How Supply Chain Leaders Can Leverage Emerging Technologies to Enhance Connectivity

Supply chain leaders can harness emerging technologies to bridge connectivity gaps and drive efficiency. Recent data shows that graph analytics helped a procurement firm cut supplier discovery time by 75%. Artificial intelligence forecasting and alternate routing improved delivery reliability by 10-20%. These results demonstrate the pressing need for leaders to assess their organization’s digital maturity and readiness for transformation.
Key Takeaways
Supply chain leaders must address disconnected operations and visibility gaps to reduce costs and improve response times.
Emerging technologies like IoT, AI, blockchain, cloud computing, and digital twins boost real-time tracking, decision-making, and supply chain resilience.
Enhanced connectivity enables real-time visibility, better collaboration, and faster, smarter decisions that improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Leaders should assess their digital maturity, build clear roadmaps, overcome adoption barriers, and measure progress to ensure successful technology integration.
Strong leadership and a culture of innovation help supply chains adapt, stay competitive, and drive continuous improvement amid disruptions.
Connectivity Challenges
Disconnected Operations
Many supply chains struggle with disconnected operations. These gaps often appear when different teams or systems do not share information quickly. For example, a mid-sized electronics manufacturer faced major delays after port congestion. Their teams tracked shipping, customs, and supplier costs in separate systems. As a result, five employees spent three weeks compiling cost data. In another case, a global manufacturer lost a million-dollar contract. Their pricing team took weeks to respond, while a competitor replied the same day. These stories show how slow reaction times and inaccurate cost forecasting can hurt business.
Disconnected systems also increase costs and reduce efficiency. The table below highlights the impact on supply chain performance:
Impact Metric | Percentage |
|---|---|
Increased operating costs | |
Lost revenue | 54% |
Missed customer deadlines | 44% |
Manual processes causing slow reaction times | 39% |
Disconnected core systems causing slow reaction times | 20% |
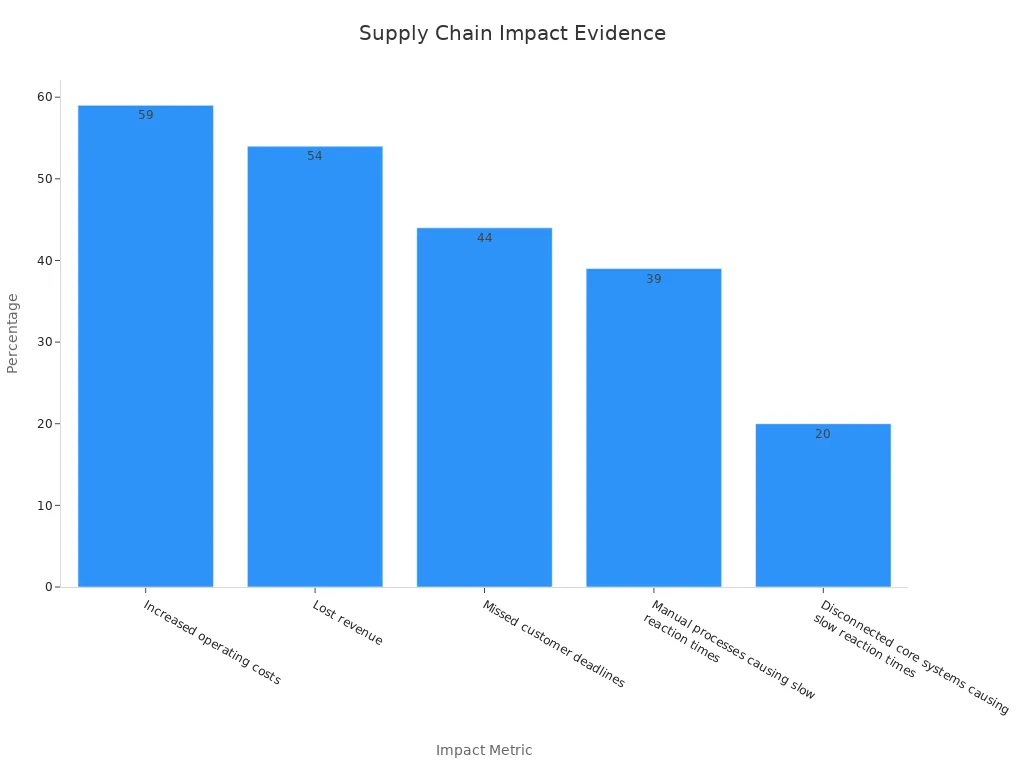
Disconnected operations make it hard for leaders to act quickly. They often miss opportunities and face higher risks.
Visibility Gaps
Visibility gaps create another major challenge. Many organizations cannot see real-time data across their supply chains. This problem often leads to shortages and wasted resources. Case studies from low- and middle-income countries show that poor data visibility causes avoidable shortages of health supplies. Outdated systems and weak staff skills make these problems worse. When teams cannot access reliable information, they struggle to manage inventory and respond to changes.
These gaps cost organizations time and money. They also make supply chains less resilient. Improving data visibility helps teams make better decisions and avoid costly mistakes. Leaders who address these gaps build stronger, more responsive supply chains.
Emerging Technologies

The supply chain technology landscape is evolving rapidly. Companies now invest in tools that connect operations, improve visibility, and support smarter decisions. The global supply chain technology market reached $23.26 billion in 2023 and is projected to double by 2030, growing at an annual rate of 11.2%. Key drivers include AI, machine learning, blockchain, IoT, robotics, automation, predictive analytics, and cloud-based solutions. North America leads adoption, while Asia-Pacific grows fastest. Manufacturing and retail sectors benefit most from automation and e-commerce expansion.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Market Size (2023) | USD 23.26 billion |
Projected Market Size (2030) | USD 48.60 billion |
CAGR (2023-2030) | 11.2% |
Key Technologies Driving Growth | AI, machine learning, blockchain, IoT, robotics, automation, predictive analytics, cloud SCM |
Impact of COVID-19 | Accelerated adoption to address supply and demand challenges |
Regional Insights | North America largest market; Asia-Pacific fastest growing; Europe focuses on sustainability |
Leading Verticals | Manufacturing and retail & e-commerce sectors due to automation and e-commerce expansion |
Component Segments | Solutions (55.1% share in 2023) and services |
Solution Segment Details | Includes TMS, planning & analytics, warehouse & inventory management, procurement, MES |
Transportation Management System | Largest share in 2023; enables real-time tracking and efficient freight planning |
Service Segment Growth | Significant CAGR; includes professional and managed services providing data-driven insights |
Market Trends | Integration of advanced tech for efficiency, visibility, responsiveness; market consolidation |
IoT and RFID
IoT and RFID technologies transform supply chain tracking and connectivity. Companies use sensors and smart tags to monitor goods, equipment, and vehicles in real time. For example, Maersk places sensors in refrigerated containers to track temperature and humidity, sending alerts if conditions change. Walmart uses RFID tags and IoT-enabled robots to scan shelves, improving inventory accuracy and reducing stockouts. General Electric integrates IoT in factories to monitor equipment and prevent downtime.
IoT sensors provide real-time location, condition, and delivery estimates for goods worldwide.
Automated tracking reduces manual errors, while RFID tags and smart shelves improve inventory control.
IoT supports route optimization and vehicle tracking, cutting delivery times and fuel use.
Predictive maintenance with IoT minimizes equipment downtime and supply chain costs.
Real-time tracking increases transparency and trust by giving customers accurate delivery updates.
IoT also boosts security by detecting unauthorized access and ensuring compliance for sensitive products.
Company/Industry | IoT/RFID Application | Impact on Supply Chain Real-Time Tracking and Connectivity |
|---|---|---|
Maersk (Logistics) | Sensors in containers monitor temperature and humidity, data sent to cloud | Real-time tracking, immediate alerts, route optimization, reduced costs |
Walmart (Retail) | RFID tags on products, IoT robots scan shelves | Real-time stock visibility, improved accuracy, automated replenishment |
General Electric (Manufacturing) | IoT in production plants | Increased efficiency, minimized downtime, better monitoring |
AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning help companies predict demand, optimize routes, and manage inventory. Amazon uses machine learning to forecast demand and manage stock, reducing shortages and excess inventory. Unilever analyzes sales data and market trends to allocate resources and cut waste. BMW uses AI to plan delivery truck routes, saving fuel and time. DHL predicts warehouse order peaks, improving staffing and service quality.
Demand forecasting improves by analyzing sales and trends, reducing stockouts and overstock.
Machine learning finds the best reorder points, lowering holding costs.
AI evaluates supplier performance and risk, building a stronger supply chain.
Route optimization uses traffic and weather data to cut delivery times and costs.
Real-time analytics enable quick responses to market changes.
AI and blockchain integration foster transparency and cost optimization.
Research and case studies, such as those at Mahindra and Mahindra, show that AI-driven demand forecasting, logistics, and production planning increase efficiency and support better decisions.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology creates a secure, shared record of every transaction in the supply chain. This transparency helps companies track products from raw materials to finished goods. For example, Maersk and IBM's TradeLens platform uses blockchain to share shipping data across partners. Pharmaceutical companies use blockchain to fight counterfeit drugs and ensure compliance.
Measurable Improvement | Description | Real-world Example |
|---|---|---|
Increased traceability | Tracks every step from raw materials to finished products | Automotive company tracking parts to ensure quality |
Improved product quality assurance | Verifies parts and materials to maintain standards | Automotive company ensuring product quality |
Prevention of counterfeiting | Ensures authenticity of products through immutable records | Pharmaceutical company counteracting counterfeit drugs |
Swift identification and resolution in recalls | Pinpoints source of issues for corrective action | Blockchain enabling rapid product recall management |
Compliance with environmental and sustainability standards | Verifies origins and compliance of raw materials | Electronics manufacturer verifying sustainability |
Increased consumer trust | Provides verifiable product origin and authenticity | Consumers able to verify product authenticity via blockchain |
Single source of truth | Immutable ledger accessible to all stakeholders | General blockchain ledger feature improving transparency and accountability |
Blockchain improves traceability, quality assurance, and consumer trust. It also speeds up recalls and supports compliance with regulations.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing gives supply chains the flexibility to scale and adapt quickly. Companies use cloud platforms to store data, run analytics, and connect partners. Cloud adoption increases demand forecast accuracy by 26%, reduces operating costs by 16%, and boosts revenue growth by 5%. Over half of executives report greater resiliency and faster scaling with cloud solutions.
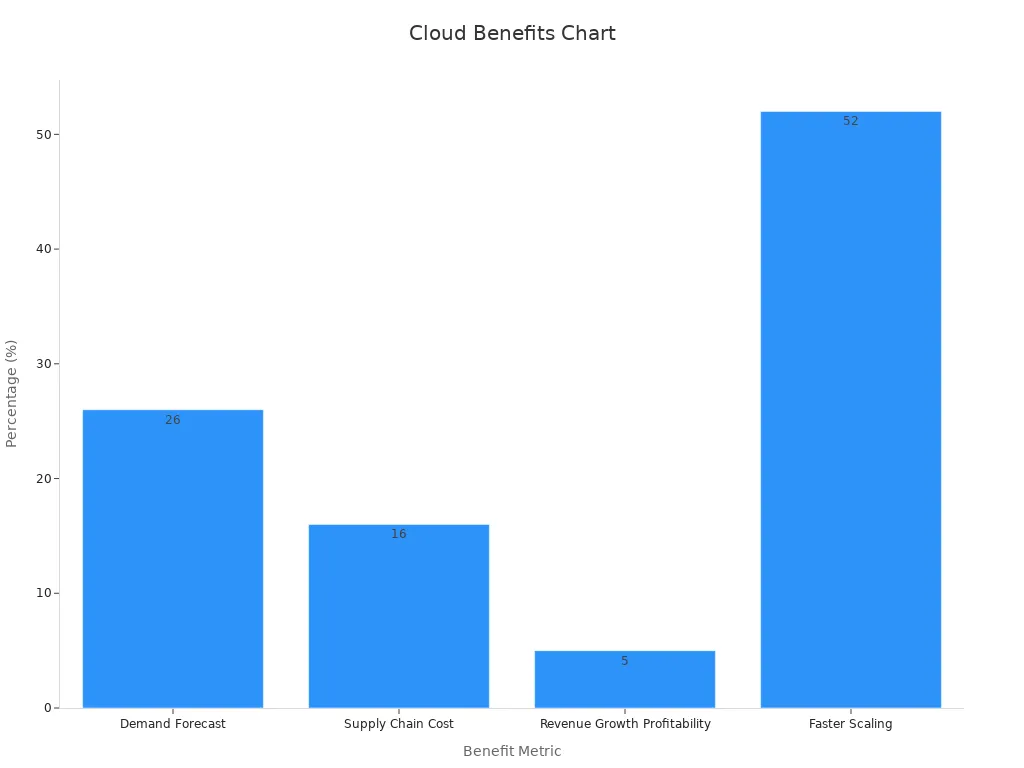
Case Study Outcome | Statistic | Relevance |
|---|---|---|
Logistics Cost Reduction | 30% | Cost savings and IT overhead reduction |
Delivery Time Improvement | 25% | Enhanced operational scalability |
Supply Chain Visibility Increase | 20% | Improved scalability and management |
Cloud systems reduce capital and operational costs, improve visibility, and allow companies to scale resources as needed.
Digital Twins
Digital twins create virtual models of supply chains, allowing companies to simulate and optimize processes. DHL uses digital twins for fleet and warehouse management, cutting downtime by 50% and transportation costs by up to 15%. Siemens applies digital twins to manufacturing, improving inventory management and predictive maintenance.
Company | Application Area | Benefits and Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
DHL | Fleet and warehouse operations | 50% less downtime, 10-15% lower transportation costs, better order fulfillment |
Siemens | Manufacturing and supply chain | Improved inventory, predictive maintenance, faster decisions |
Vita Coco, a global beverage company, built a digital twin of its supply chain to model every node, cost, and constraint. This enabled an optimized 18-month plan, saving millions of dollars and improving decision support through scenario simulation.
Digital twins help companies test changes before making them, improving resilience and efficiency.
Advanced Analytics
Advanced analytics use data to improve decision-making and network efficiency. Walmart applies real-time analytics and machine learning to predict customer behavior with up to 95% accuracy. This reduces stockouts and overstock, leading to an 8% sales increase during peak seasons and higher customer satisfaction.
1. Real-time visibility gives end-to-end control, allowing proactive monitoring of deliveries and inventory. 2. Predictive analytics improve demand forecasting, balancing inventory and enabling just-in-time strategies. 3. Supplier analytics identify risks and optimize portfolios, making supply chains more resilient. 4. Procurement optimization reduces costs and improves supplier relationships. 5. Logistics optimization uses machine learning for route planning and warehouse slotting, increasing efficiency.
Advanced analytics help companies make faster, smarter decisions and respond quickly to changes.
Note:
Emerging trends like agentic AI, ambient intelligence, and the augmented connected workforce are reshaping supply chain connectivity. Agentic AI acts as an autonomous manager, making decisions and coordinating actions without human intervention. Ambient intelligence uses low-cost sensors and smart tags for real-time visibility. The augmented workforce leverages digital tools to improve decision accuracy and productivity. These trends drive the shift toward fully autonomous, intelligent supply chains.
Benefits of Enhanced Connectivity

Real-Time Visibility
Enhanced connectivity gives supply chain leaders real-time visibility across every stage of operations. IoT sensors and cloud-based platforms provide instant updates on inventory, shipments, and production status. This transparency allows teams to spot disruptions early and respond quickly. For example, real-time data and IoT tracking enable faster, informed responses to unexpected events. Companies can monitor goods in transit, track supplier performance, and ensure compliance with regulations. As a result, they reduce the risk of shortages and improve customer satisfaction.
Better Decision-Making
Reliable, updated data supports better decisions at every level of the supply chain. Enhanced connectivity integrates large datasets from multiple sources, making it easier to analyze trends and adapt to changes. Data-driven studies show that companies with strong connectivity can reduce costs and strengthen their competitive edge. Improved demand forecasting with AI and machine learning leads to better inventory alignment and less waste. Predictive analytics and real-time monitoring also help teams manage risks and optimize costs. These capabilities transform strategic planning into actionable steps, increasing resilience and efficiency.
Enhanced connectivity empowers supply chain leaders to make agile, informed decisions that keep operations running smoothly.
Collaboration
Collaboration improves when partners share data and work together in real time. Integrated systems, such as ERP and SCM platforms, enable transparency and process synchronization. The table below highlights collaborative projects that boost integration and communication:
Project Type | Benefit | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
Vendor Managed Inventory | Joint inventory management | 15% lower inventory costs |
Sales & Operations Planning | Cross-functional alignment | Improved forecast accuracy |
Supplier Relationship Mgmt | Shared performance metrics | 20-30% cost reduction |
Collaborative Demand Planning | Synchronized planning | Fewer stock-outs and excess inventory |
These projects show that real-time data sharing and joint problem-solving lead to measurable gains in efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Efficiency and Resilience
Enhanced connectivity streamlines supply chain networks and builds resilience against disruptions. Centralized data and digital monitoring reduce transportation, inventory, and handling costs. Multi-sourcing strategies and scenario planning help companies adapt and recover quickly. Key metrics, such as Time-to-Survive and Time-to-Recover, measure how well a supply chain endures and bounces back from challenges. Companies that invest in connectivity often see improved operational efficiency, stable market share, and higher customer retention during volatile periods. Real-world examples, like Toyota’s proactive stockpiling, prove that resilience investments pay off over time.
Implementation Guide
Assess Current State
Supply chain leaders begin by evaluating their organization’s current digital maturity and technology readiness. A structured framework helps guide this assessment. The Industry 4.0 readiness model uses two main phases:
Evaluate the company’s current readiness level. This step positions the organization on a scale, such as Industry 3.0 (automation) to Industry 4.0 (full digital integration). Many companies find themselves at an intermediate stage, like Industry 3.5, showing partial readiness.
Analyze barriers to technology adoption. The DEMATEL method, a decision-making tool, identifies and ranks obstacles. Leadership and organizational policy often emerge as the most influential barriers, affecting other challenges like skills gaps or fragmented systems.
Tip:
Leaders should involve cross-functional teams in this assessment. This approach ensures a complete view of technology gaps, process bottlenecks, and organizational readiness.
A readiness assessment provides a clear starting point for digital transformation. It highlights strengths, weaknesses, and areas needing immediate attention.
Overcome Barriers
Many organizations face common barriers when adopting new technologies. These include high costs, resistance to change, lack of skilled personnel, and fragmented systems. Leaders can address these challenges with proven strategies:
Barrier | Case Study Insights | Strategies to Overcome |
|---|---|---|
High Implementation Costs | SMEs often struggle with limited resources. | Launch pilot projects, seek subsidies or tax incentives |
Resistance to Change | User resistance slows adoption. | Engage stakeholders early, provide training |
Lack of Skilled Personnel | Skills shortages limit integration. | Invest in training, partner with external experts |
Technological Fragmentation | Disconnected systems create integration issues. | Plan for integration, promote partner collaboration |
User Perceptions (Usefulness) | Perceived usefulness and ease of use affect adoption rates. | Communicate benefits, demonstrate value |
Organizational Readiness | Low readiness hinders implementation. | Align technology with current processes |
Policy and Regulatory Environment | Policy gaps slow adoption. | Advocate for supportive policies and innovation grants |
Leaders who address these barriers early build a stronger foundation for digital transformation. Training, communication, and pilot projects help teams adapt and succeed.
Measure Success
Measuring progress ensures that digital transformation delivers real value. Leaders track a mix of technology, process, financial, and customer metrics. Key performance indicators (KPIs) include:
Technology and Innovation Metrics: digital maturity, cloud deployment percentage, AI-enabled process rate, innovation rate.
Project Management KPIs: on-time and on-budget completion, resource utilization, scope management.
Organizational Change KPIs: digital adoption rate, time-to-adoption, employee engagement, agility.
Business Process KPIs: cycle time, throughput, error rate, cost and quality of output.
Financial KPIs: ROI, operating margin, revenue from digital channels.
Customer Experience KPIs: customer satisfaction (CSAT), Net Promoter Score (NPS), retention rate, time-to-value.
Operational Efficiency: reduction in manual processes, automation levels, cost savings.
Employee Enablement: digital tool usage, training completion, feedback.
Regularly review these metrics to identify areas for improvement. Continuous monitoring helps maintain momentum and ensures that technology investments deliver lasting benefits.
Supply Chain Leaders and Digital Transformation
Driving Change
Supply Chain Leaders play a central role in guiding organizations through digital transformation. They set the vision for technology adoption and align teams around shared goals. Many case studies highlight how leaders use advanced tools such as agent-based modeling, digital twins, and graph neural networks to drive measurable improvements. For example:
A leader in an ASEAN apparel network improved on-time delivery by 9 points by building trust across partners.
In a MENA pharmaceutical supply chain, leadership initiatives reduced backorders by 11% through better collaboration.
A reverse logistics program achieved a 7.8% increase in material recapture and a 5.4% reduction in unit cost after leaders applied advanced analytics and scenario testing.
Supply Chain Leaders also use decision theater tools to turn complex analytics into clear actions. These tools help teams understand data and make faster decisions. In regions like Central Africa and Eastern Europe, leaders rebuilt supply networks quickly by integrating social metrics and advanced modeling. According to a recent survey, most leaders now change strategies in response to global events. Over half have adopted AI to predict and manage disruptions, but many still face challenges with technology integration and data quality. Leaders must balance daily operations with long-term transformation to achieve lasting results.
Fostering Innovation
Innovation thrives when Supply Chain Leaders encourage new ideas and support technology-driven change. Research shows that leadership style matters. Firms led by crisis, participative, or transformational leaders maintain higher innovation performance during disruptions. These leaders help teams adapt quickly and find creative solutions. For example, companies with strong leadership see less decline in logistics innovation, even when facing geopolitical challenges.
Supply Chain Leaders foster innovation by:
Promoting a culture of experimentation and learning.
Supporting cross-functional collaboration.
Investing in training and digital skills.
Recognizing and rewarding creative problem-solving.
A table below summarizes how leadership styles impact innovation during disruptions:
Leadership Style | Impact on Innovation Performance |
|---|---|
Crisis | Mitigates negative impact |
Participative | Mitigates negative impact |
Transformational | Mitigates negative impact |
Directive | No significant effect |
By championing innovation, Supply Chain Leaders help organizations stay resilient and competitive in a changing world.
Supply Chain Leaders drive transformation by adopting emerging technologies that enhance connectivity. They build stronger networks, improve visibility, and support better decisions. Leaders who act early gain a competitive edge. Starting with high-impact projects helps teams see quick results. Continuous innovation keeps organizations ready for future challenges. Technology adoption shapes the future of supply chains.
FAQ
What is the first step for supply chain leaders to adopt new technology?
Leaders should assess their current digital maturity. This step helps them identify gaps and set clear goals for technology adoption.
How does IoT improve supply chain visibility?
IoT sensors track goods, equipment, and vehicles in real time. This data gives teams instant updates and helps them respond quickly to changes.
Are cloud-based solutions secure for supply chain data?
Cloud providers use advanced security tools, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication. Leaders should review provider certifications and set strong access controls.
Can small businesses benefit from emerging supply chain technologies?
Small businesses can start with scalable solutions like cloud platforms or RFID. These tools offer quick wins and do not require large investments.
What skills do teams need for digital supply chain transformation?
Teams need data analysis, digital literacy, and problem-solving skills. Training and ongoing learning help employees adapt to new tools and processes.
See Also
Improving Supply Chain Efficiency Through Cloud-Based Innovations
Preparing For The Newest Transport Technologies In Supply Chains
Adjusting To Technology Advances In Modern Supply Chain Systems
Shaping Tomorrow’s Logistics Through Advanced Digital Solutions
