The Ripple Effects of Tariffs on Key Sectors in 2025

Tariffs are important for global trade and industries. In 2025, their impact grows stronger. The average tariff rate may rise to 29.3%. This could cause imports to drop by $800 billion. These changes affect industries by raising costs. They also disturb supply chains, especially in the U.S. economy.
Key Takeaways
Tariffs are going up, with an average of 29.3% in 2025. This rise may cause higher prices for buyers and fewer imports.
Companies should use different suppliers to avoid tariff problems. Tools like JUSDA’s Supply Chain Management can help handle these issues well.
Knowing trade deals, like the USMCA, can help companies save money and keep customers happy when prices change.
The 2025 Tariff Landscape
Key Tariff Changes and Trends
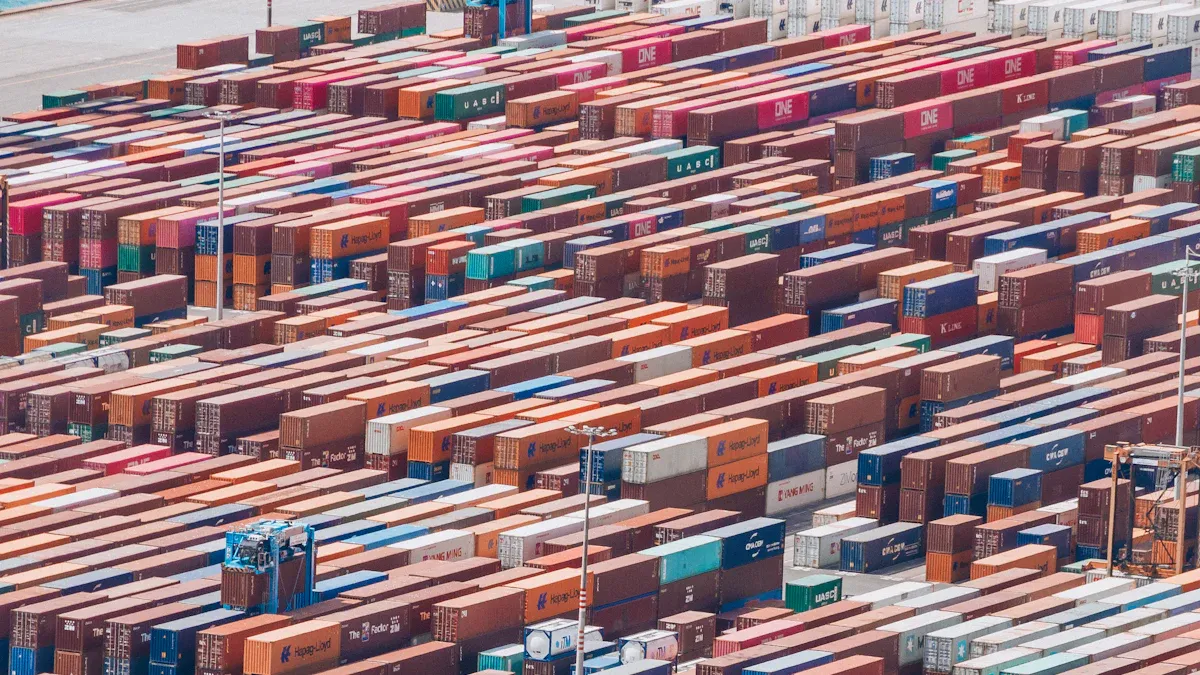
In 2025, global trade rules changed a lot. A 10% tariff now applies to all imports, affecting most industries. Steel and aluminum imports have a 25% tariff, raising production costs. Imported cars and car parts also face a 25% tariff since April 3, 2025. These changes show countries are protecting their own industries more.
Restaurants have been hit hard by these tariffs. By the end of 2025, restaurant sales may reach $1.5 trillion. This industry employs about 15.9 million workers. Higher costs for imported food have made restaurants raise prices. This shows how tariffs affect the economy overall.
Countries and Regions Most Affected
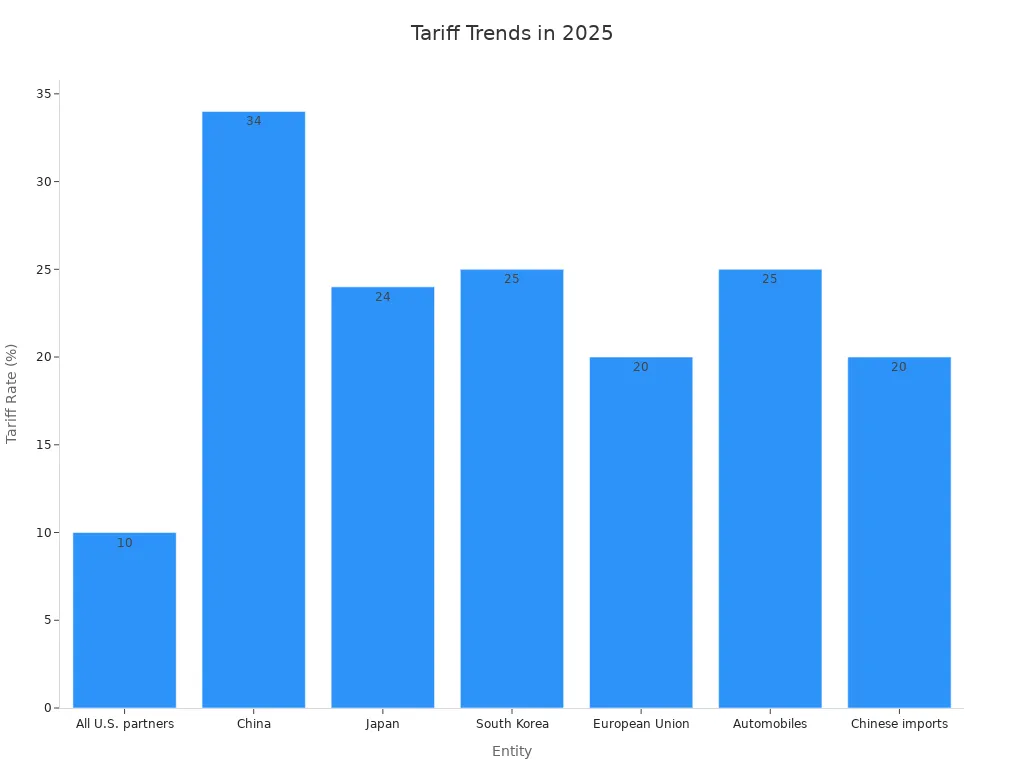
Tariff increases have caused problems for some countries and regions. The U.S. trade deficit led to higher tariffs on certain nations. China faces a 34% tariff, Japan 24%, and South Korea 25%. European Union countries deal with a 20% tariff. Mexico and Canada are mostly exempt under the USMCA, except for some goods.
Country | Tariff Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|
All U.S. partners | 10% | Standard tariff for all trading partners. |
China | 34% | Based on trade deficit with the U.S. |
Japan | 24% | Based on trade deficit with the U.S. |
South Korea | 25% | Based on trade deficit with the U.S. |
European Union | 20% | Based on trade deficit with the U.S. |
Mexico and Canada | N/A | Exempt under USMCA, except for some goods. |
Automobiles | 25% | Extra tariff on imported cars. |
Chinese imports | 20% | Extra tariff on specific goods. |
Exemptions and Special Agreements
Special agreements help reduce the impact of tariffs. For example, Mexico and Canada benefit from the USMCA deal. This protects them from most tariff increases, though some goods are still taxed.
Tariffs are like taxes on imports, raising costs for buyers. Over 30% of companies in a survey said tariffs are their biggest worry. This is up from 8.3% last quarter. Factories using Chinese imports pay the highest tariffs. Farms, however, have lower tariffs due to protections. These deals show how governments balance their needs with global trade.
Industry-Specific Impacts of Tariffs

Manufacturing Sector Challenges
In 2025, tariffs caused big problems for manufacturing. Higher costs for materials made production more expensive. Some companies had to lay off workers. For example, steel and aluminum tariffs raised costs for factories. This made it harder for them to compete worldwide. Steel jobs grew, but car and construction industries paid higher prices.
U.S. prices may rise by 7.1%, lowering buying power.
Car sales might drop by 1 million due to material costs.
Uncertain tariff rules made some factories plan to produce locally. These changes will take time to happen.
These issues show the struggle between helping local industries and keeping prices low.
Technology Industry Disruptions
The tech industry depends on global supply chains. Tariffs have made parts like wafer tools and optical modules cost more. U.S. factories may pay 15% more for wafer tools. Optical module prices could rise by 25-40%. These higher costs hurt profits and slow new technology development.
Tariffs also caused economic worries, slowing AI growth in the U.S. Companies are afraid to expand or try new tech because of rising costs. This could make it harder for the U.S. to stay competitive in the tech world.
Food and Beverage Industry Costs
The food and drink industry also felt tariff effects. Higher tariffs on imported ingredients and farm tools raised costs. Sustainable farming, which needs special tools, now costs more. Tariffs on vitamins and supplements made health products pricier.
Impact Area | Description |
|---|---|
Cost of Sustainable Practices | Tariffs on farm tools raised costs for sustainable farming. |
Ingredient Costs | Tariffs on vitamins made health products more expensive. |
Technology Costs | AI-related tariffs raised costs for food companies. |
Supply Chain Disruptions | Tariffs on plant-based imports raised costs for producers. |
Retaliatory tariffs made things worse. For example, in March 2025, China added a 100% tariff on Canadian canola oil and 25% on pork. These actions disrupted supply chains and raised prices for consumers.
Date | Event Description | Tariff Rate Change |
|---|---|---|
April 2, 2025 | U.S. raised tariffs on imports to specific rates. | Increase from 10% to individualized rates |
March 8, 2025 | China added tariffs on Canadian farm goods. | 100% on canola oil, 25% on pork |
Automotive and Aftermarket Sector Effects
The car industry faced major problems from tariffs. Higher costs for parts from China added 10% to material prices. In 2025, the average price for new cars in the U.S. hit $50,000, up from $48,000 in 2024. Canadian car prices also rose by over 10% due to U.S. tariffs.
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
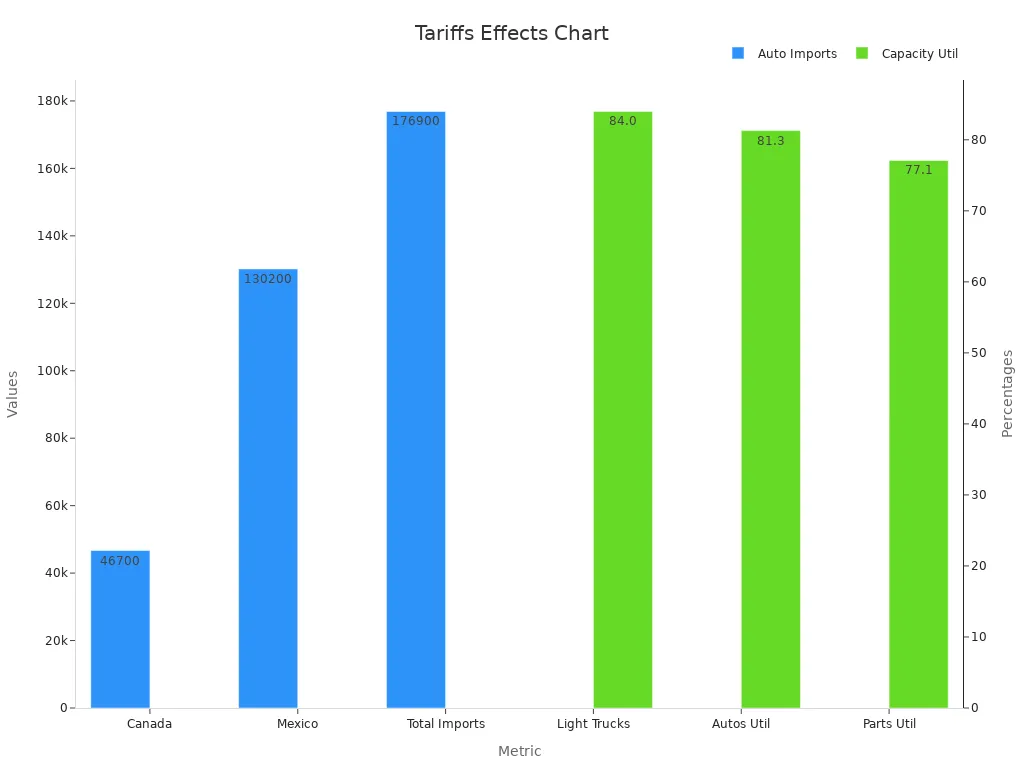
Autos imported from Canada | |
Autos imported from Mexico | 130,200 |
Total autos imported | 176,900 |
Capacity utilization (light trucks) | 84.0% |
Capacity utilization (autos) | 81.3% |
Capacity utilization (parts) | 77.1% |
Tariffs slowed production and caused part shortages. This reduced the number of cars available and raised prices. Tariffs added $455 to $6,875 to car prices, with an average increase of $3,000 per car.
Impacts on E-commerce and Retail
Online shopping and retail had mixed results from tariffs. Tariffs raised prices for both manufacturers and shoppers. But wholesale prices, demand, and profits dropped. This forced businesses to change pricing and supply plans.
Export tax rebates helped manufacturers and retailers by boosting demand.
Higher shipping costs helped retailers but hurt manufacturers. Retailers also struggled with rising freight costs.
These trends show how tariffs affect prices and profits. Businesses must adapt quickly to stay competitive.
Broader Economic Implications of Tariffs
Inflation and Consumer Prices
Tariffs in 2025 made prices rise for many goods. Everyday items now cost more than before. Tariffs are like taxes on imports, and businesses pass these costs to buyers. For example, families might pay $4,600 more each year because of tariffs. This is especially true for items like appliances, furniture, and electronics, where prices have risen quickly.
Tariffs and inflation are closely linked. A 60% tariff on Chinese goods could raise inflation by 2.2%. Smaller tariffs, like 25% on Canada and Mexico and 10% on China, could still increase inflation by 0.5% to 0.8%. These numbers show how tariffs directly affect your spending.
Economic Indicator | Projected Impact |
|---|---|
GDP Impact | U.S. growth slows, possible recession risk |
Inflation Rate |
Price increases from tariffs are not short-term. Repeated tariff hikes can keep prices high for a long time. This means people may need to change how they spend money as the economy adjusts.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Logistics
Tariffs in 2025 disrupted supply chains and shipping systems. Companies now store more goods instead of relying on quick deliveries. This change shows how uncertain trade rules have become. In February 2025, the Logistics Managers' Index (LMI) hit 62.8, the fastest growth in three years. Businesses are adjusting to these new challenges.
Impact Area | Description |
|---|---|
Production Costs | Tariffs raise costs, affecting supply chain performance. |
Supplier Relationships | Companies change suppliers due to tariff-related issues. |
Capital Investments | Spending on warehouse automation has slowed down. |
Inventory Levels | Businesses stockpile goods to avoid risks. |
These changes affect everyone. Higher production costs and more stored goods mean higher prices. Shipping delays and fewer products on shelves are also common. If all planned tariffs happen, extra costs could reach $250 billion, adding more pressure to the economy.
Global Trade and Market Responses
Global trade in 2025 changed a lot because of tariffs. Countries added tariffs on each other, slowing economic growth by 1.2%. If tariffs stay, this slowdown could reach 2.0%. The chance of a recession is now 40-50%, showing the risks to the economy.
Economic Measure | Projected Value |
|---|---|
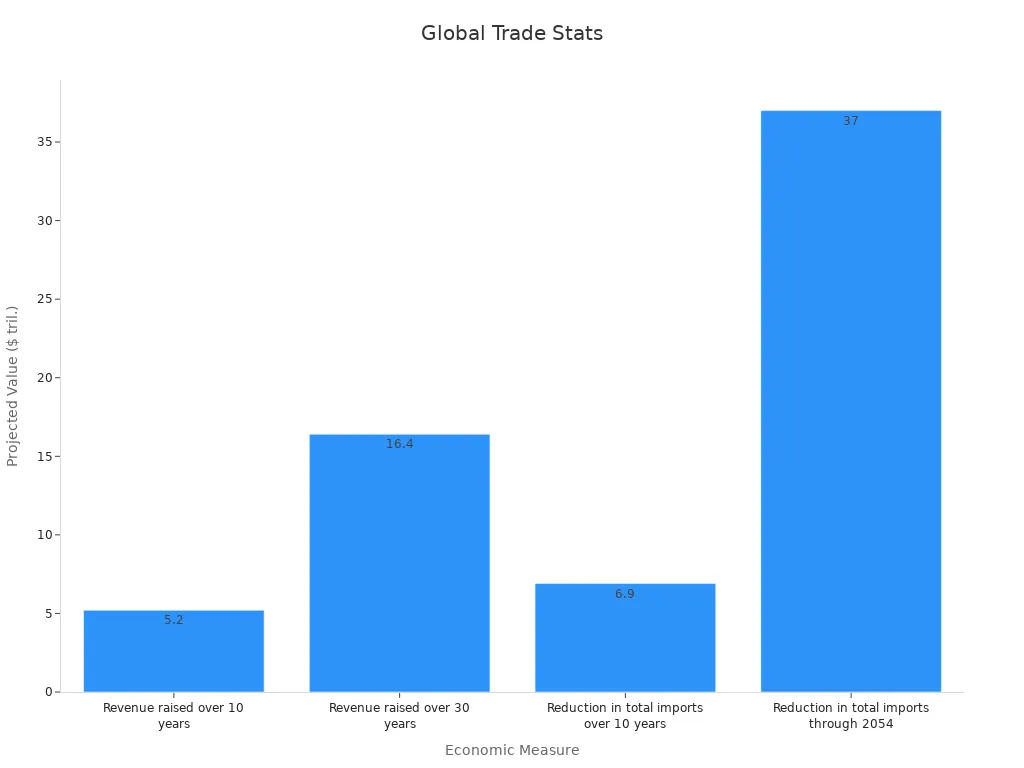
Revenue raised over 10 years | $5.2 trillion |
Revenue raised over 30 years | $16.4 trillion |
Reduction in total imports over 10 years | $6.9 trillion |
Reduction in total imports through 2054 | $37 trillion |
Tariffs also change what people buy. Higher prices make people choose local products instead of imports. This shift can change markets and global trade patterns. However, the overall loss from tariffs could reach $1.4 trillion. In the U.S., prices may rise by 2.7%, and GDP per person might drop by 0.9%. These numbers show how tariffs impact the global economy.
Strategies for Businesses to Adapt to Tariffs

Diversifying Suppliers and Strengthening Supply Chains with JUSDA
When tariffs disrupt trade, strong supply chains are crucial. You can lower risks by using suppliers from different regions. This reduces reliance on one country and keeps operations steady. JUSDA’s Supply Chain Management Platform helps manage these challenges. It uses AI and live data to improve tracking and efficiency. For example, it helps monitor shipments, work with suppliers, and manage inventory better.
Using these tools helps businesses handle tariff problems quickly. Companies with diverse supply chains face fewer issues and save money. This approach also supports sustainability by using resources wisely and cutting waste.
Using Trade Agreements and JusTrade Services
Knowing trade agreements can help with tariff problems. Deals like the USMCA lower or remove tariffs on some goods. JusTrade, JUSDA’s customs service, makes this process easier. It offers smart tools to follow rules and avoid delays. Its SAAS platform helps manage cross-border shipping smoothly.
Businesses using trade agreements often keep more customers during price changes. For example, TechNow Electronics switched to subscriptions, boosting customer value by 28%. JusTrade’s customs expertise can help you reduce tariff effects and succeed.
Focusing on Local Production and New Ideas
Making products locally lowers dependence on imports and tariffs. Investing in U.S. factories helps control costs and keep items in stock. Midwest Kitchen Supplies grew its “Made in America” line, keeping 22% more customers.
Innovation is also important. Tools like automation and AI cut production costs and improve efficiency. These technologies also support eco-friendly goals. As tariffs rise, focusing on local production and innovation ensures steady growth and success.

JUSDA Solutions
To provide you with professional solutions and quotations.
Tariffs in 2025 changed industries and economies everywhere. Electronics companies lost up to 15% of profits. Farmers lost billions because of fewer export sales. Car makers paid $3 billion more for steel and aluminum.
Industry | Impact Details | Losses/Cost Increases |
|---|---|---|
Electronics | Tariffs on parts raised costs, making items pricier. | Up to 15% profit loss |
Clothing & Textiles | Factories moved, raising prices for clothes and fabrics. | Big price increases |
Automobiles | Steel and aluminum tariffs raised production costs. | $3 billion extra globally |
Food & Agriculture | Farmers lost money as exports dropped due to tariffs. | Billions in revenue loss |
Small businesses had a harder time than big companies. They lacked resources to handle rising costs. Many depended on fewer suppliers, making them more at risk.
Smart strategies can help businesses adjust. JUSDA’s tools make supply chains better and safer. JusTrade helps with customs, keeping trade smooth. These solutions help businesses succeed in a connected global market.
See Also
Exploring Five Key Trends Shaping Supply Chain Efficiency
Examining How Global Trade Policies Affect National Economies
Understanding Current Trends in Logistics Risk Management
