U.S. Cancels De Minimis Exemption and its impact on air logistics from China

The United States' recent cancellation of the de minimis exemption has sent shockwaves through the air logistics industry, particularly for shipments originating in China. This policy shift immediately impacted airfreight demand and pricing.
Airfreight demand from China and Hong Kong to the US dropped by 1% week-over-week.
The Asia Pacific region experienced a 7% week-on-week decline in overall demand.
Air cargo rates surged by 4%, with the average spot rate reaching $3.94 per kilogram.
"John Lash, group vice president of product strategy at supply chain platform e2open, stated that the cancellation would reshape international B2C e-commerce, forcing companies like Shein and Temu to rethink their logistics strategies due to the loss of duty-free shipping for individual parcels."
Businesses and consumers now face increased costs, as tariffs of up to 35% and additional filing fees are applied to goods shipped from China. These changes could lead to price hikes of 20-50% for consumers and force businesses to overhaul their logistics strategies. The air logistics industry must navigate these challenges while grappling with more complex customs processes and longer delivery times, fundamentally altering the trade landscape.
Understanding the De Minimis Exemption
Historical context and its role in U.S.-China trade
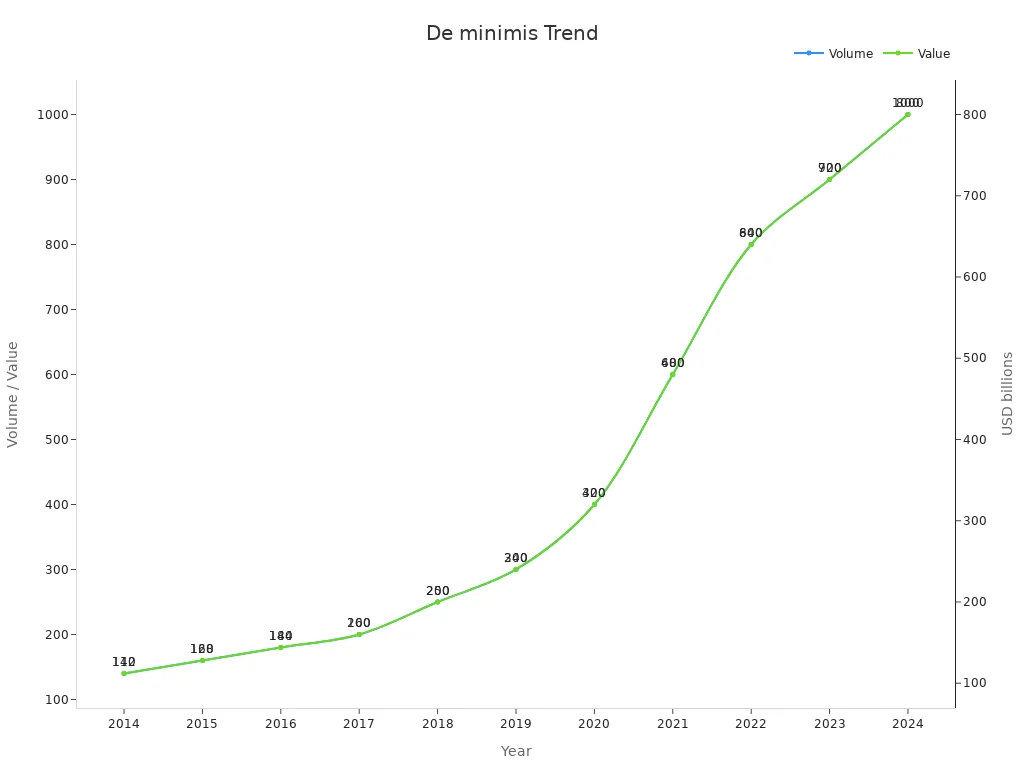
The de minimis exemption has played a pivotal role in shaping U.S.-China trade dynamics. Initially designed to facilitate the import of souvenirs and small items, the policy evolved into a cornerstone of modern e-commerce. Over the years, the volume of shipments utilizing the exemption has grown exponentially, reflecting its importance in global trade.
Year | De Minimis Shipments (millions) |
|---|---|
2014 | 140 |
2023 | 1,000 |
The rise of cross-border e-commerce platforms like Shein and Temu further amplified the significance of the exemption. These companies relied heavily on the policy to ship low-cost goods directly to U.S. consumers without incurring additional tariffs. By 2024, daily shipments under the exemption reached approximately 4 million, underscoring its critical role in facilitating trade between the two nations.
Reasons for the cancellation, including economic and political factors
The cancellation of the de minimis exemption stems from a combination of economic and political considerations. Economically, the U.S. government aims to increase revenue from customs duties. Over the next decade, the cancellation is projected to generate an estimated $23.5 billion in additional revenue. This move also addresses concerns about the rapid growth of de minimis shipments, which surged from 139 million in 2014 to over 1.4 billion in 2024. The total retail value of these shipments exceeded $50 billion, highlighting the scale of untaxed imports entering the U.S. market.
Description | Value |
|---|---|
Estimated Revenue from customs duties (2024–2034) | $23.5 billion |
Increase in de minimis shipments (past decade) | From 139 million to over 1.4 billion |
Total retail value of de minimis shipments | Over $50 billion |
Politically, the cancellation aligns with broader efforts to address trade imbalances with China. Policymakers argue that the exemption disproportionately benefited Chinese exporters, allowing them to flood the U.S. market with low-cost goods. By eliminating the exemption, the U.S. seeks to level the playing field for domestic manufacturers and reduce reliance on Chinese imports. This decision also reflects growing tensions in U.S.-China trade relations, as both nations pursue policies to protect their economic interests.
Impact on Air Logistics from China

Decline in air freight demand and volume
The cancellation of the de minimis exemption has triggered a noticeable decline in air freight demand from China to the United States. E-commerce shipments, which previously dominated air cargo lanes, are now facing reduced volumes as businesses reassess their logistics strategies. The removal of duty-free privileges for goods valued under $800 has dampened consumer demand for low-cost imports, directly impacting air cargo operations.
Spot rates for air freight from China to the U.S. surged by 12% in late March, reaching $4.53 per kilogram, as businesses rushed to ship goods before the tariff deadline.
The exemption's cancellation is expected to further suppress air cargo demand, particularly for e-commerce shipments that relied heavily on the policy's cost-saving benefits.
This decline in demand has created challenges for air logistics providers, who now face underutilized cargo space and reduced profitability. As businesses scale back shipments, air carriers may struggle to maintain operational efficiency, leading to potential overcapacity on key routes.
Rising shipping costs and pricing adjustments
The cancellation of the de minimis exemption has also led to significant increases in shipping costs. Tariffs on Chinese goods have surged to 145%, drastically raising import expenses for businesses. Importers are now forced to either absorb these costs or pass them on to consumers, resulting in higher retail prices and reduced purchasing power.
Importers may reduce or cancel shipments to avoid the new tariff costs, contributing to decreased demand and potential overcapacity on shipping lanes.
Shippers are redirecting cargo to tariff-free countries, intensifying competition and driving up rates on alternative routes.
Delays in cargo pickup and increased cargo abandonment are becoming more common as importers struggle with the new duties, causing congestion in container ports.
These pricing adjustments are reshaping the air logistics landscape, compelling businesses to explore new strategies for cost management. Some companies are shifting their sourcing to countries unaffected by the tariffs, while others are renegotiating contracts with freight forwarders to secure more favorable rates.
Operational challenges for air carriers and freight forwarders
Air carriers and freight forwarders are grappling with a range of operational challenges stemming from the policy change. The increased complexity of customs clearance processes has placed additional burdens on logistics providers, requiring them to invest in compliance measures and documentation.
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Customs Clearance | Involves compliance with regulations and documentation; delays can lead to increased costs and dissatisfied customers. |
Cargo Security | Ensuring security against theft and tampering; requires robust protocols and collaboration with reputable carriers. |
Capacity Constraints | Limited aircraft availability and peak seasons can lead to increased rates and challenges in meeting demand; strategic partnerships and planning are essential to mitigate this issue. |
Regulatory Compliance | Constantly changing regulations require businesses to stay updated and maintain accurate records; collaboration with knowledgeable freight forwarders can aid in navigating these complexities. |
The cancellation of the de minimis exemption has also heightened the risk of cargo abandonment, as importers struggle to manage the financial and logistical implications of the new tariffs. Freight forwarders must now adapt to these challenges by enhancing their operational efficiency and leveraging technology to streamline processes. Strategic partnerships and proactive planning will be critical for air logistics providers to navigate this evolving landscape.
Effects on E-commerce and Consumers
Increased costs for e-commerce businesses
The cancellation of the de minimis exemption has significantly increased costs for e-commerce businesses, particularly those relying on low-value shipments from China. The removal of duty-free entry for goods under $800 has forced businesses to pay higher tariffs and comply with formal customs procedures. Starting May 2, postal shipments from China now incur duties of 120% or $100 per item, with this figure rising to $150 per item by June 1. These additional costs have drastically raised landed costs for many e-commerce companies, making it harder to maintain competitive pricing.
The financial burden is further compounded by the introduction of a 125% reciprocal tariff, effective April 10, which adds to the existing 20% tariffs. This sharp increase in duties has left businesses with limited options: either absorb the costs, which reduces profit margins, or pass them on to consumers, potentially lowering demand. The total value of imports claiming the exemption in fiscal year 2024 reached $64.6 billion, highlighting the scale of the impact on the e-commerce sector.
Delays in shipping and delivery times
Shipping delays have become a significant challenge for e-commerce operations. Delivery times have surged to nearly four times the usual average as of July 2024. Factors such as low water levels in the Panama Canal and geopolitical disruptions like rebel attacks in the Red Sea have forced ships to reroute, adding up to two weeks to shipping schedules. Labor shortages have further exacerbated the issue, with 37% of logistics organizations reporting high staffing deficits and 61% indicating that transportation operations are the most affected.
These delays not only frustrate customers but also increase operational costs for businesses. Companies must spend more on refunds, discounts, or expedited replacements to meet customer expectations. Additionally, overtime labor costs arise from addressing backlogged orders, further straining resources.
Changes in business models and sourcing strategies
The policy change has prompted e-commerce businesses to reevaluate their models and sourcing strategies. Many companies are shifting their focus to alternative markets or suppliers to mitigate the impact of higher tariffs. For instance, businesses are exploring partnerships with manufacturers in countries unaffected by the new duties, such as those in Southeast Asia or Latin America. This diversification reduces dependency on Chinese imports and helps maintain competitive pricing.
Some companies are also investing in localized production or warehousing to minimize shipping costs and delivery times. By storing inventory closer to target markets, businesses can reduce the need for international shipping and avoid the complexities of customs clearance. These strategic adjustments reflect the industry's resilience and adaptability in navigating the challenges posed by the cancellation of the de minimis exemption.
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
Increased customs processing and documentation requirements
The cancellation of the de minimis exemption has introduced more stringent customs processing and documentation requirements for businesses. Companies must now comply with mandatory safety and security data reporting for various transportation modes. These changes have added complexity to trade processes, requiring businesses to adapt their operations.
Date | Requirement Description | Impact on Trade Processes |
|---|---|---|
April 1, 2025 | Mandatory safety and security data reporting for maritime carriers | Companies must adapt their global trade processes to comply with new documentation needs. |
September 1, 2025 | Mandatory safety and security data reporting for road and rail carriers | Increased complexity in customs clearance processes necessitating accurate documentation. |
To meet these requirements, businesses must:
Evaluate operational processes to ensure compliance.
Assess partners and suppliers for adherence to new regulations.
Review logistics service providers and IT systems for compatibility.
Adapt data management practices to handle increased documentation needs.
These adjustments demand significant time and resources, posing challenges for companies unprepared for the heightened regulatory environment.
Adjustments to tariff structures and duty payments
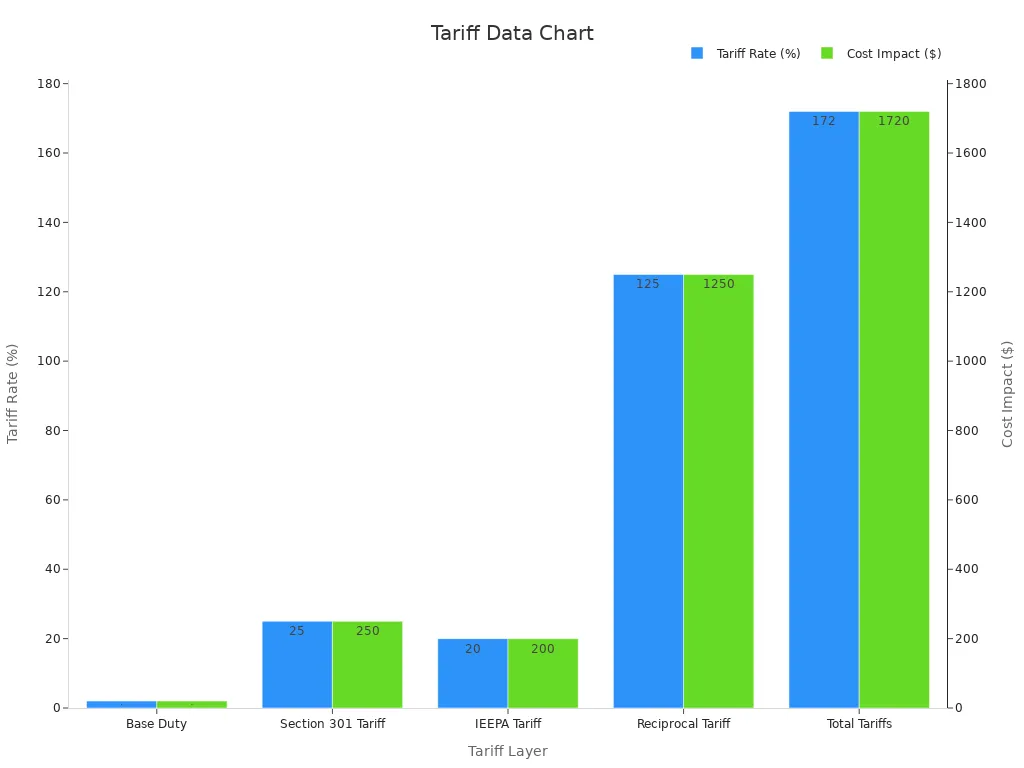
The revised tariff structures have drastically increased the cost of importing goods from China. Effective May 2, 2025, all imports from China and Hong Kong are excluded from the de minimis exemption, subjecting them to multiple layers of tariffs.
Tariff Layer | Rate | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
Base Duty | 2% | $20 |
Section 301 Tariff | 25% | $250 |
IEEPA Tariff | 20% | $200 |
Reciprocal Tariff | 125% | $1,250 |
Total Tariffs | 172% | $1,720 |
Total Landed Cost | — | $2,720 |
For instance, a $600 shipment of hair accessories from China now incurs a total cost of $1,320 for postal shipments and $1,530 for non-postal shipments. These adjustments have forced businesses to reevaluate their pricing strategies and supply chains.
Strategies for businesses to navigate compliance hurdles
To address these challenges, businesses are adopting innovative strategies. Many companies are implementing centralized compliance teams and leveraging automated classification software to improve tariff accuracy. This approach has helped reduce costs and avoid penalties.
Challenge | Solution | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
Complex tariff classifications leading to cost overruns. | Implemented a centralized compliance team and automated classification software. | Improved tariff accuracy and saved millions in duties and penalties. |
Additionally, businesses are diversifying their supply chains by sourcing from countries unaffected by the new tariffs. This strategy minimizes dependency on Chinese imports and mitigates the financial impact of the policy change. By investing in technology and exploring alternative markets, companies are positioning themselves to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape effectively.
Long-term Implications for Global Trade and Logistics

Shifts in trade routes and supply chains
The cancellation of the de minimis exemption is expected to reshape global trade routes and supply chains. Businesses that previously relied on low-cost imports from China are now exploring alternative sourcing options. Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa are emerging as attractive regions for manufacturing and trade. These shifts aim to reduce dependency on Chinese goods while mitigating the financial impact of increased tariffs.
Logistics providers are also adapting to these changes by diversifying their operations. Many companies are investing in regional hubs closer to consumer markets to minimize shipping costs and delivery times. This trend aligns with the growing demand for urban warehouses, as 70% of consumers now expect same-day or next-day delivery.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Urban Warehouse Demand | 76% of consumers expect free returns, and 70% anticipate faster deliveries. |
These adjustments highlight the evolving nature of supply chains, emphasizing the importance of flexibility and proximity to end-users.
Broader impacts on U.S.-China trade relations
The removal of the de minimis exemption has intensified trade tensions between the U.S. and China. This policy change directly targets Chinese exporters, who previously benefited from duty-free access to the U.S. market. The resulting tariffs have disrupted trade volumes, with an estimated $50 billion in imports linked to de minimis trade now subject to duties.
The exemption allowed shipments valued at $800 or less to enter the U.S. duty-free.
Its removal will significantly affect trade volumes and consumer prices.
Higher tariffs could lead to increased costs for U.S. consumers on low-value imports.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Missing Imports | Upwards of $100 billion in 'missing imports,' with $50 billion linked to de minimis trade. |
Price Impact | Increased costs for U.S. consumers due to higher tariffs on low-value imports. |
This policy shift underscores the growing economic divide between the two nations, with long-term implications for bilateral trade relations.
The cancellation of the de minimis exemption has reshaped air logistics, e-commerce, and global trade. Businesses face higher costs, operational hurdles, and shifting trade routes. E-commerce shippers are exploring ocean freight and regional warehousing to mitigate customs delays.
Air cargo may lose B2C volume, while ocean freight and domestic trucking could gain.
The shift to B2B2C models is accelerating, driving innovation in logistics.
Adapting to this evolving landscape will require resilience and strategic foresight.
FAQ
Will consumers see higher prices due to this policy?
Yes, consumers will likely face price increases of 20-50% on imported goods. Businesses must pass on higher tariffs and shipping costs, making low-cost products less accessible. This shift may also reduce demand for cross-border e-commerce.
What strategies can businesses use to navigate compliance challenges?
Businesses can implement centralized compliance teams and automated classification software to improve tariff accuracy. Diversifying supply chains by sourcing from tariff-free countries also helps reduce dependency on Chinese imports and mitigates financial risks.
Are there opportunities for innovation in logistics despite the challenges?
Yes, logistics providers can leverage technology like real-time tracking and automation to enhance efficiency. Sustainability initiatives, such as using electric vehicles and optimizing delivery routes, offer long-term benefits while addressing current disruptions.
See Also
Exploring the Future of LTL Freight Solutions Today
Achieving Success in International Trade Through JUSDA
Discovering Innovations in Sea Freight Logistics for 2024
Understanding Advanced Manufacturing with JUSDA's Logistics Insights
Sustainable Practices in Logistics: JUSDA's Growth Strategies Revealed
