Fortifying Japan’s Auto Supply Chain: Strategies for an Uncertain Future
Japan’s reputation for automotive excellence is built on a finely tuned, but vulnerable, supply chain. For decades, the industry has honed its ability to bounce back from natural disasters like earthquakes and tsunamis, often emerging even stronger. However, recent years have presented a new wave of challenges. The global chip shortage has exposed a critical dependence on semiconductors, impacting production lines across Japan. Simultaneously, the looming threat of climate change brings the potential for more frequent and severe natural disasters. This confluence of factors has forced Japan’s automakers and their intricate network of suppliers to re-evaluate long-held practices and seek innovative solutions to fortify their supply chain for an increasingly uncertain future.
Overview of Japan's Automotive Industry
Historical Context
Evolution of the automotive industry in Japan
Local inventors initiated the development of the Japanese automotive industry. A Panhard-Levassor car arrived in Japan in 1898. This event inspired local inventors to create the first Japanese cars. The 1960s marked a significant era for Japanese automakers. They launched kei cars, which dramatically boosted sales. Kei cars made automobiles more affordable for the average person in Japan. The development of small high-performance cars further contributed to the industry's growth. Modern automobile manufacturing techniques also played a crucial role.
Key milestones and developments
The Japanese automotive industry achieved global recognition in 1985. This milestone reflected massive growth and development. Japanese automakers introduced innovative technologies and designs. These advancements enhanced vehicle performance and reliability. The industry focused on producing fuel-efficient and compact vehicles. Japanese automakers gained a competitive edge in the global market. The emphasis on quality and innovation became a hallmark of Japanese vehicles.
Current Market Landscape
Major players in the industry
Japan hosts several major automotive manufacturers. Toyota, Honda, Nissan, and Mazda lead the industry. These companies have established a strong global presence. Toyota stands as the leading automotive manufacturer worldwide. Honda and Nissan also hold significant market shares. Mazda focuses on producing stylish and efficient vehicles. These companies contribute significantly to Japan's economy.
Market share and economic impact
The Japanese automotive industry ranks third globally. The industry produced approximately 8.3 million vehicles in 2020. Exports to the United States totaled $49 billion that year. The automotive sector employs over 1 million people in Japan. This highlights the industry's economic significance. The industry plays a vital role in Japan's economic stability. The focus on innovation and efficiency ensures continued growth.
Components of the Automotive Supply Chain
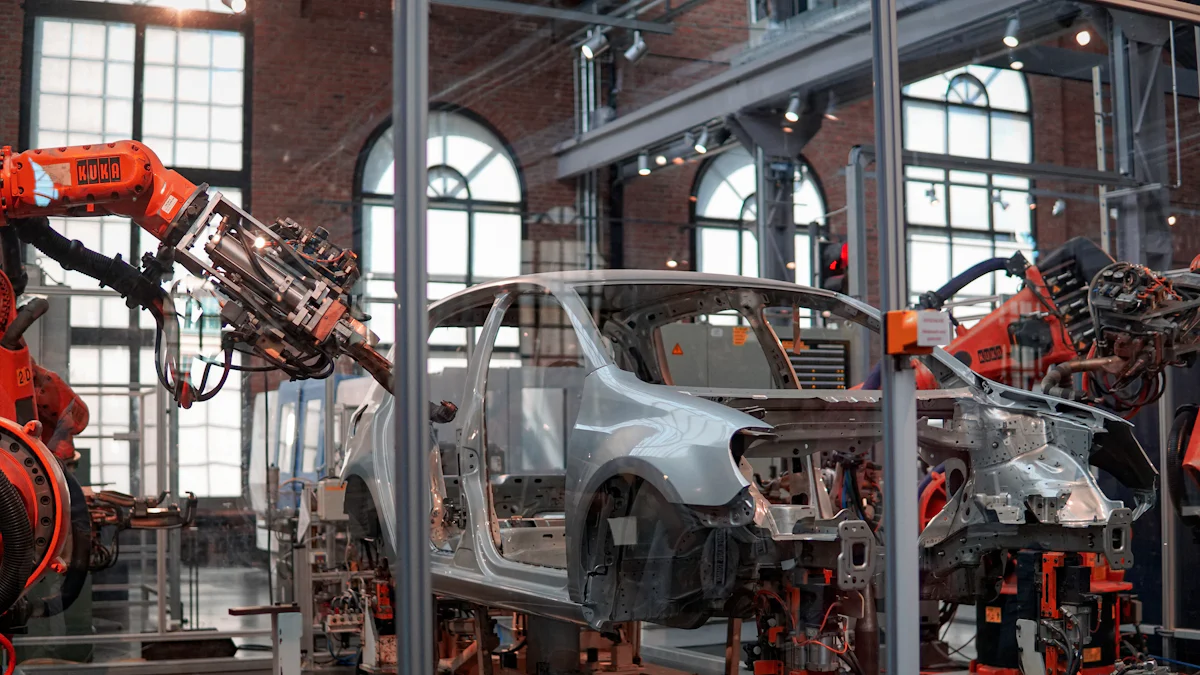

Raw Material Suppliers
Key materials used in automotive manufacturing
The Automotive Supply Chain in Japan relies on a variety of raw materials. Steel, aluminum, and plastics form the backbone of vehicle production. Rubber and glass also play essential roles in manufacturing. These materials contribute to the durability and safety of vehicles. The quality of raw materials directly impacts the final product.
Major suppliers and their roles
Several major suppliers dominate the Japanese Automotive Supply Chain. Nippon Steel supplies high-grade steel for automotive use. Sumitomo Chemical provides essential plastics and rubber components. Asahi Glass manufactures specialized glass for vehicles. Each supplier plays a crucial role in maintaining quality standards. Collaboration between automakers and suppliers ensures efficient production.
Manufacturing and Assembly
Production processes and technologies
Japanese automakers utilize advanced production processes. Lean manufacturing techniques optimize efficiency. The Automotive Supply Chain benefits from just-in-time inventory systems. This approach minimizes waste and reduces costs. Precision engineering enhances the quality of assembly. Continuous improvement remains a core principle in manufacturing.
Role of automation and robotics
Automation revolutionizes the Automotive Supply Chain in Japan. Robotics streamline assembly lines and increase productivity. Automated systems perform tasks with high precision. This technology reduces human error and enhances safety. Robotics also allow for flexible manufacturing processes. The integration of automation supports rapid production changes.
Distribution and Logistics
Transportation networks and strategies
Efficient transportation networks support the Japanese Automotive Supply Chain. Railways and highways facilitate the movement of goods. Shipping companies ensure timely delivery to international markets. Logistics strategies focus on reducing transit times. Distribution centers optimize the flow of automotive parts. These networks maintain the competitiveness of Japanese automakers.
Challenges in distribution
The Automotive Supply Chain faces several distribution challenges. Natural disasters can disrupt transportation networks. Fluctuating fuel prices impact logistics costs. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in supply chains. Companies must adapt to changing regulations and trade policies. Overcoming these challenges requires strategic planning and innovation.
Dynamics Influencing the Automotive Supply Chain
Technological Advancements
Impact of innovation on supply chain efficiency
Innovation drives efficiency in the Automotive Supply Chain. Advanced technologies streamline processes and reduce costs. Automation plays a crucial role in enhancing productivity. Robotics perform tasks with precision and speed. Artificial intelligence optimizes inventory management. These innovations minimize waste and improve resource utilization. The Automotive Supply Chain benefits from increased reliability and accuracy.
Adoption of new technologies
Japanese automakers adopt cutting-edge technologies rapidly. Electric vehicles (EVs) represent a significant shift in the industry. The transition to EVs requires changes in the supply chain. Battery production becomes a focal point for manufacturers. Companies invest in research and development for sustainable solutions. The integration of new technologies ensures competitiveness. The Automotive Supply Chain adapts to meet evolving consumer demands.
Economic and Political Factors
Trade policies and regulations
Trade policies impact the Automotive Supply Chain significantly. Tariffs affect the cost of importing raw materials. Regulations influence manufacturing standards and practices. Japanese automakers navigate complex international trade agreements. Compliance with global standards ensures market access. Political stability plays a role in supply chain resilience. Companies must remain agile to adapt to policy changes.
Economic trends affecting the supply chain
Economic trends shape the dynamics of the Automotive Supply Chain. Fluctuations in currency exchange rates affect export prices. Economic growth influences consumer purchasing power. The demand for vehicles varies with economic conditions. Companies adjust production levels based on market forecasts. Strategic planning mitigates risks associated with economic volatility. The Automotive Supply Chain remains responsive to global economic shifts.
Environmental and Sustainability Concerns
Initiatives for sustainable supply chains
Sustainability initiatives enhance the Automotive Supply Chain. Companies focus on reducing carbon emissions and waste. Renewable energy sources power manufacturing facilities. Recycling programs minimize environmental impact. Slade, an expert in supply chain management, states, "Companies pursuing environmental sustainability have an edge in terms of productivity." Sustainable practices improve supplier relationships and processes. The commitment to sustainability strengthens brand reputation.
Impact of environmental regulations
Environmental regulations influence supply chain operations. Compliance with emissions standards is mandatory for automakers. Regulations drive innovation in eco-friendly technologies. The Automotive Supply Chain adapts to meet stringent requirements. Companies invest in cleaner production methods and materials. Sustainability becomes a competitive advantage in the industry. The focus on environmental responsibility shapes future strategies.
Japan's automotive supply chain showcases remarkable efficiency and innovation. Major players like Toyota and Honda lead the industry with advanced manufacturing techniques. The global automotive industry can learn from Japan's focus on sustainability and technology. Japanese companies pursue environmental sustainability to gain productivity and improve supplier relationships. The future of the automotive sector leans toward electric vehicles. Japanese manufacturers adapt their supply chains for this shift. Global connections enhance production capabilities. Japanese automakers expand local production and strengthen ties with overseas partners. These strategies ensure continued leadership in the evolving automotive landscape.
See Also
Maximizing Your Automotive Supply Chain's Potential
Expert Guidance for Navigating Automotive Supply Chain Challenges
Revolutionizing Supply Chains with Robotics Technology
Tomorrow's Logistics Revolution with AI in the Supply Chain
Efficiently Addressing High-Tech Manufacturing's Supply Chain Challenges
