Third-Party Overseas Warehouse Industry Analysis and Outlook

The third-party overseas warehouse industry shows remarkable momentum, driven by booming global e-commerce and the need for resilient supply chains. Recent data highlights this rapid expansion, with the global 3PL market valued at $955.8 billion in 2021 and projected to reach nearly $2 trillion by 2030 at an 8.5% CAGR. Companies recognize the strategic importance of overseas warehousing for scaling operations.
Metric | Value/Projection |
|---|---|
$150 billion | |
Market Size (2033) | Over $280 billion |
Distribution Capacity | >20 billion cubic feet |
Key Takeaways
Third-party overseas warehouses help businesses store products abroad, speeding up delivery and cutting shipping costs.
The global market for these warehouses is growing fast, with Asia-Pacific leading in size and growth due to strong e-commerce and manufacturing.
Advanced technology like automation and AI improves warehouse accuracy, speed, and efficiency, supporting better customer service.
Using third-party warehouses strengthens supply chains by reducing risks, improving local fulfillment, and handling returns smoothly.
To succeed, companies should invest in technology, focus on sustainability, expand in key regions, and build strong partnerships.
Definition
What Is a Third-Party Overseas Warehouse
A third-party overseas warehouse is a storage facility owned and operated by an external logistics provider. Businesses use these warehouses to store goods in foreign markets without owning the facility. This model allows companies to expand internationally and reach customers faster. The provider manages the setup, receives inventory from suppliers, and aligns operations with client standards. They handle the intake process, which includes unloading, documenting, and storing products. Secure storage uses bins, pallets, or shelves, and costs depend on the space or quantity used.
Third-party overseas warehouses act as an extension of a business’s supply chain. They manage inbound and outbound logistics, order fulfillment, and customer service, allowing companies to focus on their core activities.
Key Services
Third-party overseas warehouses offer a wide range of services that go beyond simple storage. These include:
Receiving and inventory management with real-time tracking.
Kitting and assembly to prepare products for shipping.
Pick and pack order fulfillment using advanced technology.
Shipping services that use volume discounts to lower costs.
Returns management and customer support.
Value-added warehousing and distribution, such as labeling or repackaging.
Integration with warehouse management systems (WMS) for efficiency.
The adoption of automation and robotics has improved inventory accuracy and delivery speed. E-commerce fulfillment and international transportation management, including customs brokerage, have had a major impact on the market.
Industry Scope
The scope of third-party overseas warehousing covers many aspects of international logistics. Providers offer warehousing in strategic locations to reduce shipping times and costs. They manage receiving, storage, and inventory control, including special needs like cold storage. Their global networks connect carriers, warehouses, and distribution centers, supporting international shipping and market expansion.
3PLs coordinate multi-modal transport, such as air, ocean, rail, and road.
They help businesses test new markets without building their own facilities.
Providers support compliance with international regulations and offer flexibility to handle demand changes.
Outsourcing to a third-party overseas warehouse helps companies save costs, improve efficiency, and focus on growth.
Market Overview

Global Market Size
The third-party overseas warehouse industry operates within the broader third-party logistics (3PL) market. This market continues to expand as global trade and e-commerce accelerate. In 2024, the global 3PL market reached $1.19 trillion. Projections indicate steady growth, with the market expected to surpass $2.2 trillion by 2033. The following table summarizes key figures:
Metric | Value (USD) | Year/Period |
|---|---|---|
Global 3PL Market Size | $1.19 Trillion | 2024 |
Global 3PL Market Size | $1.29 Trillion | 2025 |
Projected Global 3PL Market Size | $2.57 Trillion | 2034 |
CAGR (2025-2033) | 2025-2033 |
The third-party overseas warehouse segment forms a vital part of this market, supporting international distribution, inventory management, and last-mile delivery for cross-border e-commerce.
Regional Shares
Asia Pacific leads the third-party overseas warehouse industry, holding the largest share of the global 3PL market. In 2023, this region accounted for approximately 42.4% of total revenue. North America follows closely, with the United States driving much of the regional growth. Europe, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa also participate in the market, but their shares remain smaller compared to Asia Pacific and North America.
Asia Pacific: 42.4% market share in 2024
North America: Significant share, led by the U.S.
Other Regions: Europe, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa contribute to global growth but at a slower pace
Asia Pacific’s dominance results from robust manufacturing bases, advanced logistics infrastructure, and the rapid rise of e-commerce platforms. Many global brands choose to establish overseas warehouses in China, Japan, and Southeast Asia to reduce shipping times and costs.
Growth Rates
The third-party overseas warehouse industry demonstrates strong growth momentum. The global 3PL market expects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.01% from 2025 to 2033. Asia Pacific outpaces other regions, with a forecasted CAGR of 9% during the same period. Several factors drive this expansion, including the complexity of global supply chains, increased technology adoption, and the surge in cross-border e-commerce.
Industry Sector | CAGR (%) | Time Period | Growth Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
Global 3PL Market | 7.01 | 2025-2033 | E-commerce, international trade, tech adoption |
Asia Pacific 3PL Market | 9.00 | Forecast Period | E-commerce, manufacturing, logistics investment |
Global Shipping & Logistics | 6.5 | 2024-2030 | Supply chain complexity, sustainability |
Asia Pacific’s higher growth rate signals expanding opportunities for logistics providers and e-commerce businesses seeking to scale internationally.
The industry’s robust growth, especially in Asia Pacific, highlights the strategic importance of third-party overseas warehouses in supporting global commerce and supply chain resilience.
Growth Drivers
E-Commerce Surge
E-commerce continues to drive the third-party overseas warehouse industry. Online shopping has become a daily habit for millions of consumers worldwide. In 2023, global e-commerce sales reached $6.3 trillion, according to eMarketer. This figure is expected to grow to $8.1 trillion by 2026. Businesses need fast and reliable delivery to meet customer expectations. Third-party overseas warehouses help companies store products closer to buyers. This reduces shipping times and improves customer satisfaction. Many brands now use these warehouses to handle high order volumes during peak seasons.
Note: Fast delivery and local inventory have become key factors for e-commerce success.
Globalization
Globalization has expanded trade across borders. Companies now sell products to customers in many countries. Third-party overseas warehouses support this trend by providing storage and fulfillment in foreign markets. They allow businesses to enter new regions without building their own facilities. This lowers entry barriers and reduces risk. Companies can test demand in new markets and scale operations quickly. Globalization also increases competition, so businesses must offer better service and faster shipping.
🌍 Global reach helps brands grow faster.
📦 Overseas warehouses make cross-border trade easier.
Supply Chain Optimization
Supply chain optimization remains a top priority for businesses. Complex supply chains can cause delays and increase costs. Third-party overseas warehouses streamline logistics by managing inventory, order fulfillment, and returns. They use advanced technology to track products in real time. This improves accuracy and reduces errors. Companies benefit from lower shipping costs and better inventory control. Efficient supply chains help businesses respond quickly to market changes.
Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
Faster Delivery | Higher customer satisfaction |
Lower Costs | Improved profit margins |
Real-Time Tracking | Better inventory management |
Efficient supply chains give companies a strong advantage in global markets.
Challenges
Quality Control
Quality control remains a top concern for any third-party overseas warehouse. Companies rely on order fulfillment metrics to measure performance and spot issues. These metrics include picking error rates, inventory accuracy, and product damage rates. Picking errors often range from 1% to 3%, showing how often mistakes happen with orders. Inventory accuracy usually stays above 99%, which helps keep stock records reliable. Product damage and return rates also signal quality problems that can hurt customer satisfaction. Warehouses use incoming goods inspections, proper storage, and barcode tracking to reduce errors. Advanced warehouse management systems give real-time updates and help teams fix problems quickly. Mastery of these key performance indicators builds trust and supports business growth.
Infrastructure
Strong infrastructure forms the backbone of efficient overseas warehousing. Many providers invest in modern facilities, advanced equipment, and digital systems. However, some regions face challenges like outdated buildings, limited automation, or poor transportation links. These gaps can slow down order processing and increase the risk of delays. Reliable power, internet, and security systems are also essential for smooth operations. Companies must choose warehouse partners with proven infrastructure to avoid disruptions and maintain service quality.
Costs
Managing costs presents a major challenge for businesses using third-party overseas warehouse solutions. Bulk shipping by sea can lower per-unit costs, while storing goods in local warehouses helps avoid repeated tariffs. Cheaper last-mile shipping from domestic warehouses also reduces expenses. However, rising tariffs and shipping fees can still impact profits. Some fulfillment networks cut costs by up to 35% through bulk shipping and fewer markups. Fast response times, real-time inventory control, and scalable solutions help prevent delays and extra charges. AI-powered storage and smart warehouse locations further reduce last-mile delivery costs. Avoiding customs delays and strict tariff enforcement also protects against unexpected expenses.
Regulation
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity. Each country has its own rules for customs, product safety, and data protection. Changes in regulations can disrupt operations or increase costs. Warehouses must follow local laws and keep up with new requirements. Failure to comply can lead to fines, shipment delays, or even bans. Companies need partners who understand the legal landscape and can adapt quickly. Staying informed and proactive helps businesses avoid regulatory pitfalls and maintain smooth cross-border trade.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific leads the third-party overseas warehouse industry. The region holds a 28.8% share of the global warehousing market in 2024, with revenue reaching $311.3 billion. Rapid e-commerce growth and urbanization drive demand for advanced logistics solutions. The market expects to grow to $531.6 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 9.3%. Asia Pacific also dominates the warehouse management systems market, holding a 26.9% share in 2023. By 2030, the region will likely lead global revenue in both warehousing and management systems.
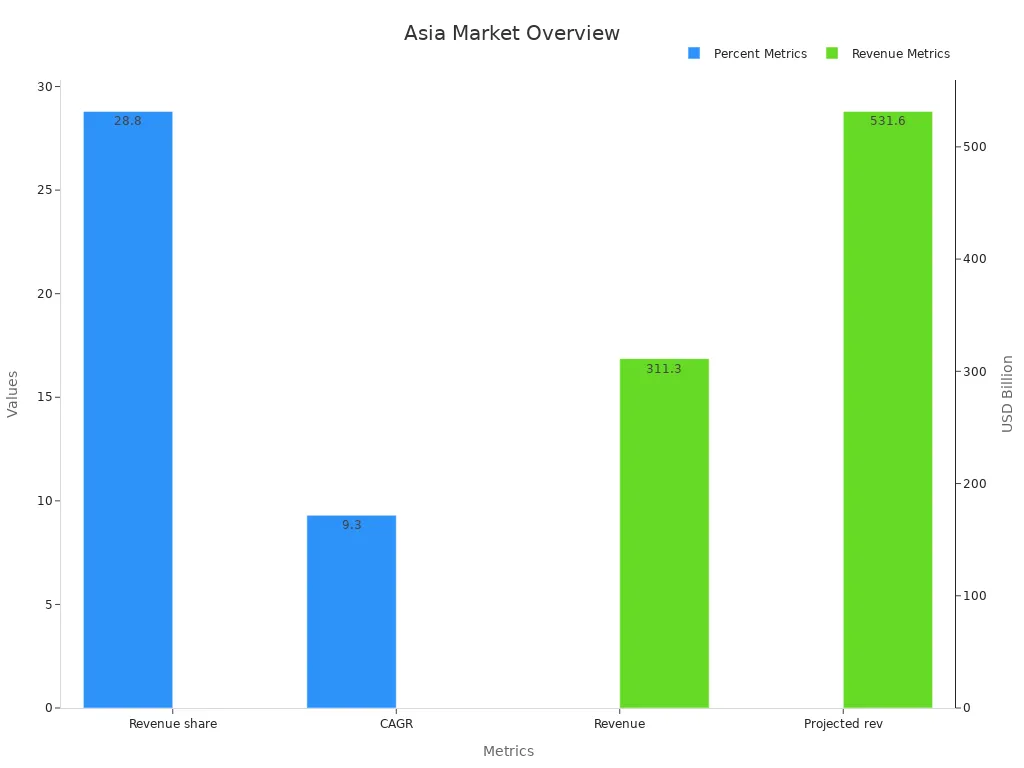
Asia Pacific’s strong manufacturing base and investment in logistics infrastructure support its leadership. However, infrastructure restrictions and customs bottlenecks remain challenges.
North America
North America offers tailored logistics solutions for a mature market. Companies benefit from advanced technology and established supply chains. The region faces challenges with system integration and adapting to new digital platforms. Businesses must balance innovation with the complexity of existing operations.
Europe
Europe provides customized services to address diverse laws and infrastructure. The region’s logistics sector supports cross-border trade within the European Union. Regulatory compliance and complex customs procedures present ongoing challenges. Providers must adapt to frequent changes in regulations.
Latin America
Latin America adapts logistics solutions to meet regional needs. The market shows potential for growth as e-commerce expands. Limited transportation infrastructure and customs inefficiencies create obstacles. Companies must invest in local partnerships to overcome these barriers.
Middle East
The Middle East supports emerging markets with a focus on geopolitical and infrastructural considerations. Logistics providers face insufficient transportation infrastructure and logistical bottlenecks. Growth opportunities exist as the region invests in new trade hubs and technology.
Region | Opportunities | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
North America | Tailored logistics solutions addressing mature market needs | Complexity in integration with existing systems |
Europe | Customized services considering diverse laws and infrastructure | Regulatory compliance and customs procedures complexity |
Asia-Pacific | Growing demand driven by e-commerce and urbanization | Infrastructure restrictions, customs bottlenecks, and developing economy constraints |
Latin America | Logistics solutions adapted to regional needs | Limited transportation infrastructure and customs inefficiencies |
Middle East & Africa | Support for emerging markets with geopolitical and infrastructural considerations | Insufficient transportation infrastructure and logistical bottlenecks |
Globalization, technology, and sustainability shape opportunities and challenges in each region. Providers must adapt strategies to local market conditions for success.
The third-party overseas warehouse industry continues to expand, with global 3PL market projections reaching over $2.6 trillion by 2033. Asia-Pacific leads in warehouse space and growth, while regions like South America show rapid rebounds and unique challenges. This industry remains vital for global logistics, supporting resilient supply chains and efficient trade. To succeed, stakeholders should adopt technology, diversify supply sources, and invest in sustainable solutions. Monitoring industry trends and adapting quickly will help businesses stay competitive.
FAQ
What is the main benefit of using a third-party overseas warehouse?
A third-party overseas warehouse helps companies reach customers faster. It reduces shipping times and costs. Businesses can focus on growth while experts handle storage and delivery.
How do third-party overseas warehouses handle returns?
Providers use digital tools to track returns. They process items quickly and restock or recycle them. This system improves customer satisfaction and supports sustainability goals.
Are third-party overseas warehouses suitable for small businesses?
Yes. Small businesses can use these warehouses to test new markets. They avoid large investments in infrastructure. Providers offer flexible solutions that fit different business sizes.
What technology improves overseas warehouse operations?
Automation, AI, and integrated platforms boost efficiency. These tools help manage inventory, speed up order processing, and reduce errors. Companies gain better visibility and control over their supply chains.
See Also
How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Future Supply Chains
Advantages Of Automated Warehouses In Modern Manufacturing
JUSDA Introduces Innovative Warehousing To Boost Efficiency
