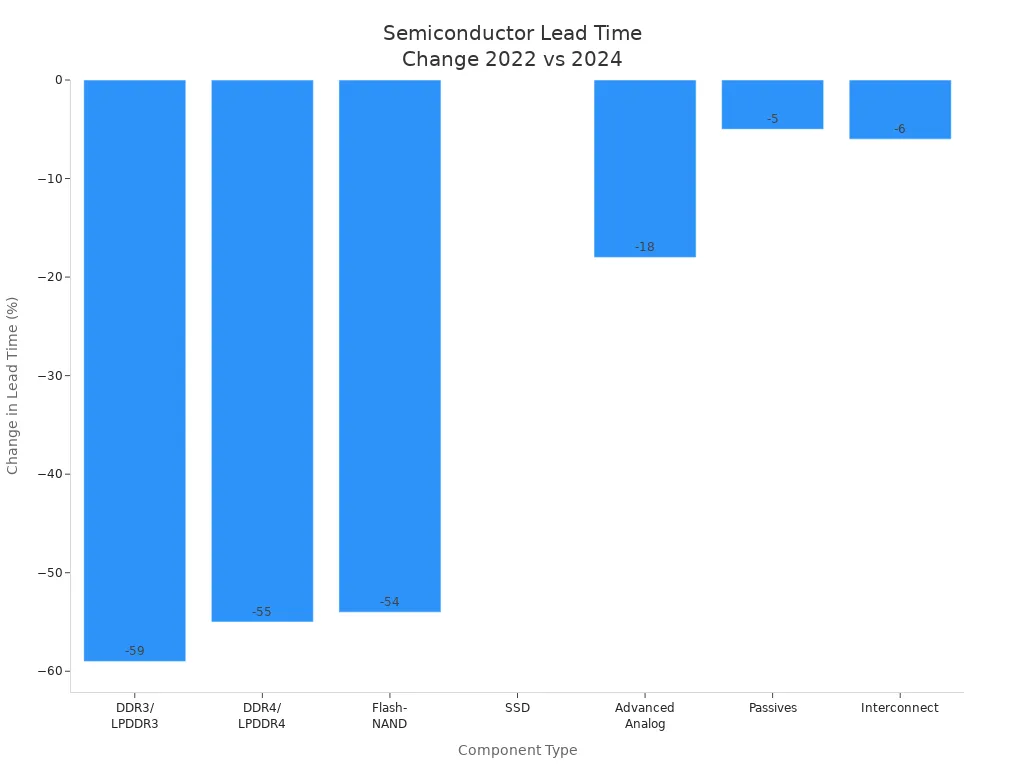
These improvements reflect a broader trend across the industry. IC sales are expected to grow 23% year-over-year in Q1 2025, driven by strong demand for AI chips. Investments in AI chip development are projected to exceed $250 billion in 2025. Fab capacity is also expanding, with 300mm fabs set to add 5.1 million wafers per month by 2026—a 29% increase. Equipment investments are forecasted to reach $113 billion in 2024, with continued growth into 2025.
Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
IC Sales Growth | Expected to grow 23% YoY in Q1 2025 due to AI demand. |
AI Chip Investments | Projected to exceed $250 billion in 2025. |
Fab Capacity Increase | 300mm fabs to add 5.1 million wafers/month by 2026. |
Equipment Investments | Forecasted to reach $113 billion in 2024. |
JUSDA’s global warehouse network has played a key role in supporting this recovery. With over 155 service points and more than 2.5 million square meters of warehouse space worldwide, JUSDA ensures that manufacturers and suppliers can access reliable storage and distribution solutions. Advanced inventory management systems, such as JusLink and eVMI, provide real-time tracking and transparency, helping companies respond quickly to changing market conditions.
Role of Global Investment and Expansion
Global investment in semiconductor manufacturing continues to accelerate. Major foundries and memory producers have announced significant capital expenditures to expand capacity and modernize production lines. In 2024, foundry investments are projected at $59 billion, rising to $65 billion in 2025. Memory investments remain strong, with $34 billion in 2024 and $33 billion in 2025. Total fab equipment spending is expected to reach $116 billion in 2025.
Investment Area | 2024 Projection | 2025 Projection |
|---|---|---|
Foundry | $59 billion | $65 billion |
Memory | $34 billion | $33 billion |
Total Fab Equipment Spending | $111 billion | $116 billion |
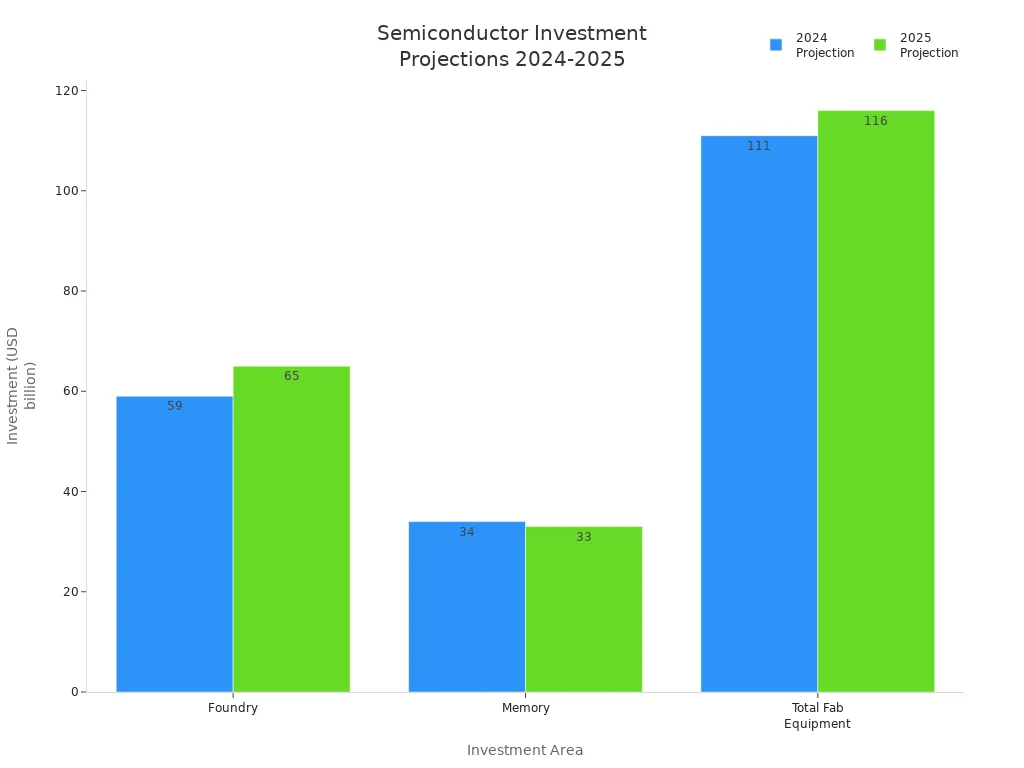
Leading companies such as TSMC, Samsung, and Intel are driving investments in logic and foundry sectors. Memory leaders like Micron, SK Hynix, and Kioxia are building next-generation fabs. Other manufacturers, including Texas Instruments and NXP, are enhancing power semiconductor production. These investments support the industry’s ability to meet rising demand and reduce the risk of future shortages.
JUSDA’s extensive global footprint supports this wave of expansion. The company operates warehouses in key regions, including China, Hong Kong, Japan, Vietnam, India, the United States, and Mexico. JUSDA’s facilities offer specialized services such as bonded storage, clean rooms, and value-added logistics. This infrastructure enables seamless movement of materials and finished goods, supporting both established and emerging markets.
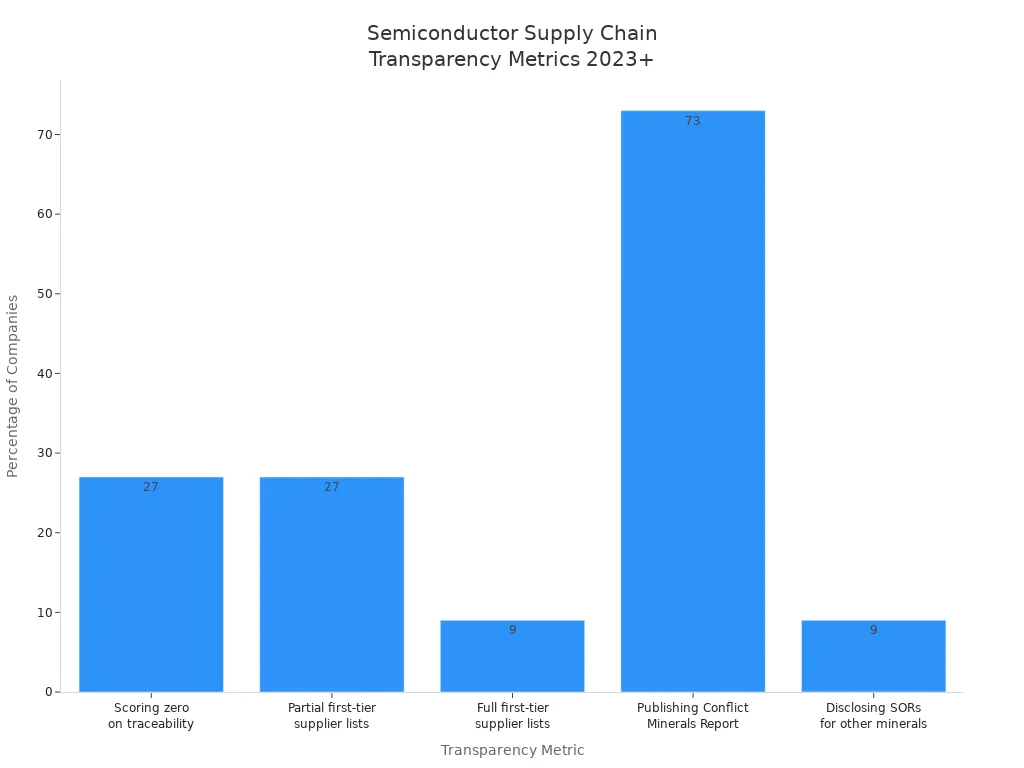
Supply chain transparency and traceability have also improved. More companies now disclose supplier lists and publish conflict minerals reports. JUSDA’s digital platforms, including JusLink, enhance visibility across the supply chain, allowing real-time collaboration and risk management.
Metric | Percentage |
|---|---|
27% | |
Companies disclosing partial first-tier supplier lists | 27% |
Companies disclosing full first-tier supplier lists | 9% |
Companies publishing Conflict Minerals Report | 73% |
Companies disclosing SORs for critical minerals other than 3TG | 9% |
JUSDA’s commitment to innovation, efficiency, and collaboration positions it as a key partner in the ongoing stabilization of the semiconductor supply chain. The company’s global network and advanced digital solutions help manufacturers and suppliers navigate a rapidly changing market, ensuring resilience and growth.
Disruptions and Challenges in Recent Years
Causes of Semiconductor Shortages
The global semiconductor industry faced a series of disruptions between 2020 and 2023. Several factors contributed to these shortages:
Pandemic-induced demand shifts changed the landscape. The COVID-19 pandemic drove a surge in demand for electronics as people worked and learned from home.
Supply chain fragility became apparent. Many companies relied on just-in-time manufacturing, which left little room for error when disruptions occurred.
Geopolitical tensions, especially trade restrictions between the US and China, created new bottlenecks in chip distribution.
Capacity limitations slowed recovery. Building new semiconductor fabrication plants required significant time and investment, restricting the ability to quickly increase supply.
Automotive miscalculations played a role. Early in the pandemic, car manufacturers canceled chip orders. When demand rebounded, they struggled to secure enough chips.
These combined challenges exposed vulnerabilities in the global supply chain and highlighted the need for greater resilience.
Impact on Manufacturing and Consumers
The semiconductor shortage had far-reaching effects on multiple industries and consumers worldwide.
The automotive industry suffered production cuts. Automakers such as Ford, GM, and Toyota halted product lines, resulting in billions of dollars in lost revenue.
Consumer electronics companies, including Apple and Samsung, experienced manufacturing delays. Consumers faced longer wait times and higher prices for devices.
Industrial and manufacturing sectors saw slowed adoption of automation and IoT devices. Companies experienced increased downtime and limited innovation.
Healthcare and medical device production slowed. Delays in sourcing chips affected the availability of essential medical equipment.
The table below summarizes the impact on product availability and pricing across key sectors:
Sector | Impact on Availability | Impact on Pricing |
|---|---|---|
Automotive | Reduced production, fewer vehicles available | Higher prices, longer wait times |
Consumer Electronics | Fewer products available, longer wait times | Increased prices for gadgets |
Healthcare | Delayed delivery of medical devices | Potentially higher costs for equipment |
Industrial | Slowed production due to chip delays | Increased operational costs |
Defense | Delays in military equipment production | Potentially higher costs |
Note: These disruptions underscored the importance of robust supply chain strategies and ongoing investment in manufacturing capacity.
Recovery Drivers: Innovation and Collaboration

The recovery of the global supply chain relies on innovation and collaboration. Companies have adopted new technologies and formed strong partnerships to build resilience. JUSDA stands at the forefront of this transformation, offering advanced warehouse solutions and digital platforms that support efficient and transparent operations.
JUSDA’s Warehouse Solutions for Supply Chain Efficiency
JUSDA’s global warehouse network provides a solid foundation for supply chain stability. With over 155 service points and more than 2.5 million square meters of warehouse space, JUSDA supports industries such as electronics, automotive, and consumer goods. The company’s warehouses in China, Vietnam, the United States, and other regions offer specialized services, including bonded storage, clean rooms, and value-added logistics.
JUSDA uses advanced inventory management systems like JusLink and eVMI. These systems enable real-time tracking and control, giving clients transparency and flexibility. Companies benefit from value-added services such as picking, packing, labeling, and kitting. JUSDA’s clean room facilities meet strict environmental standards, making them ideal for high-tech products.
Collaboration between manufacturers and logistics providers has improved supply chain resilience. Legislation such as the Promoting Resilient Supply Chains Act encourages cross-agency coordination. This approach allows manufacturers to align their operations with national strategies and work closely with logistics partners like JUSDA.
JUSDA’s warehouse solutions help companies reduce inventory costs, optimize capital usage, and improve product quality. These advantages support faster recovery and long-term growth.
JusLink’s AI-Powered Supply Chain Management
Digital transformation drives the next phase of supply chain recovery. JusLink, JUSDA’s intelligent supply chain platform, uses AI to enhance efficiency and risk management. The platform integrates IoT, cloud computing, and big data, providing real-time visibility across the supply chain.
JusLink’s AI features deliver measurable benefits:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Predictive Risk Management | AI systems analyze geopolitical developments and trade policy changes to recommend proactive adjustments. |
Supply Chain Intelligence | Companies report 60% faster response times to disruptions and 35% better inventory optimization. |
Automated Compliance Management | Processes complex documentation to identify compliance issues and vulnerabilities. |
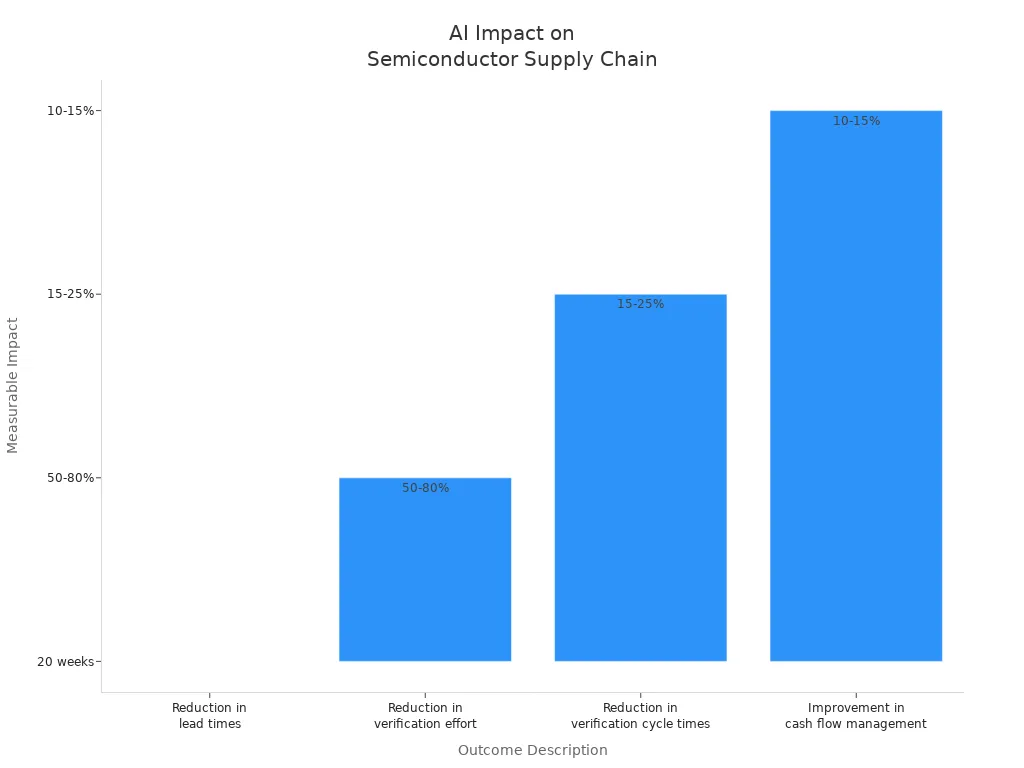
JusLink’s AI-powered management has led to significant improvements:
Outcome Description | Measurable Impact |
|---|---|
Reduction in lead times | |
Reduction in verification effort | 50-80% |
Reduction in verification cycle times | 15-25% within the first year |
Improvement in cash flow management | 10-15% |
Faster response to demand changes | Enables capturing market opportunities |
JusLink’s intelligent agents support production planning, inventory management, and risk control. The platform’s AI assistant, JusElsa, uses natural language processing to help users track shipments, assess risks, and generate reports. Companies using JusLink can respond quickly to market changes and manage risks more effectively.
Generative AI is driving demand for AI-enabling chips, leading to revenue growth in the semiconductor industry. Companies use digital twins to improve chip design and efficiency. The rise of AI has also boosted the market value of leading technology firms.
Industry Partnerships and Government Support
Strong partnerships and government support play a vital role in supply chain recovery. Recent collaborations between original equipment manufacturers, foundries, and governments have increased. These partnerships ensure better access to industry insights and early demand forecasts.
Partnerships between OEMs, foundries, and governments have increased to ensure a more resilient supply chain.
Strong relationships with key suppliers provide better access to industry insights and early demand forecasts.
Government initiatives, such as the U.S. CHIPS Act, aim to boost domestic chip production and enhance supply chain resilience.
Government programs provide significant funding and incentives:
Program/Measure | Amount (in billions) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
CHIPS for America Fund | Oversight of semiconductor funding | |
Semiconductor manufacturing incentives | $39 | Domestic manufacturing incentives |
R&D and workforce measures | $11 | Research and development, workforce support |
Semiconductor manufacturing investment tax credit | $24 | Tax credit for manufacturing investments |
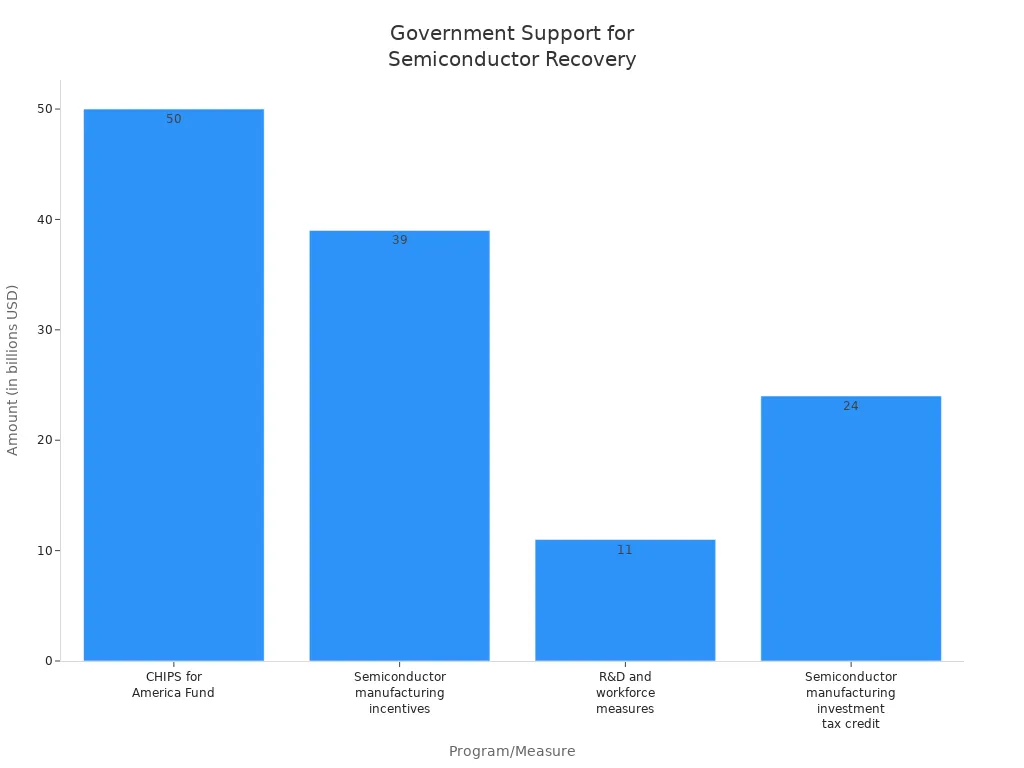
The CHIPS & Science Act lowers costs, creates jobs, and strengthens supply chains. It also addresses competition with other countries. The U.S. Department of Commerce’s new survey will provide insights into the capabilities and challenges facing the U.S. semiconductor supply chain.
The next chapter in recovery will focus on AI-led innovation, resilient sourcing, and sustainability. Companies are moving from just-in-time to buffered inventory strategies to ensure stability. Integration of production, market, and supplier data supports agile decision-making and enhances resilience.
JUSDA’s commitment to innovation, efficiency, and collaboration positions it as a key partner in this new era. The company’s digital solutions and global network help clients navigate a rapidly changing market and build a stronger, more resilient supply chain.
Ongoing Risks and Future Outlook
Semiconductor Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
The global semiconductor supply chain continues to face several vulnerabilities despite recent stabilization. Key risks include:
Geopolitical tensions, especially between the US and China, disrupt supply chains through sanctions and trade restrictions.
Export restrictions, such as those imposed by China on Nexperia, create production bottlenecks.
Just-in-time manufacturing practices reveal fragility during disruptions.
Labor shortages in the US semiconductor industry hinder domestic production scaling.
A blockade of Taiwan could halt the flow of vital semiconductor components worldwide.
Differences in work culture affect production efficiency, with US engineers prioritizing work-life balance compared to East Asian counterparts.
The industry relies heavily on East Asian countries for critical production stages, with companies like TSMC and SK Hynix playing pivotal roles.
Export controls on advanced microchips to China may lead to retaliatory measures, impacting global markets.
Memory product supply and demand trends have caused oversupply, price declines, and inventory backlogs. Manufacturers like Samsung and Kioxia have responded with production cuts to restore balance.
Memory suppliers are shifting from inventory-based models to forecast-driven production. This transition helps prevent excess stock and supports pricing stability, which is crucial for a more stable semiconductor supply chain.
Strategies for Long-Term Resilience
Leading companies implement several strategies to build long-term supply chain resilience:
Prioritize capital deployment based on demand signals to ensure flexibility.
Build sustainability into operations to meet regulatory expectations.
Invest in talent ecosystems by partnering with educational institutions and communities.
Reengineer supply chains for volatility by qualifying secondary suppliers and modularizing capacity.
Companies also diversify manufacturing operations to reduce dependence on single regions or suppliers. They use digital twins and predictive analytics for proactive risk management. Investment in talent and sustainability strengthens the workforce and supports environmentally friendly practices.
Global semiconductor collaboration allows organizations to access new markets and technologies. For example, TSMC, Robert Bosch, Infineon, and NXP Semiconductors formed a joint venture in Germany to enhance manufacturing services within the EU.
Technology Integration | Impact on Supply Chain |
|---|---|
AI-driven supply chain intelligence | |
AI-powered freight audit solutions | Ensures compliance and adaptability |
AI-driven systems for geopolitical analysis | Improves risk management and production stability |
JUSDA remains committed to digital supply chain solutions and global expansion. The company’s JusLink platform leverages AI and real-time data to enhance visibility, risk management, and operational efficiency. JUSDA’s global network and advanced technology help clients adapt to ongoing risks and build a resilient future.
Several factors drive the stabilization of the semiconductor supply chain:
Strong demand from AI infrastructure and industrial automation
Growth in automotive electronics and recovery in consumer devices
Industry experts highlight ongoing risks, including:
Cybersecurity threats and climate change
Supply shortages and regulatory changes
JUSDA and digital platforms like JusLink will continue to lead with real-time data sharing and resilient strategies. Their commitment to innovation and collaboration positions them to shape the future of global supply chains.

JUSDA Solutions
To provide you with professional solutions and quotations.
FAQ
What types of warehousing services does JUSDA provide?
JUSDA offers general storage, bonded warehouses, distribution centers, and finished goods storage. The company also provides clean room facilities that meet strict environmental standards for technology brands.
How does JusLink improve supply chain management?
JusLink uses AI, IoT, and cloud computing to provide real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and risk management. Companies gain better control over inventory, faster response to disruptions, and improved decision-making.
What industries benefit from JUSDA’s solutions?
Industry | Example Applications |
|---|---|
Electronics | Manufacturing, logistics |
Automotive | Parts, finished vehicles |
FMCG | Distribution, warehousing |
Medical Health | Equipment, supply chain |
Does JUSDA support global operations? 🌏
JUSDA operates over 155 service points worldwide, with warehouses in China, Vietnam, the United States, Japan, India, Mexico, and more. This global network supports seamless logistics and supply chain management for international businesses.
See Also
Understanding Inflation's Impact on Supply Chain Challenges
A Complete Guide to Overcoming Supply Chain Challenges
Exploring Jusda's Supply Chains and Global Market Needs
Transforming Supply Chains Through IoT Innovations and Trends
Enhancing High-Tech Manufacturing Supply Chains for Better Efficiency
