Chinese Air Freight Faces Turbulence Amid Rising US Tariff Barriers

The US has canceled the de minimis rule for small packages, leading to the implementation of US tariffs on small parcels starting in May 2025. This change introduces tariffs of up to 30% on items valued under $800, significantly increasing shipping costs. Freightos predicts that air cargo prices could rise by as much as 50% for air-shipped goods. Small packages, which are prevalent in online shopping, will now be subject to stricter regulations. Previously, only 2% of these shipments were registered, but under the new rules, all packages must be pre-registered. This adjustment fundamentally alters the shipping landscape on a global scale.
Key Takeaways
The US will remove the de minimis rule. Starting May 2025, small packages from China will face tariffs up to 30%. This will make shipping more expensive.
Online stores like Shein and Temu might change their plans. Higher costs could mean higher prices for shoppers.
Chinese air shipping companies will pay more and follow stricter rules. They must find better ways to ship to stay in business.
The new tariffs might slow online shopping between countries. Shoppers may spend less on things they don’t really need.
New markets give Chinese sellers fresh chances. They are adjusting to new trade rules and trying to reduce the effects of US tariffs.
The New US Tariffs on Small Parcels
Changes to the de minimis exemption policy
The de minimis exemption policy has changed a lot for goods from China. Before, this rule let small shipments enter the U.S. without paying taxes. This helped online shopping grow between countries. In 2016, the tax-free limit went up from $200 to $800, causing more packages to be shipped worldwide. From 2013 to 2017, international mail grew from 150 million to over 500 million packages each year. These changes made shipping cheaper and customs easier for businesses and buyers.
But starting February 2025, stricter rules apply. Goods from China no longer get tax-free entry, even if they cost less than $800. This is a big change from past policies that made trade easier for small packages. Now, these shipments face a 30% tax, making it more expensive for businesses that depend on low-cost exports.
Note: Removing the de minimis exemption for Chinese goods shows a shift in U.S. trade rules. The focus is now on tougher regulations and higher taxes.
Key drivers behind the tariff adjustments
There are several reasons why the U.S. added tariffs on small packages. One big reason is to fix trade problems. Higher taxes aim to cut imports and support U.S. factories. This plan helps the economy grow and backs local businesses.
Another reason is how trade deals are changing. Global trade agreements often lower taxes slowly but don’t remove them completely. Deals between two countries or regions might end tariffs over 5 to 10 years. Since there’s no such deal with China, high taxes on Chinese goods, including small packages, remain.
The U.S. also wants to protect its industries from cheap foreign goods. Areas like semiconductors, medicines, and chemicals face tough competition. By adding tariffs, the government hopes to help American companies and stop unfair trade practices.
Goods and industries most affected
The new tariffs affect many products and industries. Items like electronics, clothes, and everyday goods, popular in online shopping, now cost more due to the 30% tax. These extra costs will likely make prices higher for shoppers.
Industries that use materials from China also face problems. For example:
Medicines and chemicals, which are big U.S. imports, are hit hard.
The semiconductor industry, already dealing with supply chain issues, now has higher costs.
Energy, wood, and minerals, making up 20% of U.S. imports, face extra taxes.
These tariffs bring big financial challenges. A 25% tax could add $79.7 billion in the first year, while a 10% tax would mean $36.2 billion more. If taxes go up to 50%, the extra cost could reach $132.8 billion. These numbers show how much the new rules affect businesses and buyers.
Insight: While tariffs aim to help U.S. industries, they might also hurt supply chains and raise costs for American companies and stores.
Challenges for China’s Air Logistics Sector

Higher costs and lower profits
The end of the de minimis exemption has raised costs for China’s air logistics companies. They now pay more tariffs on small packages, which hurts their profits. Businesses that depended on cheap exports must either pay these extra costs or charge customers more. Both choices are tough. Raising prices may lower demand, while paying the costs themselves reduces already small profits.
The global chemical industry is also struggling with higher costs. Prices for raw materials, energy, and tariffs have gone up. This has made it harder for manufacturers to make money. Companies must either pay these costs or increase prices, which can reduce sales.
Smaller profits are a big problem as costs rise and supply chains face issues. Many companies can’t raise prices because of competition, which puts financial pressure on them, especially smaller businesses.
The air logistics industry depends on online shopping between countries. Higher product prices mean fewer orders, leaving cargo space unused. This waste makes profits even smaller, creating a cycle of rising costs and falling earnings.
Tougher customs rules and challenges
The new US tariffs on small packages have made customs rules stricter. Air freight companies now deal with more paperwork, correct tariff codes, and strict US Customs rules. These extra steps take more time and money to complete.
Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
Check all documents carefully and get help from experts. | |
Wrong Tariff Codes | Use correct codes to avoid fines. Ask professionals for advice. |
Customs Checks | Follow US rules to prepare for inspections. |
Extra Taxes | Learn about tariffs early and include them in your budget. |
Shipping Delays | Stay in touch with your freight forwarder to solve problems quickly. |
These challenges slow down shipping and increase mistakes. A single error in paperwork or codes can lead to fines, delays, or goods being taken away. For air freight companies, which rely on speed, these problems hurt their ability to compete.
Changing shipping methods to handle tariffs
To deal with higher tariffs, Chinese logistics companies are trying new shipping methods. They are using flexible routes and options to save money and deliver on time. Predictive tools are also helping. By guessing future demand and problems, companies can plan better and avoid risks.
Method | Advantages |
|---|---|
Cuts costs by using different routes or methods, ensuring faster deliveries. | |
Predictive Tools | Helps plan for demand and problems, reducing risks and saving resources. |
Better Logistics Technology | Tracks shipments in real-time and shows how tariffs affect costs, improving decisions. |
New technology is also important. Real-time tracking helps companies predict delays and understand tariff costs. These tools help them make better choices and keep services running smoothly despite the new rules.
Tip: Companies using advanced tools and technology can better handle today’s trade challenges.
By using these methods, Chinese air logistics companies hope to stay strong in a market changed by the end of the de minimis exemption and new US tariffs on small packages.
Impact on E-Commerce Platforms

Effects on Shein, Temu, and other platforms
New US tariffs on small packages are causing problems for e-commerce platforms like Shein and Temu. These platforms, known for low prices, now face higher costs due to a 30% tax on goods under $800. Experts believe these extra costs will likely raise prices for shoppers, making the platforms less competitive in the U.S.
Analysts say Shein and Temu might need to change their business plans to adjust.
Some think these platforms could even leave the U.S. market if the trade war gets worse.
The fast-fashion industry, which depends on cheap production and quick delivery, faces big challenges.
With rising tariffs and the end of the de minimis rule, these platforms are looking for new strategies. They may try changing their supply chains or focusing on other global markets.
Changes in consumer behavior and pricing strategies
The tariff changes are also affecting how people shop and how prices are set. A University of Michigan survey showed a 9.8% drop in consumer confidence in February 2025. This drop happened because people worry about higher prices caused by tariffs. Many shoppers are now buying in bulk to avoid future price hikes.
Behavior | Description |
|---|---|
Stockpiling | Shoppers buy more items now to avoid paying higher prices later. |
Reduced Discretionary Spending | People spend less on non-essential items due to economic worries. |
Retailers are changing their pricing plans to deal with these issues. Some are taking on part of the tariff costs to keep customers happy. Others are passing the costs to shoppers. This has made price-sensitive buyers more careful, which could lower demand for non-essential goods.
Note: Platforms that don’t adjust their pricing plans may lose customers as people look for cheaper options.
Potential slowdown in cross-border e-commerce growth
Higher tariffs are also slowing down cross-border e-commerce growth. For example, Canada’s economy is already feeling the effects. Its GDP growth dropped to 1.3% in 2024, partly due to weaker global trade and rising tariffs. Canadian exports fell by 2.8% in Q3 2024 compared to the same time in 2023, showing how trade barriers are affecting economies.
The fast-growing cross-border e-commerce industry now faces big challenges. Problems like supply chain delays, sudden policy changes, and limited market access make it harder for businesses to succeed.
Higher tariffs make price-sensitive shoppers buy less.
Delays in managing inventory slow down product deliveries.
Retaliatory tariffs block access to some markets, making trade harder.
These issues together could slow the fast growth of cross-border e-commerce. Businesses now need to rethink their plans to survive in a world with stricter trade rules.
Broader Implications for Global Trade
Ripple effects on air cargo rates and capacity
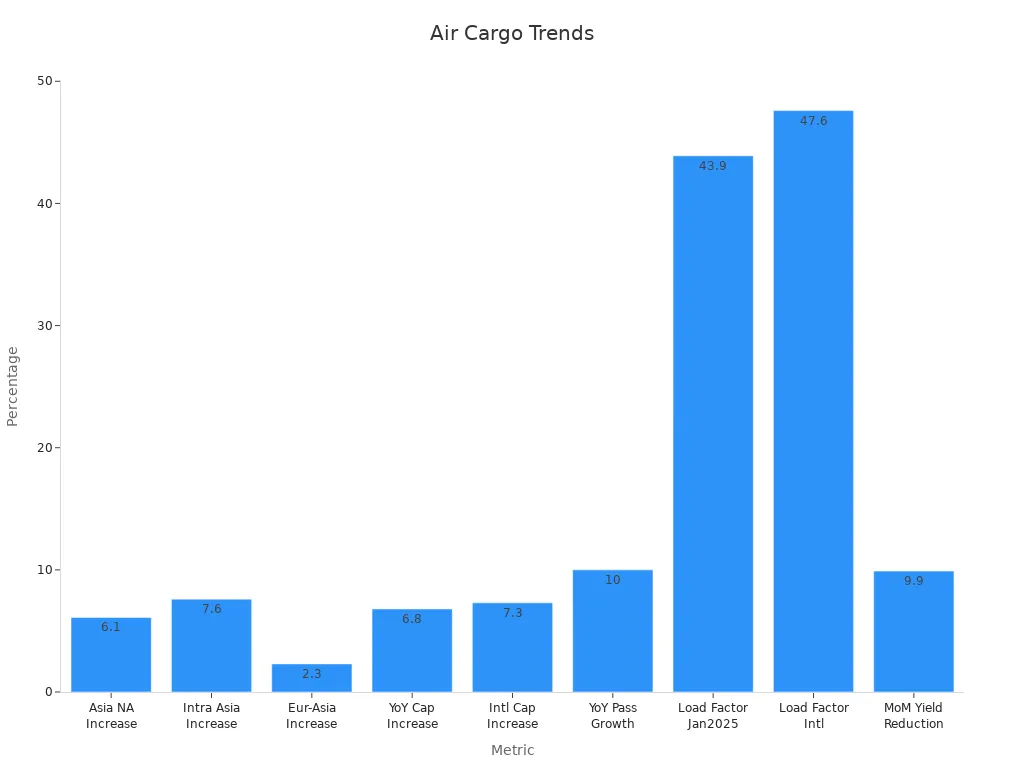
Removing the de minimis rule has disrupted air cargo costs and space. Freight companies now face higher expenses, leading to pricier shipping rates. For example:
Asia-North America air cargo costs rose by 6.1%.
Intra-Asia shipping rates increased by 7.6%.
These changes show the growing money problems in global freight. Space adjustments are also a big issue. International air freight space grew by 7.3%, reaching 53 billion tonne-kilometers. But in January 2025, only 43.9% of this space was used. This mismatch between space and demand wastes resources and complicates shipping.
Shifts in trade flows and emerging market opportunities
New tariff rules are changing how countries trade. Nations that relied on cheap labor are now focusing on technology and education. For example:
Brazil and India are training workers for skilled jobs.
These changes help them compete better in global markets.
Emerging markets offer new chances for exporters. Governments are helping key industries with subsidies and new rules. For instance, the European Union’s digital trade rules are shaping global policies. These shifts show the need to adapt to changing trade systems.
Governments support important industries with special programs.
Technology is changing how countries trade goods.
Education investments create skilled workers for better jobs.
Long-term impacts on global supply chain dynamics
These changes also affect supply chains over time. Predictive tools, like logistic regression, help companies plan for risks and demand. This helps businesses handle surprises and improve operations.
Real-time data and IoT tools are also important. Old supply chains used outdated information, causing mistakes. Now, modern tools let companies react quickly to market changes. This makes supply chains faster and stronger.
Logistic regression helps predict risks and future needs.
IoT tools use live data to adjust to market shifts.
Advanced analytics improve decisions in shipping and trade.
These tools show the need for strong systems to manage global trade challenges.
The new US tariffs on small packages have caused big problems for China’s air freight sector. Higher costs, tougher customs rules, and less demand for cheap exports have made things harder. Companies now need new ideas to stay in the game.
Even with these problems, experts think China’s air freight industry will still grow. It might grow 7% each year from 2024 to 2029. The China Freight and Logistics Market could also rise from 1.31 trillion USD in 2025 to 1.78 trillion USD by 2030, growing 6.27% yearly.
To handle the tariff issues, Chinese companies are trying smart solutions:
Using different suppliers from many countries to spread risks.
Making products locally in areas without tariffs to save money.
Changing designs to use local parts or fit lower-tax categories.
By focusing on these strategies and new markets, businesses can adjust to trade changes and stay strong.
FAQ
Which industries are most affected by the tariff changes?
Industries using Chinese imports, like electronics, clothes, and chemicals, are hit hardest. Higher tariffs raise costs for making and selling products. This affects businesses needing cheap materials and shoppers wanting low prices.
How are e-commerce platforms adapting to the new tariffs?
Platforms like Shein and Temu are finding new supply chains and markets. They might change prices or focus on areas with fewer trade rules. These steps help them stay competitive despite higher costs.
Are there opportunities for Chinese air freight companies in emerging markets?
Yes, regions like ASEAN, Latin America, and Russia are growing markets. These areas need more Chinese goods. By trading with these regions, air freight companies can recover losses from U.S. tariffs.
See Also
Exploring Innovations in Sea Freight Logistics for 2024
Addressing Global Supply Chain Growth Challenges Effectively
Understanding Current Trends in Logistics Risk Management
