Correctly Understand the Full-service vs. Semi-managed Trend

Service models have transformed various industries by offering tailored solutions. Companies increasingly adopt full-service or semi-managed models to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Understanding these models has become crucial, especially in the context of cross-border e-commerce. Platforms now highlight these models to attract diverse sellers and streamline operations. Correctly understand the nuances of these service models to make informed decisions and optimize business strategies.
Understanding "Full-service" and "Semi-managed" Models
Definition of Full-service Model
Key Characteristics
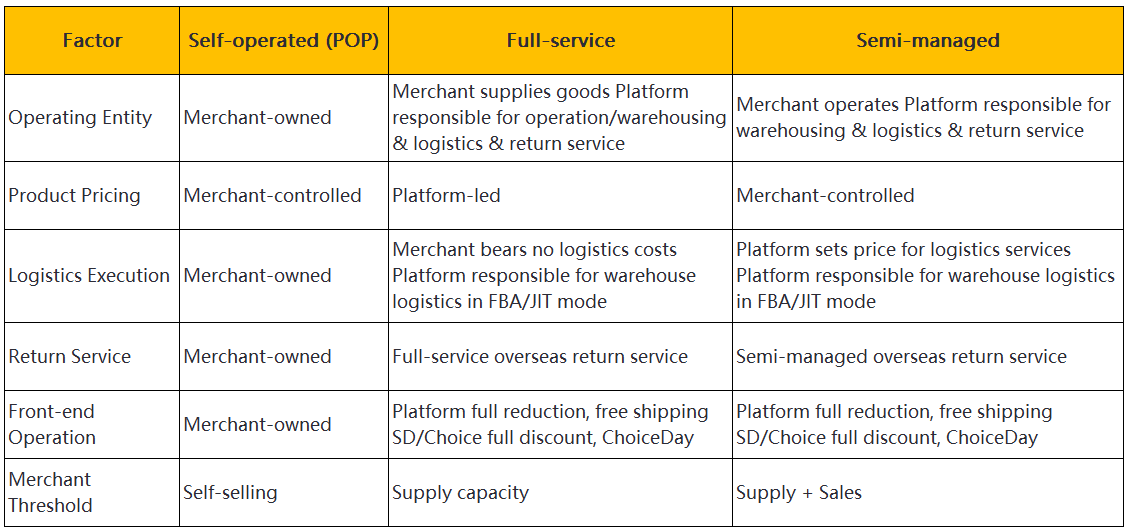
The full-service model involves the e-commerce platform taking complete responsibility for various aspects of store operations. The platform handles warehousing, distribution, and after-sales service. Merchants focus on supplying merchandise. This model often targets lightweight and small-sized products. Categories include 3C accessories and fashion apparel. The platform sets product prices and manages returns. Sales activities are conducted by the platform.
Common Industries Utilizing Full-service
Industries that frequently utilize the full-service model include consumer electronics and fashion retail. These sectors benefit from the platform's comprehensive management. Merchants in these industries often lack the operational capabilities to manage logistics and customer service independently. Full-service models enable these merchants to scale their operations quickly.
Definition of Semi-managed Model
Key Characteristics
The semi-managed model offers a balance between platform control and seller autonomy. Merchants operate their stores independently. The platform manages warehousing and logistics. Merchants retain control over pricing and sales strategies. The platform collaborates on logistics and returns. This model provides greater flexibility and personalization. Sellers may choose their logistics partners. The platform assists with customer service.
Common Industries Utilizing Semi-managed
Semi-managed models are popular in industries requiring operational flexibility. Examples include specialized retail and niche markets. Vendors in these sectors benefit from the platform's robust infrastructure. The model meets the diverse needs of vendors in today's dynamic e-commerce environment. Sellers gain insights into consumer needs while maintaining operational autonomy.
Differences Between the Two Models
Scope of Services
Full-service Scope
The full-service model encompasses a broad range of services. The e-commerce platform manages warehousing, distribution, and after-sales service. Merchants focus solely on supplying products. The platform sets product prices and handles all sales activities. This comprehensive approach ensures high-quality control and reliability.
Semi-managed Scope
The semi-managed model offers a more balanced approach. Merchants operate their stores independently. The platform manages warehousing and logistics. Merchants retain control over pricing and sales strategies. The platform assists with customer service and returns. This model provides flexibility and allows merchants to personalize their operations.
Cost Implications
Full-service Costs
Full-service models often involve higher costs. The platform charges fees for managing warehousing, distribution, and customer service. These costs can be significant but provide value through comprehensive management. Merchants benefit from reduced operational burdens.
Semi-managed Costs
Semi-managed models typically offer cost efficiency. Merchants pay for warehousing and logistics services. The platform charges lower fees compared to full-service models. Merchants save money by retaining control over pricing and sales strategies. This cost structure appeals to vendors seeking operational flexibility.
Control and Flexibility
Full-service Control
Full-service models limit merchant control. The platform dictates product prices and manages all sales activities. Merchants have little influence over operational decisions. This model suits vendors who prefer to focus on product supply rather than business operations.
Semi-managed Flexibility
Semi-managed models provide greater flexibility. Merchants control pricing and sales strategies. The platform supports logistics and customer service. Merchants can choose their logistics partners and tailor their operations. This flexibility allows vendors to adapt to market changes and consumer needs.
Pros and Cons of Full-service and Semi-managed Models
Pros of Full-service Model
Comprehensive Management
The full-service model offers comprehensive management. The e-commerce platform handles warehousing, distribution, and customer service. Merchants focus on supplying products. This approach ensures high-quality control and reliability. Platforms manage all operational aspects, reducing the burden on merchants.
Reduced Client Burden
Full-service models significantly reduce the client burden. Merchants do not need to worry about logistics or after-sales service. The platform takes care of these tasks. This allows merchants to concentrate on product quality and supply. The platform's support boosts merchant competitiveness.
Cons of Full-service Model
Higher Costs
Full-service models often come with higher costs. The platform charges fees for managing warehousing, distribution, and customer service. These fees can be substantial. Merchants must weigh the benefits against these costs. The comprehensive management provided by the platform justifies the expense for many merchants.
Less Client Control
Full-service models offer less client control. The platform sets product prices and manages sales activities. Merchants have limited influence over operational decisions. This model suits vendors who prefer focusing on product supply. Merchants seeking more control may find this model restrictive.
Pros of Semi-managed Model
Cost Efficiency
Semi-managed models provide cost efficiency. Merchants pay for warehousing and logistics services. The platform charges lower fees compared to full-service models. Merchants save money by retaining control over pricing and sales strategies. This cost structure appeals to vendors seeking operational flexibility.
Greater Client Control
Semi-managed models offer greater client control. Merchants set their own product prices and manage sales activities. The platform assists with logistics and customer service. Merchants can choose their logistics partners. This flexibility allows vendors to adapt to market changes and consumer needs.
Cons of Semi-managed Model
Increased Client Responsibility
The semi-managed model places more responsibility on merchants. Merchants must handle pricing, sales strategies, and customer interactions. This increased responsibility can become overwhelming for merchants without adequate resources. The platform provides support for logistics and warehousing, but merchants must manage other operational aspects. This model requires merchants to invest time and effort into their business operations.
Potential for Mismanagement
Mismanagement risks increase under the semi-managed model. Merchants control critical aspects of their operations, including pricing and sales strategies. Inexperienced merchants may struggle with these responsibilities. Poor management can lead to operational inefficiencies and customer dissatisfaction. The platform offers support, but merchants must ensure effective management of their stores. Correctly understanding the balance between autonomy and support is crucial for success.
Six Major Cross-border E-commerce Platforms with Managed Service Models

Temu
Overview
Temu has emerged as a prominent cross-border e-commerce platform. The platform emphasizes low prices and social sharing marketing. Temu aims to attract budget-conscious consumers. The platform leverages social media to boost visibility and engagement.
Service Model
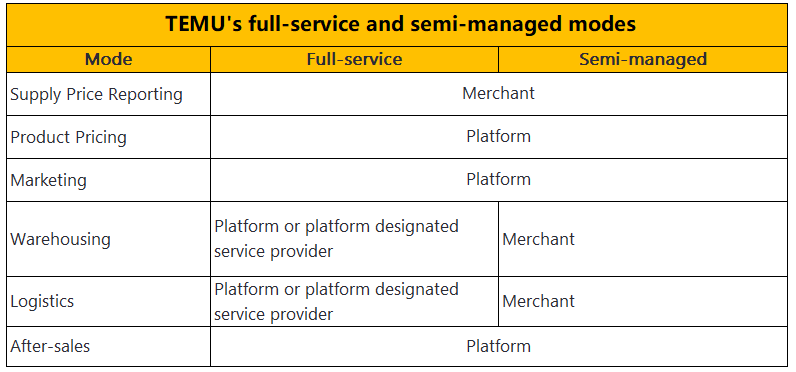
Temu adopts a semi-managed service model. Merchants handle pricing and sales strategies independently. The platform manages warehousing and logistics. This approach allows vendors to maintain control over their operations. Temu supports merchants with customer service and returns management. The platform's infrastructure ensures efficient logistics and delivery.
TikTok Shop
Overview
TikTok Shop integrates e-commerce with the popular short-video platform. The platform targets a younger audience. TikTok Shop uses short videos to promote products. This strategy enhances user engagement and drives sales.
Service Model
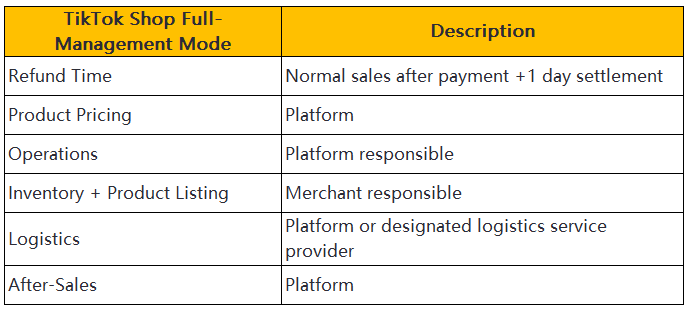
TikTok Shop operates under a semi-managed model. Merchants control product pricing and sales activities. The platform handles warehousing and logistics. TikTok Shop assists with customer service and returns. This model provides flexibility for vendors. Merchants can leverage TikTok's extensive reach to boost sales. The platform's robust infrastructure supports seamless operations.
AliExpress
Overview
AliExpress is a global e-commerce platform. The platform offers a wide range of products. AliExpress focuses on building a global logistics infrastructure. The platform aims to tap into diverse markets worldwide.
Service Model
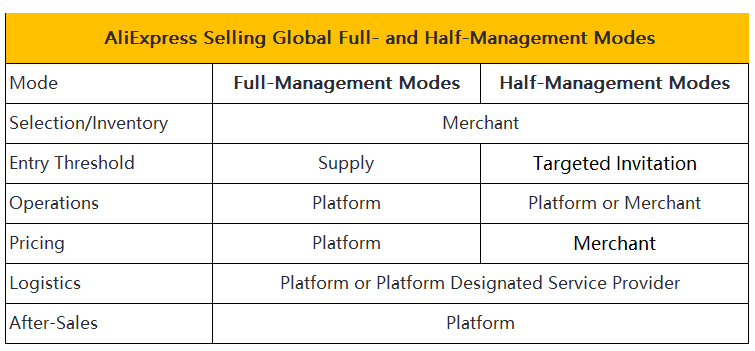
AliExpress employs a semi-managed service model. Merchants manage their stores independently. The platform oversees warehousing and logistics. AliExpress supports customer service and returns. This model balances autonomy and support. Merchants benefit from the platform's extensive reach and infrastructure. AliExpress enables vendors to scale their operations efficiently.
Lazada
Overview
Lazada stands as a leading e-commerce platform in Southeast Asia. The platform offers a wide range of products, catering to diverse consumer needs. Lazada focuses on providing a seamless shopping experience. The platform leverages advanced technology and robust logistics infrastructure. Lazada aims to dominate the Southeast Asian market.
Service Model
Lazada employs a semi-managed service model. Merchants manage their stores independently. The platform oversees warehousing and logistics. Lazada supports customer service and returns. This model balances autonomy and support. Merchants benefit from the platform's extensive reach and infrastructure. Lazada enables vendors to scale their operations efficiently.
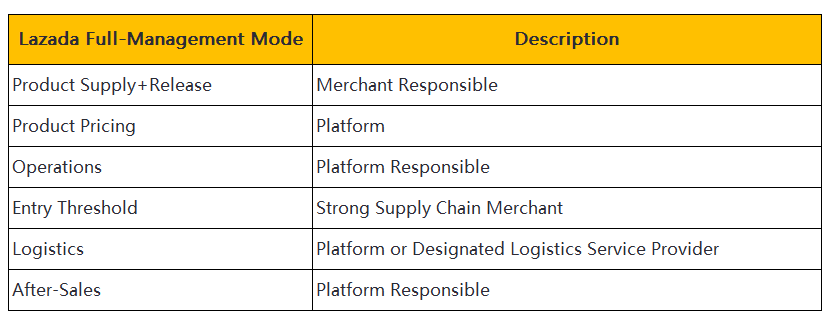
Shopee
Overview
Shopee has emerged as a prominent e-commerce platform in East Asia. The platform offers a user-friendly interface and a wide range of products. Shopee focuses on enhancing the shopping experience through innovative features. The platform aims to become the mainstream e-commerce platform in East Asian markets.
Service Model
Shopee adopts a semi-managed service model. Merchants handle pricing and sales strategies independently. The platform manages warehousing and logistics. Shopee assists with customer service and returns management. This approach allows vendors to maintain control over their operations. Shopee supports merchants with robust infrastructure and extensive reach.
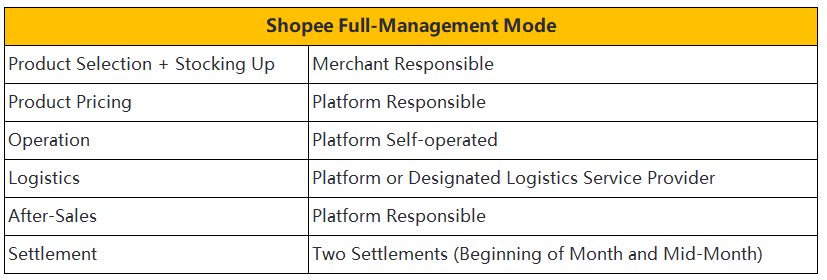
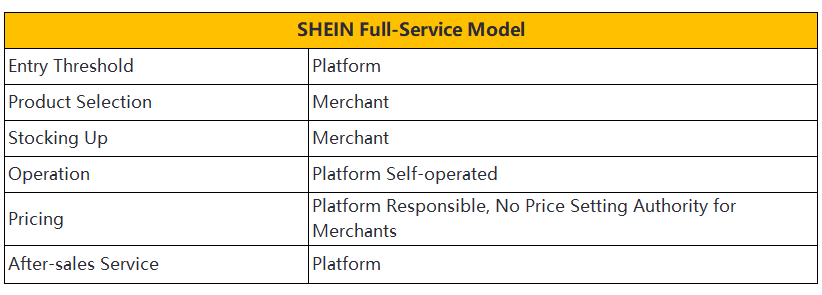
SHEIN
Overview
SHEIN has gained popularity as a global fashion e-commerce platform. The platform offers trendy and affordable fashion items. SHEIN targets a young and fashion-conscious audience. The platform leverages social media to boost visibility and engagement. SHEIN aims to provide a seamless shopping experience.
Service Model
SHEIN operates under a semi-managed service model. Merchants control product pricing and sales activities. The platform handles warehousing and logistics. SHEIN supports customer service and returns. This model provides flexibility for vendors. Merchants can leverage SHEIN's extensive reach to boost sales. The platform's robust infrastructure ensures efficient logistics and delivery.
The blog has explored the key differences between full-service and semi-managed models. Choosing the right service model is crucial for optimizing business strategies. Each model offers unique benefits and challenges. Merchants should align their choice with their operational capabilities and business goals.
Consider JUSDA's services for cross-border e-commerce needs. JUSDA provides tailored solutions to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Engage with JUSDA for further consultation and elevate your e-commerce operations.
See Also
Revolutionizing Supply Chain Management with Cloud-Based Solutions
Decoding High-Tech Manufacturing Consulting for Success
Maximizing Benefits of High-Tech Manufacturing Warehouses through Automation
Harnessing Advanced Inventory Techniques to Empower Your Business
Achieving High-Tech Manufacturing Success through Lean Logistics Navigation
