Understanding Tariffs and Their Economic Impact on Trade

Tariffs, as taxes imposed on imported goods, significantly influence trade by altering prices and supply dynamics. They can disrupt supply chains and increase costs for businesses, while shoppers often face higher prices and limited choices. In 2024, the U.S. imported $1.3 trillion worth of goods from countries subject to tariffs, such as Mexico, China, and Canada, showcasing how tariffs affect the economy. JUSDA provides expert solutions to help businesses navigate these challenges effectively, ensuring resilience and operational efficiency.
Key Takeaways
Tariffs are taxes on goods brought from other countries. They make items cost more and reduce what buyers can pick from.
Companies pay more and may face delivery problems because of tariffs. Adjusting to these issues is important to stay competitive.
Tools like JUSDA and JusTrade help companies handle tariff problems. They make work easier and save money.
What Are Tariffs and How Do They Affect the Economy?
Definition and Types of Tariffs
Tariffs are taxes on goods brought into a country. They help control trade between nations. By raising import costs, tariffs make foreign goods pricier. This often leads people to buy local products instead.
There are different kinds of tariffs, each with a unique goal:
Tariff Type | Description |
|---|---|
Specific Tariffs | A set fee for each unit of an imported item, like $5 per ton of steel. |
Ad Valorem Tariffs | A tax based on a percentage, such as 10% on imported cars. |
Import Quotas | Limits on how much of a product can be imported to protect local businesses. |
Voluntary Export Restraints | Deals where exporting countries agree to send fewer goods to other nations. |
In the past, countries like the U.S. used tariffs over 20% to protect their industries. These tariffs aimed to balance trade and support local businesses.
The Purpose of Tariffs in Trade Policy
Governments use tariffs for many reasons. One main reason is to protect local industries from foreign competition. Tariffs make imports cost more, helping local businesses sell more. For example, during the Great Depression, the U.S. created the Smoot-Hawley Tariffs to protect its economy.
Tariffs are also used in trade talks. Countries may add tariffs to push others into fair agreements. For instance, the America First Trade Policy shows how tariffs can reduce dependence on foreign goods and improve national security.
Another purpose of tariffs is to raise money for governments. Before income tax started in 1913, tariffs were a big source of U.S. income. Today, they still bring in money but are less important.
Tariffs also fix trade problems and ensure fair competition. For example, they stop dumping, where foreign companies sell items at very low prices to take over markets.
Mechanisms of Tariff Implementation and Collection
Setting and collecting tariffs involves several steps. Governments first sort imported goods using systems like the Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS). This system decides the tariff rate. Importers then report their goods to customs with detailed paperwork.
Customs workers calculate the tariff based on the goods' value or amount. Importers pay the tariff before their goods are released. Following customs rules is important to avoid fines or delays. For example, a furniture importer recently changed their product code under HTS, lowering their tariff costs.
Businesses use tools to manage tariffs better. These tools predict costs, find savings, and adjust to tariff changes. Checking customs bonds regularly also avoids surprise expenses.
Tip: Platforms like JusTrade make customs easier. JusTrade uses AI and big data to help with tariffs, ensuring correct classification and faster processing.
The Impact of Tariffs on Consumers, Businesses, and the Economy
Effects on Consumers: Prices, Choices, and Purchasing Power
Tariffs make imported goods cost more for shoppers. When businesses pay higher prices, they charge you more too. This means you can buy fewer things with the same money. For example, tariffs on clothes or gadgets can raise store prices. This makes it harder to afford these items.
Tariffs also limit the variety of products you can buy. Companies may stop selling certain items because of high costs. This leaves you with fewer options. A study by the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco shows how tariffs affect spending. It found that many things you buy, like durable goods, are often imported.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Survey Data | Data from German phone users to check spending habits. |
Consumption Expenditures | |
Import Content | Research on how much of what you buy is imported. |
When tariffs rise, you might spend less on fun items. Instead, you may focus on buying only what you really need.
Effects on Businesses: Costs, Supply Chains, and Competitiveness
Tariffs make running a business more expensive. If you own a business, you might pay more for materials or products. This lowers your profits and makes it harder to compete with others.
Tariffs also mess up supply chains. Companies face delays, extra fees, and customs rules. This slows down production and deliveries. Studies show these problems:
Tariffs make supply chains less efficient and harder to manage.
A 2002 study found tariffs caused job losses in industries needing imports.
Research showed washing machine tariffs raised prices for related items.
If your business depends on imports, tariffs may force you to find new suppliers. You might also need to change your prices, which can hurt your business.
Effects on the National Economy: Inflation, GDP, and Trade Balances
Tariffs affect the whole economy by raising prices. When goods cost more, your money buys less, and the economy slows. Tariffs also lower GDP by reducing trade. If businesses export less due to tariffs, the economy grows slower.
Trade balances, which compare imports and exports, also change. High tariffs may cut imports for a while but can lead to trade deficits later. The table below shows trade deficits and surpluses in different regions:
Country/Region | |
|---|---|
China | 26.9 |
European Union | 23.8 |
Mexico | 16.0 |
South and Central America | 3.5 |
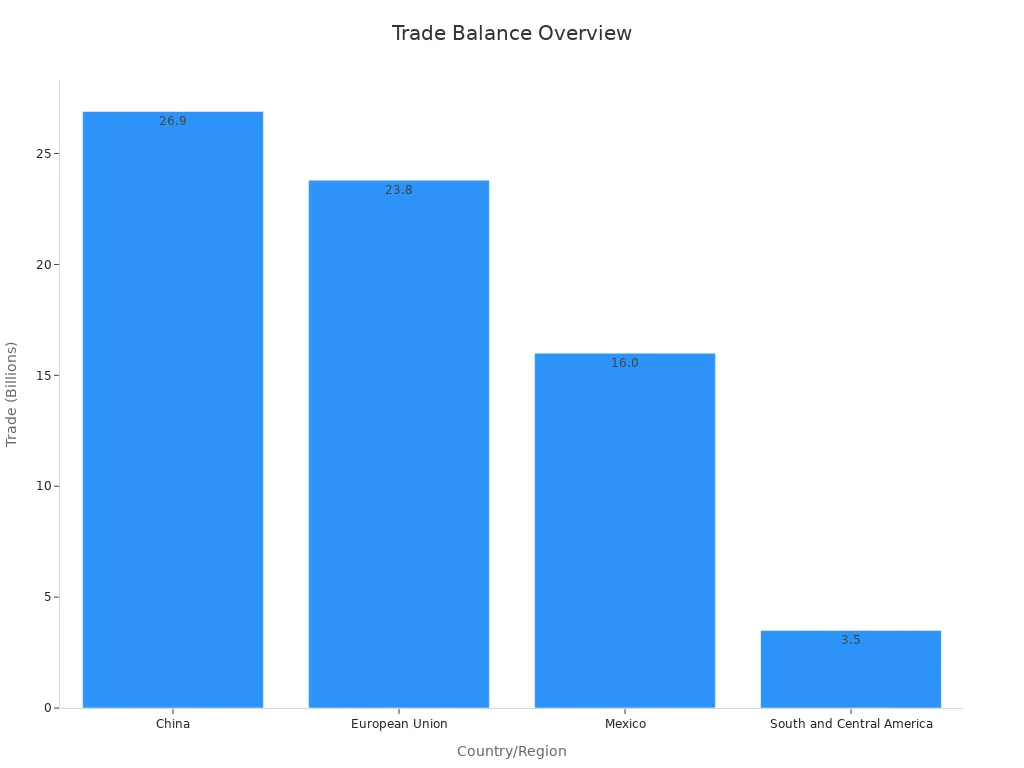
These numbers show how tariffs change global trade. If your job depends on international trade, these shifts can affect your work and income.
How JUSDA and JusTrade Help Businesses Mitigate Tariff Challenges
Dealing with tariffs can be tricky, but JUSDA and JusTrade make it easier. If you run a business, these tools help with customs and supply chains. JusTrade uses smart technology to classify goods and follow customs rules. This reduces mistakes and speeds up the process.
JUSDA’s platform helps with planning, shipping, and managing inventory. These tools help you adjust to tariff changes and stay efficient. For example, JUSDA helped Sharp cut shipping costs by 20% and speed up orders.
Using these tools can help your business handle tariffs better. This keeps you competitive even when tariffs make things harder.
Broader Economic Consequences of Tariffs
Trade Wars and Retaliatory Measures
Tariffs can lead to trade wars between countries. In these wars, nations add tariffs to fight back. This can cause economic problems and higher prices for people. For example, the U.S.-China trade war raised costs and hurt industries. Some say tariffs push for new ideas and growth. But they also make goods expensive and businesses less competitive. Trade wars can harm relationships between countries, making deals harder later.
Disruptions to Global Supply Chains
Tariffs make global supply chains harder to manage. Companies may need new suppliers or move factories to avoid tariffs. This causes delays and higher costs. Since 2020, foreign investments in North America grew by 134%. This shows how businesses adjust to tariff changes. By 2023, Mexico and Canada became top U.S. trade partners. Tariffs are changing how countries trade with each other.
Long-Term Impacts on International Trade Relations
Tariffs can hurt trust between trading countries. This may split global markets and weaken partnerships. Studies of Trump-era tariffs showed they didn’t fix trade deficits. Instead, they caused global money problems and slowed cooperation. Tariffs can lead to long-term harm in trade relations.
JUSDA's Role in Addressing Supply Chain Disruptions
JUSDA helps businesses deal with tariff problems. Its tools make supply chains work better, even with disruptions. For example, JUSDA improves customs and inventory management. This helps companies adjust faster to tariff changes. Using technology, JUSDA reduces the effects of tariffs on global trade.
Historical Examples of Tariffs and Lessons Learned

The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930
The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930 is a famous example of tariffs' effects. It raised taxes on over 20,000 imported goods to help U.S. industries during the Great Depression. The goal was to cut imports and increase local production. But it caused problems. Other countries fought back with their own tariffs, reducing global trade. From 1929 to 1931, exports dropped by 1.7% of the 1929 GDP. This made up 21% of the GDP loss in the first two years of the Depression.
President Hoover called the act "vicious" and "obnoxious." Experts agree it made the crisis worse. It shows that high tariffs can hurt trade and slow recovery.
The U.S.-China Trade War and Its Implications
The U.S.-China trade war is a recent example of tariffs' impact. The U.S. added tariffs on Chinese goods to fix trade gaps and protect security. In 2024, the U.S. trade deficit with China was $295 billion, the lowest since 2009. But tariffs also disrupted supply chains and raised business costs. U.S. exports to China were over $195 billion, showing how important this trade is.
Leaders also worried about stolen ideas, costing $225 to $600 billion yearly. These actions show the challenge of protecting jobs while keeping trade partnerships strong.
Insights for Modern Trade Policies
History shows tariffs can help or hurt economies. The Tariff Act of 1789 helped trade and raised money. In the 1800s, tariffs gave 95% of federal income. But by the 1900s, income tax replaced tariffs as the main revenue source. Modern policies must learn from the past. High tariffs, like the Smoot-Hawley Act, can lead to retaliation and harm trade. Leaders should balance protection with teamwork to support the U.S. economy and global trade.

JUSDA Solutions
To provide you with professional solutions and quotations.
Tariffs change trade by impacting costs, companies, and economies. Balancing local protection with global teamwork helps growth last. JUSDA and JusTrade make handling tariffs easier with smart tools.
What’s next for tariffs in world trade:
More protectionism might make markets unstable.
JUSDA helps you adjust and succeed in this changing world.
See Also
Exploring How Global Trade Policies Shape Economic Landscapes
Understanding The Importance Of Supply Chains In Global Trade
Achieving Success In International Trade Through JUSDA Solutions
