Tariffs and Their Role in Global Economic Slowdowns

Tariffs are taxes on goods brought in or sent out. They change costs for companies and affect global trade. In 2025, higher tariffs caused a 0.2% fall in trade. They also led to a 0.6% decrease in GDP growth. These changes hurt industries everywhere, showing how tariffs impact the world economy.
Key Takeaways
Tariffs make things cost more for businesses and shoppers. This raises prices on items people buy daily, making it tough for families to afford essentials.
Tariffs hurt global trade, lowering exports and shrinking industries. Companies must adjust by finding new suppliers and markets to compete.
JUSDA helps businesses handle supply chain problems caused by tariffs. Their tools make work smoother and cut costs, helping companies succeed despite challenges.
The Direct Impact of Tariffs on Global Trade

Higher Costs for Businesses and Shoppers
Tariffs make imported goods cost more. Businesses often raise prices for shoppers to cover these costs. This means everyday items become pricier, making it harder for families to afford them. For companies, tariffs increase the cost of making products, especially when they need imported materials. For example, U.S. factories paid more when steel and aluminum tariffs were added. These higher costs made U.S. products less attractive worldwide, lowering sales and profits.
Other countries often respond with their own tariffs, making things worse. During President Trump’s time, American farmers lost money because of these actions. The government had to pay $61 billion to help them. Big companies like Boeing also suffered. China stopped buying their planes, which hurt their business. These examples show how tariffs can upset economies and cause problems for businesses over time.
Less Trade and Fewer Market Opportunities
Tariffs make global trade harder by raising prices and limiting access. When imported goods cost more, people buy less, and businesses invest less. This lowers trade and makes it harder for exporters to sell their products. For instance, U.S. farm exports to some countries dropped by 10%, and the farming industry shrank by 5%. Technology exports also fell by 7%, showing how tariffs hurt many industries.
The effects of less trade are big. Prices went up by 1.2% because imported goods cost more. Car prices rose by 8%, making it tough for buyers and sellers. Tariffs are expected to cost the U.S. economy $1.4 trillion, showing how much they can harm global trade in the long run.
Supply Chain Problems and JUSDA’s Help
Tariffs mess up supply chains by raising costs and causing delays. Companies struggle to get materials, especially in industries like electronics, cars, and farming. These problems lead to slower production, fewer supplies, and higher costs. For example, shipping delays happen because of complicated customs rules and other countries’ tariffs.
JUSDA helps fix these problems with smart supply chain solutions. Its Supply Chain Management Collaboration Platform uses AI and big data to make customs faster, manage supplies better, and organize shipping. JUSDA’s JusTrade service also simplifies customs, cutting delays and keeping production on track. With services in nearly 20 countries, JusTrade helps businesses handle tricky customs rules and keep supply chains running smoothly.
JUSDA’s tools help companies deal with tariff issues by improving supply chains and cutting costs. Its cloud storage tracks supplies in real time, and its smart customs system reduces delays. These services help businesses stay strong and compete in global markets despite tariff challenges.
Broader Economic Effects of Tariffs
GDP Shrinkage and Slower Growth
Tariffs hurt the world economy by slowing growth and shrinking GDP. They make goods cost more and disrupt trade, reducing business activity. In 2025, global GDP growth was expected to be 1.6%, which is 0.3% lower than earlier predictions. The chance of a worldwide recession also grew to 40%, up from 30% earlier in the year. These numbers show how tariffs can harm economies everywhere.
Statistic Description | Value | Impact |
|---|---|---|
2025 GDP growth forecast | 1.6% | Down 0.3% from earlier estimates |
Q4 2025 GDP growth expectation | 1.4% | Down from 2.1% at the year's start |
Global recession risk | 40% | Up from 30% at the start of 2025 |
U.S. GDP drop from 10% tariff | 1% | Through 2026 |
Global GDP drop from 10% tariff | 0.5% | Through 2026 |
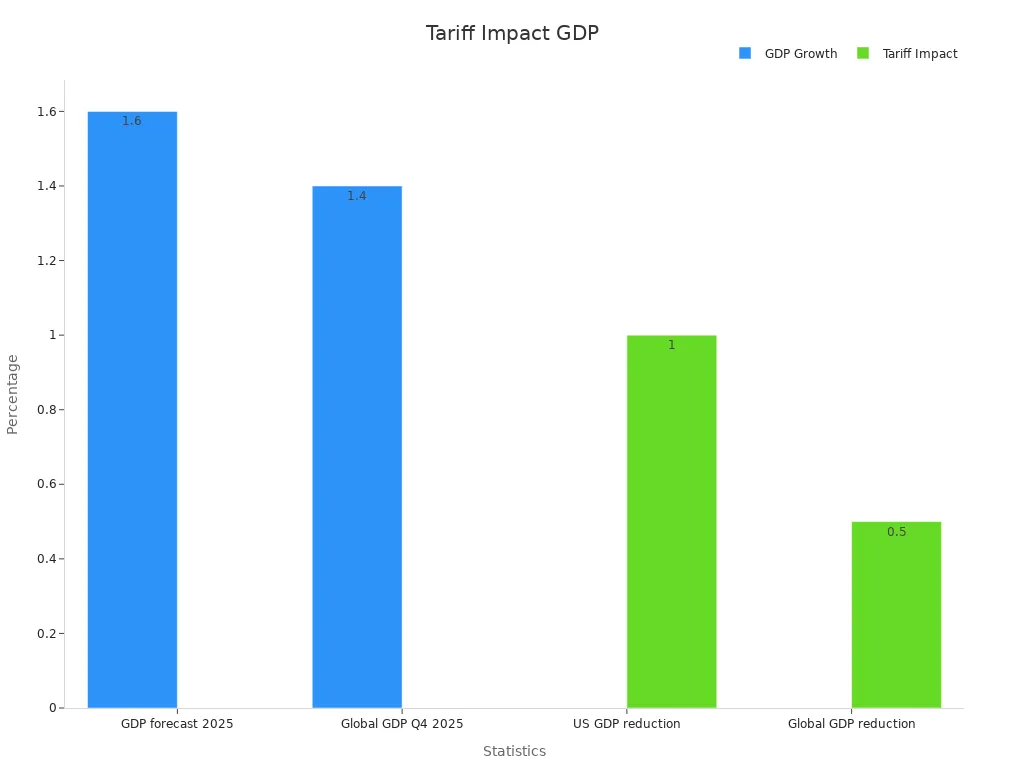
Tariffs do more than just lower GDP. Businesses spend more on goods, leaving less money to grow. Shoppers face higher prices, so they buy less. This slows down the economy over time.
Trade Policy Confusion and Investor Worries
Unclear trade rules and tariffs make investors nervous. Companies find it hard to plan when tariffs and deals keep changing. This stops businesses from investing and slows the economy. For example, a 20% tariff could cut growth by 2-2.5% and raise inflation by 2%. People also feel less confident, with the Consumer Confidence Index dropping to 92.9, the lowest in 12 years.
Economic Indicator | Impact of Tariffs |
|---|---|
GDP Growth | Dropped to 0% |
Core Inflation | Rose to 3.8% |
Consumer Spending | Fell due to higher costs |
Corporate Confidence | Dropped because of uncertainty |
Forecast Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Tariff Rate Impact | 20% tariff could cut growth by 2-2.5% |
Inflation Projection | Inflation could rise by 2% |
Consumer Confidence Index | Fell to 92.9, lowest in 12 years |
Earnings Growth Forecast | Lowered to 6%-7% for 2025 |
Confusing trade policies also increase recession risks. The Consumer Sentiment Index fell to 50.8, showing people are worried. Companies struggle to predict profits, with many lowering their growth goals. These problems show how tariffs and unclear trade rules can hurt the economy.
Industry-Specific Problems: Factories, Farms, and Tech
Tariffs hit industries like manufacturing, farming, and technology the hardest. In factories, tariffs on materials like steel and aluminum raise costs. Companies like Ford and GM pay more and pass these costs to buyers. This lowers demand and hurts profits.
In farming, tariffs make exports harder and hurt farmers. The U.S.-China trade fight caused many farmers to lose money or go bankrupt. Big farm companies got government help, but small farms struggled to survive.
Tariffs raise import prices, protecting local goods but costing shoppers more.
Trump’s tariffs caused farmers to lose money, leading to bailouts and bankruptcies.
Big farm businesses gained more from tariffs than small farms.
Tech companies also face problems. Apple pays more for parts from tariff-hit areas, raising product prices. This makes items like phones and laptops harder to sell. Brands like Nike and Adidas also lose money because of tariffs on Chinese goods.
Impact Area | Description |
|---|---|
Supply Chain Changes | Companies may switch to countries with lower tariffs. |
Pricing Adjustments | Businesses may raise prices, lowering customer demand. |
Market Competition | Tariffs hurt global competition and lead to trade fights. |
Competitiveness Studies | Tariffs protect local industries but can harm the economy overall. |
Bilateral Trade Effects | Retaliatory tariffs can cause trade wars and global problems. |
U.S.-China Trade War Case | Shows how tariffs disrupt trade and supply chains. |
These industry problems show why businesses need smart strategies. Companies should find new suppliers, cut costs, and explore other markets to handle tariff challenges.
Global Responses to Tariff Challenges

Government Actions to Reduce Tariff Problems
Governments have created plans to lessen tariff impacts. Many countries give money to help industries hurt by higher costs. For example, the U.S. gave billions to farmers during the China trade war. Tax breaks and grants encourage companies to make goods locally, cutting import needs. Some nations made deals to lower tariffs on certain products. These actions help keep economies steady and protect businesses from tariff troubles.
Business Changes: New Supply Chains with JUSDA Help
Companies are changing supply chains to handle tariffs better. Many moved production from China to places like Vietnam or South Korea. Relying on one supplier or location can be risky during tough times. JUSDA helps businesses build stronger supply chains. Its smart tools use AI to improve shipping and sourcing. With JUSDA, companies save money, work faster, and stay successful despite trade changes.
New supply chains lower risks from global tensions.
Flexible sourcing helps during tariff hikes.
JUSDA’s tools track supplies and manage inventory in real time.
Working Together Through Trade Deals
Trade agreements help solve tariff problems. Groups like the WTO help countries settle fights and cut tariffs. Regional deals, like the CPTPP, support free trade between members. These partnerships grow economies by lowering trade barriers. When countries work together, they reduce tariff issues and make the global economy stronger.
Mitigating Tariff Effects with JusTrade
Making Customs Clearance Easier for Global Trade
JusTrade makes customs clearance simple for businesses facing tariff issues. Its smart SAAS platform uses AI and big data to speed up processes. Tasks like sorting goods and handling paperwork are automated to avoid mistakes. This helps companies stick to schedules and deliver on time. JusTrade works in almost 20 countries, helping businesses follow customs rules. These faster processes save time and cut costs, even during tough economic times.
Improving Supply Chains with JusTrade's SAAS Platform
JusTrade's SAAS platform makes supply chains work better by giving real-time updates. It links teams like purchasing, shipping, and finance for smooth communication. Companies can track shipments, check stock, and spot delays early. This helps them adjust to trade changes and deal with tariffs. JusTrade also finds better shipping routes and lowers costs. By fixing supply chains, JusTrade helps businesses stay strong in a changing economy.
Helping Industries Hit Hard by Tariffs
Tariffs hurt industries like factories, farms, and tech companies. JusTrade offers special solutions to solve these problems. For factories, it speeds up customs to get materials on time. Farmers use JusTrade to export crops quickly, avoiding waste. Tech companies rely on JusTrade for smooth shipping of parts across borders. By helping these industries, JusTrade supports growth and keeps businesses running despite tariff challenges.

JUSDA Solutions
To provide you with professional solutions and quotations.
Tariffs have hurt the global economy by slowing growth and trade. In 2025, GDP growth might only reach 1.6%, with a drop in 2026. JusTrade helps reduce these effects by improving supply chains. Studies show future trade depends on flexible strategies. As tariff fights continue, businesses must find new ways to handle rising tariffs and their effects.
Scenario | 2025 GDP Growth | 2026 GDP Growth |
|---|---|---|
Baseline | 2.4% | 1.7% |
Upside | 2.7% | >3% |
Downside | 1.6% | -2.1% |
See Also
Exploring How Global Trade Policies Affect National Economies
Understanding the Importance of Supply Chains in Global Trade
Analyzing Inflation: Strategies for Managing Supply Chain Issues
Addressing Challenges of Supply Chain Growth in Global Markets
Achieving Success Through Supply Chain Transparency in E-commerce
