Standardize Location Coding and Item Information Management-duplicate

Imagine you manage inventory across multiple locations, but each team uses different codes and item names. You face confusion, errors, and wasted time. Recent industry studies show that inconsistent data can cost companies millions each year and lead to costly mistakes, such as overstocking, lost revenue, or compliance failures. When you Standardize Location Coding and item information, you improve data quality, streamline operations, and make smarter decisions. Reliable data helps you avoid risks and build trust across your business.
Key Takeaways
Standardizing location codes and item data reduces errors, saves time, and improves data accuracy across your business.
Using clear, consistent codes helps teams avoid confusion and supports faster, smarter decision-making.
Implementing strong data structures and management systems like PIM and MDM creates a single source of truth for your product information.
Follow key steps like data gathering, cleansing, taxonomy building, and governance to keep your data reliable and secure.
Good change management and regular reviews ensure your standardization efforts succeed and adapt as your business grows.
Why Standardize Location Coding

Data Consistency
You face many challenges when you do not standardize location coding. Different teams may use their own acronyms, abbreviations, or even handwriting styles. This leads to confusion and errors. For example, one person might write “Main St” while another writes “main street.” These small differences can cause big problems in your data systems.
When you use non-standard codes, you create barriers for your IT and operations teams. They spend extra time fixing mistakes and matching data from different sources. You may also lose valuable insights because your data does not match up.
Here are some common problems caused by non-standardized location codes:
Data inconsistencies and inaccuracies from different formats and terms.
Extra manual work for your IT and coding teams.
Delivery errors and miscommunication.
Loss of insights due to uncoded or proprietary data.
Address Component | Challenge Due to Non-Standardization | Impact on Organizations |
|---|---|---|
Street Names | “main street” vs. “Main St” | Confusion and errors in data processing |
Unit Designations | “apt 2” vs. “Apt 2” | Delivery errors and miscommunication |
City Names | Inconsistent formatting | Hindered data matching and validation |
State Abbreviations | “Miss.” vs. “MO” | Errors in address matching and geocoding |
Postal Codes | “12345” vs. “12345-6789” | Undeliverable mail and customer dissatisfaction |
When you standardize location coding, you remove these barriers. You create a single source of truth for your data. This helps everyone in your organization work with the same information.
Inventory Accuracy
You need accurate inventory data to run your warehouse smoothly. Standardize location coding to make sure every item has a unique and clear place in your system. When you use barcodes, RFID tags, or serial numbers, you track items in real time. This reduces manual errors and helps you find products quickly.
RFID technology lets you scan many items at once, even if you cannot see them. This speeds up inventory counts and improves accuracy. When you connect these unique codes to your warehouse management system, you always know where your products are. You can spot problems early and fix them before they grow.
Honeywell’s research shows that using system-directed processes and scanning storage locations can push inventory accuracy above 99.88%. Clear and consistent labeling, regular audits, and technology like barcodes all help you keep your inventory data sharp. You pick orders faster, make fewer mistakes, and keep your customers happy.
Item Information Management

Data Structure
You need a strong data structure to manage item information effectively. Accurate item identification forms the foundation of your inventory system. When you know exactly what each item is, you avoid confusion and mistakes. This accuracy supports better inventory tracking, sales fulfillment, and customer satisfaction.
A well-structured data model brings many advantages:
It defines clear validation rules and business logic, so your data stays accurate.
It organizes information logically, making it easy for you and your team to find what you need.
It supports scalability, so your system grows with your business.
It creates a common language for everyone, from warehouse staff to IT teams.
A good data structure also helps you enforce business rules, optimize performance, and support data governance. You can manage access, track changes, and ensure compliance with regulations. This structure lets you retrieve data quickly and make informed decisions.
PIM and MDM Systems
Product Information Management (PIM) and Master Data Management (MDM) systems help you standardize and centralize item data. Both systems aim to create a single source of truth, but they serve different purposes.
Aspect | Product Information Management (PIM) | Master Data Management (MDM) |
|---|---|---|
Primary Focus | Centralizes, enriches, and syndicates product information for sales and marketing. | Consolidates data across the enterprise for a trusted single source of truth. |
Scope | Sales, marketing, and external partners. | Enterprise-wide, covering products, customers, suppliers, and more. |
Data Management | Detailed product content, digital assets, and localization. | Standardization, relationship management, and cross-functional consistency. |
Use Cases | Omnichannel content, workflow automation, sales enablement. | Data quality, governance, integration, and reporting. |
Golden Record | Sales and marketing product data. | Master record shared across all systems. |
Users | Sales, marketing, content teams. | IT, data governance, business users. |
Complementarity | Feeds enriched content into MDM. | Provides analytics and process foundation. |
PIM works best when you need to manage complex product catalogs and deliver consistent information across many channels. MDM suits you if you want to unify data from different departments and ensure compliance. Many organizations use both systems together for the best results.
When you implement PIM or MDM, you gain real benefits:
You streamline operations with a single data source.
You improve decision-making with reliable data.
You speed up product launches and market expansion.
You enhance customer experience with accurate product details.
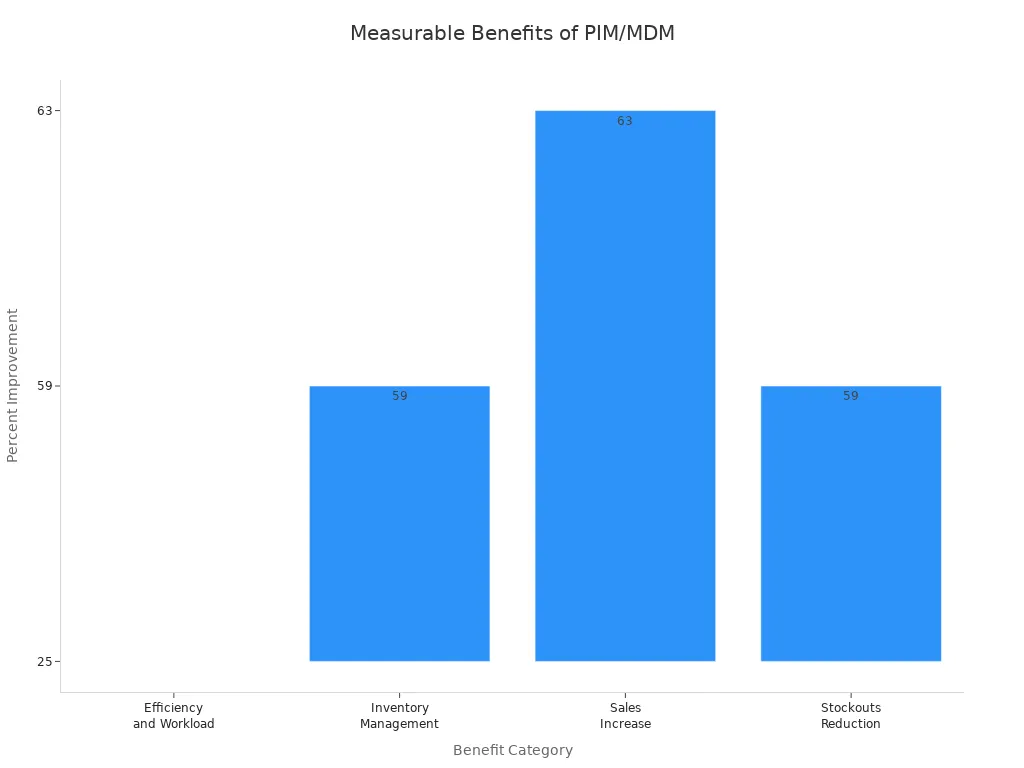
You also strengthen data governance, support compliance, and enable better collaboration with suppliers and partners. With the right systems and structure, you set your business up for growth and success.
Standardization Steps
Data Gathering
You start by collecting all relevant location and item data. Define your data collection methods and clarify the purpose behind each data point. This step helps you focus on what matters most for your business. Document every part of the process, using standardized naming conventions to keep everything consistent.
Follow these best practices for effective data gathering:
Clearly outline why you collect each type of data and how you will use it.
Use standardized forms and templates to avoid confusion.
Gather only the data you need. Too much information can slow down your system and increase costs.
Store your data securely and organize it for easy access.
Test your data collection methods before and after you launch them. Use sampling and validation to check for errors.
Protect your data with strong security measures, including role-based access and regular backups.
Use automation tools like online forms, APIs, and ETL platforms to speed up data collection and reduce manual work.
Tip: When you Standardize Location Coding from the start, you prevent many errors and make future steps much easier.
Validation and Cleansing
Once you gather your data, you need to clean and validate it. This step ensures your information is accurate, complete, and ready for use. You want to remove duplicates, fix errors, and fill in missing details.
Here is a step-by-step approach:
Identify problems such as duplicates, missing values, or inconsistent formats.
Standardize formats for addresses, dates, and other key fields.
Use automated tools to remove duplicate entries.
Fill in missing data using logical methods or imputation.
Check for consistency in capitalization, language, and data types.
Correct errors with validation tools and spell-checkers.
Normalize data from different sources to a single standard.
Consider AI-powered tools to automate detection and correction.
Note: Clean data forms the backbone of any effort to Standardize Location Coding and item information. Without this step, your system will always struggle with errors.
Taxonomy and Codes
You need a clear taxonomy and coding system to organize your data. Start by defining what you want to organize, such as products or locations, and who will use the taxonomy. Build a hierarchy with broad categories at the top and more specific ones below.
Follow these steps to create an effective taxonomy:
Define the scope and audience for your taxonomy.
Create a structure with clear, non-overlapping categories.
Review your actual items and locations to ensure everything fits.
Validate your taxonomy with experts and end users. Gather feedback and make adjustments.
Set up governance processes for proposing and approving changes.
Secure support from leadership to maintain the taxonomy over time.
Use automation tools to help classify data and reduce manual work.
A well-designed taxonomy makes it easier to Standardize Location Coding and manage item information. It also helps your team find and use data quickly.
Step | Description |
|---|---|
Define Scope | Decide what to organize and who will use it |
Build Hierarchy | Create broad-to-specific categories |
Review Items | Ensure all data fits into the structure |
Validate | Test with users and experts |
Govern | Set rules for changes and updates |
Automate | Use tools to speed up classification |
Governance
Strong governance keeps your data standardized over time. You need clear rules, roles, and processes to manage your location and item data. Good governance ensures data quality, security, and compliance.
Key pillars of data governance include:
Data Quality: Regular validation and cleansing keep your data accurate and reliable.
Data Integration: Combine data from different sources for a unified view.
Data Privacy and Security: Protect sensitive information and follow regulations.
Data Architecture: Design systems that support your business needs.
You can choose from several governance models:
Centralized: One team manages all policies and standards.
Decentralized: Each department handles its own governance.
Federated: Central policies exist, but departments implement them.
Distributed: Teams share governance responsibilities.
Assign clear roles such as data owners, stewards, and custodians. Use frameworks like DAMA-DMBOK or the PwC Enterprise Data Governance Framework to guide your efforts. Regularly review your policies and update them as your business grows.
When you Standardize Location Coding and item information, you set the stage for better decision-making, lower risk, and smoother operations. Good governance ensures these benefits last.
Examples and Benefits
Inventory Optimization
When you Standardize Location Coding and item information, you unlock powerful inventory optimization. Many companies have seen big improvements by using automation and better data.
Holocene’s clients use robotic process automation, electronic data interchange, and mobile stock control to boost inventory visibility and accuracy.
A retail chain cut storage costs by 25% after switching to a centralized, automated inventory system. This change made stock levels clear and helped managers make better decisions.
A global manufacturer improved order fulfillment rates by 30% with predictive analytics for supply chain planning.
About 73% of warehouses plan to use mobile stock control, showing a strong move toward standardized and accessible data.
Automated stock replenishment based on real-time sales data reduces errors and keeps inventory accurate.
Metso’s experience shows the value of standardization. By integrating Servigistics with SAP and standardizing inventory planning across 39 locations, Metso saved over EUR 30 million in the pilot phase. Later, they added multi-echelon inventory optimization and saved another EUR 11.6 million, with an 18% increase in inventory turns. You can see how standardized data and integrated systems lead to better planning and faster response to changes.
Operational Efficiency
Standardization brings clear, measurable gains in operational efficiency.
Industry Sector | Standardization Initiative | Measurable Improvement | Mechanisms Behind Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
Manufacturing | Standardized production protocols | Consistent operations, KPI monitoring | |
Retail | Standardized inventory management/training | 25% fewer stock discrepancies | Real-time analytics, uniform processes |
Financial Services | Standardized loan processing | Faster approvals, fewer errors | Streamlined workflows, enhanced trust |
You can boost efficiency by training employees on standard procedures and using technology like ERP systems. Automated workflows cut down on mistakes and save time. Tracking key performance indicators helps you measure progress and keep improving.
Integration
When you Standardize Location Coding and item data, you make it easier to connect systems and share information.
Automating manual processes saves time and money by reducing labor and material costs.
Error rates drop when you compare results before and after automation.
Productivity rises as teams complete tasks faster and with fewer mistakes.
Risk goes down because you avoid outages and data breaches.
Companies see real value, such as revenue growth and lower maintenance costs.
Cost of Quality Analysis shows that investing in prevention and appraisal activities lowers the cost of failures like rework and warranty claims. Cost-Benefit Analysis helps you see the return on investment by comparing development costs to labor savings and fewer errors. These tools help you choose the best projects for your business.
Pitfalls to Avoid
Change Management
You will likely face resistance when you introduce standardization. Many employees worry about change, especially if they do not understand the benefits. Common issues include change fatigue, poor communication, and lack of leadership support. You may also see low motivation if staff feel left out or overwhelmed.
Change oversaturation can cause burnout and fatigue.
Poor communication leads to confusion and misalignment.
Employees resist change when they do not see clear benefits.
Lack of executive sponsorship weakens the project.
Limited training and resources slow progress.
A culture resistant to change blocks new initiatives.
Tip: Secure visible support from senior leaders. Communicate openly and often. Involve employees in decisions and provide training. Celebrate small wins to build momentum. Align changes with your company’s mission and values. Listen to feedback and adapt your approach as needed.
Compliance
Maintaining compliance with standardized data practices requires ongoing effort. You need to set clear rules and monitor adherence across your organization. Without strong compliance, data quality drops and risks increase.
Establish clear transformation rules for data formats.
Use automated tools and manual checks to clean data.
Roll out standardization in phases, starting with pilot teams.
Train staff on protocols and their roles.
Monitor and review processes regularly with audits and feedback loops.
Protect data privacy and limit access to authorized users.
Update processes as regulations and business needs change.
Assign data owners and stewards for accountability.
Regular training and cross-department collaboration help you maintain compliance and adapt to new requirements.
System Integration
System integration often fails when you overlook key lessons from past projects. You must define clear goals, communicate openly, and manage risks from the start.
Pitfall | How to Avoid It |
|---|---|
Set specific, measurable goals | |
Maintain strict scope control | |
Poor communication | Keep open channels with all teams |
Ignoring risks | Identify and address risks early |
Lack of flexibility | Stay adaptable to changing needs |
You should review progress often, assign clear roles, and learn from each project. These steps help you avoid costly mistakes and ensure your standardization efforts succeed.
Standardizing location coding and item information management brings clear benefits. You improve data quality, reduce errors, and support business growth. Key steps include data normalization, format standardization, and regular cleansing.
Start by auditing your current data, training your team, and setting validation rules.
Keep tracking progress with KPIs and update your practices as your business changes. Regular reviews and feedback help you stay efficient and compliant.
FAQ
What is location coding and why does it matter?
Location coding assigns unique identifiers to places in your system. You use these codes to track inventory, shipments, and assets. Standardized codes help you avoid confusion and errors. You improve accuracy and speed up operations.
How do you choose the right item information management system?
You evaluate your business needs, data volume, and integration requirements. You compare features like scalability, security, and ease of use. You select a system that supports your workflow and future growth.
What are common mistakes in standardizing data?
You may skip data cleansing, ignore user feedback, or use inconsistent formats. You risk errors and inefficiency.
Tip: Always validate your data and involve your team in the process.
How often should you review standardized codes and item data?
You review codes and item data at least once a year. You check for changes in business processes, regulations, or technology. Regular reviews keep your data accurate and relevant.
Can you automate standardization processes?
You can automate many steps using software tools. Automation helps you clean, validate, and organize data faster.
You reduce manual errors
You save time
You improve consistency
See Also
Unlocking Inventory Efficiency Through JUSDA's Expert Strategies
How JUSDA Transforms Logistics For Maximum Efficiency Gains
Leveraging JUSDA's Technology To Boost Logistics Performance
Exploring JUSDA's Logistics Innovations For High-Tech Manufacturing
Mastering Lean Logistics To Achieve High-Tech Manufacturing Goals
