Retail Warehousing Decisions In-House Versus Outsourced Solutions

Retailers face a pivotal decision in determining how to manage their warehousing operations. This choice directly influences their ability to meet customer expectations while maintaining operational efficiency. Balancing cost and scalability adds complexity to the equation. The Warehousing Game demands more than just logistical planning; it requires strategic foresight to align warehousing solutions with business goals. Retailers who master this game gain a competitive edge, while those who misstep risk operational setbacks and dissatisfied customers.
Key Takeaways
Managing your own warehouse gives control and flexibility. Businesses can adjust operations to fit their needs. This helps keep customers happy and loyal to the brand.
Hiring another company for warehousing saves money and grows easily. It lets businesses quickly adapt to changes without spending a lot upfront.
Using new technology and training workers is very important. Machines can lower costs and make tracking inventory more accurate.
Companies should think about their needs like cost, control, and growth. This helps them pick the best warehouse option for their business stage.
Checking warehouse plans often keeps them matching business goals. It also helps companies stay strong in a changing retail world.
Pros and Cons of In-House Warehousing

Benefits of In-House Warehousing
In-house warehousing offers retailers unparalleled control over their operations. By managing their own facilities, businesses can tailor processes to align with their unique needs, ensuring a seamless customer experience. This approach enhances brand perception and builds trust among consumers.
Optimized Inventory Control: Companies that manage their own warehouses can implement advanced systems to track inventory in real time. This reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking, which can lead to lost sales or unnecessary expenses. Efficient inventory tracking also eliminates discrepancies, improving customer satisfaction and operational accuracy.
Enhanced Order Fulfillment: Automation in in-house warehouses can significantly lower order processing costs by up to 30%. Brands using AI-driven demand forecasting have reported a 50% reduction in inventory holding costs. These technologies streamline operations, ensuring faster and more accurate order fulfillment.
Customer Retention: Studies show that acquiring new customers costs 5-7 times more than retaining existing ones. Efficient in-house warehousing ensures timely deliveries and accurate orders, which are critical for maintaining customer loyalty.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Automation can significantly lower costs associated with order processing, enhancing efficiency in inventory control. | |
50% reduction in inventory holding costs | Brands using AI for demand forecasting can drastically cut down on costs related to holding excess inventory. |
5-7 times more cost to acquire new customers | Emphasizes the importance of efficient order fulfillment to retain existing customers and reduce costs. |
In addition to cost savings, in-house warehousing allows businesses to adapt quickly to market changes. For example, companies can adjust inventory levels or shift strategies without waiting for third-party approval. This agility is especially valuable during peak seasons or unexpected demand surges.
A case study highlights how a retailer improved its goods inwards (GI) department by optimizing warehousing operations. By streamlining the process of managing incoming parts from suppliers, the company minimized throughput time and enhanced overall efficiency. This demonstrates the operational strengths of in-house warehousing when executed effectively.
Drawbacks of In-House Warehousing
Despite its advantages, in-house warehousing comes with significant challenges. The high costs and resource demands can strain a company’s finances, particularly for small or growing businesses.
Cost Escalation: Leasing warehouse space, purchasing equipment, and hiring skilled labor require substantial upfront investment. Unrealistic assumptions in resource allocation models can lead to inaccurate budgeting, further escalating costs. Without proper training in cost prediction tools, businesses may struggle to allocate resources effectively.
Operational Complexity: Managing a warehouse involves coordinating multiple processes, from inventory tracking to order fulfillment. A lack of communication and collaboration among teams can hinder efficiency, leading to delays and errors. This complexity increases as businesses scale, making it harder to maintain smooth operations.
Limited Flexibility: Seasonal demand fluctuations pose another challenge. During peak periods, companies may need to hire temporary staff or expand storage capacity, both of which add to operational costs. Conversely, during off-peak times, these resources often remain underutilized, reducing profitability.
Tip: Businesses should carefully evaluate their ability to manage these challenges before committing to in-house warehousing. Investing in training and technology can mitigate some of these risks, but the financial and operational burden remains significant.
Pros and Cons of Outsourced Warehousing
Advantages of Outsourcing Warehousing
Outsourcing warehousing offers businesses a cost-effective and scalable solution to meet their logistics needs. By partnering with third-party logistics providers (3PLs), companies can focus on their core competencies while leveraging the expertise of specialized teams.
Cost Savings: Outsourcing eliminates the need for upfront investments in infrastructure, technology, and staffing. Businesses only pay for the space and services they use, reducing capital expenditures. Shipping companies often provide discounts ranging from 15% to 35% for 3PL partners, further lowering operational costs.
Scalability: Outsourced warehousing allows companies to adjust their storage and fulfillment needs based on order volume. This flexibility is particularly beneficial during peak seasons or when expanding into new markets. Businesses can avoid delays associated with building new warehouses, ensuring they remain agile in dynamic environments.
Access to Expertise: 3PLs bring years of experience and advanced technology to the table. Their innovations, such as automated inventory management systems, streamline operations and improve accuracy. Companies benefit from these resources without incurring the costs of development or implementation.
Geographic Reach: Many 3PLs operate extensive networks of warehouses, enabling businesses to store products closer to their customers. This reduces shipping times and costs, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Note: According to FreightWaves, 43% of shippers outsource their warehouse operations, highlighting the widespread adoption of this model in the supply chain industry.
Outsourcing also provides businesses with the freedom to focus on growth strategies. By delegating logistics to experts, companies can allocate resources to marketing, product development, and customer engagement.
Disadvantages of Outsourcing Warehousing
While outsourcing offers numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges that businesses must carefully evaluate. Relying on third-party providers introduces risks that can impact operations and customer satisfaction.
Limited Control: Outsourcing requires businesses to trust their partners with critical operations. Companies may have less oversight over staffing, inventory management, and order fulfillment processes. This dependency can lead to misaligned priorities, especially if the 3PL focuses on high-volume clients.
Operational Rigidity: Third-party providers often operate within fixed capabilities. Customizing processes or making adjustments to meet unique business needs may involve additional costs or delays. Geographic limitations can also arise if the vendor lacks warehouses in optimal locations.
Data Security Risks: Sharing sensitive information, such as inventory levels and customer data, with 3PLs exposes businesses to potential breaches. Companies must ensure their partners adhere to strict security protocols to mitigate these risks.
Instability: The thin-margin nature of the 3PL industry can lead to frequent bankruptcies. Disruptions in service can negatively impact operations, leaving businesses scrambling for alternatives.
Tip: Businesses should conduct thorough due diligence before selecting a 3PL partner. Evaluating their track record, financial stability, and compliance standards can help mitigate risks.
Outsourcing may also restrict a company’s ability to build proprietary systems and capabilities. While it offers short-term cost savings, businesses must weigh these against the long-term implications of reduced control and flexibility.
In 2019, the average time to build a warehouse in the EU was 180 days, according to World Bank Development Indicators. Outsourcing eliminates this waiting period, but companies must ensure the chosen provider aligns with their strategic goals. Balancing the benefits and drawbacks of outsourcing is essential for making informed decisions in the warehousing game.
Key Factors in the Warehousing Game
Cost Considerations
Cost plays a pivotal role in determining the right warehousing solution. Businesses must evaluate both short-term expenses and long-term investments to ensure financial sustainability. While in-house warehousing demands significant upfront costs for infrastructure, equipment, and staffing, outsourcing offers a pay-as-you-go model that reduces initial financial strain. However, the challenge of cost remains significant when implementing automation. Long-term investments in automation are expected to transform the entire supply chain, making it a strategic consideration for many companies.
The ROI for automation projects often requires a payback period of over five years for standard and larger implementations.
Despite high initial costs, companies increasingly adopt automation as a long-term investment to enhance efficiency and reduce labor dependency.
Cost Factor | Percentage of Companies Considering |
|---|---|
Safety Costs | |
Training Costs | 47% |
Turnover Costs | 42% |
Labor Availability | 42% |
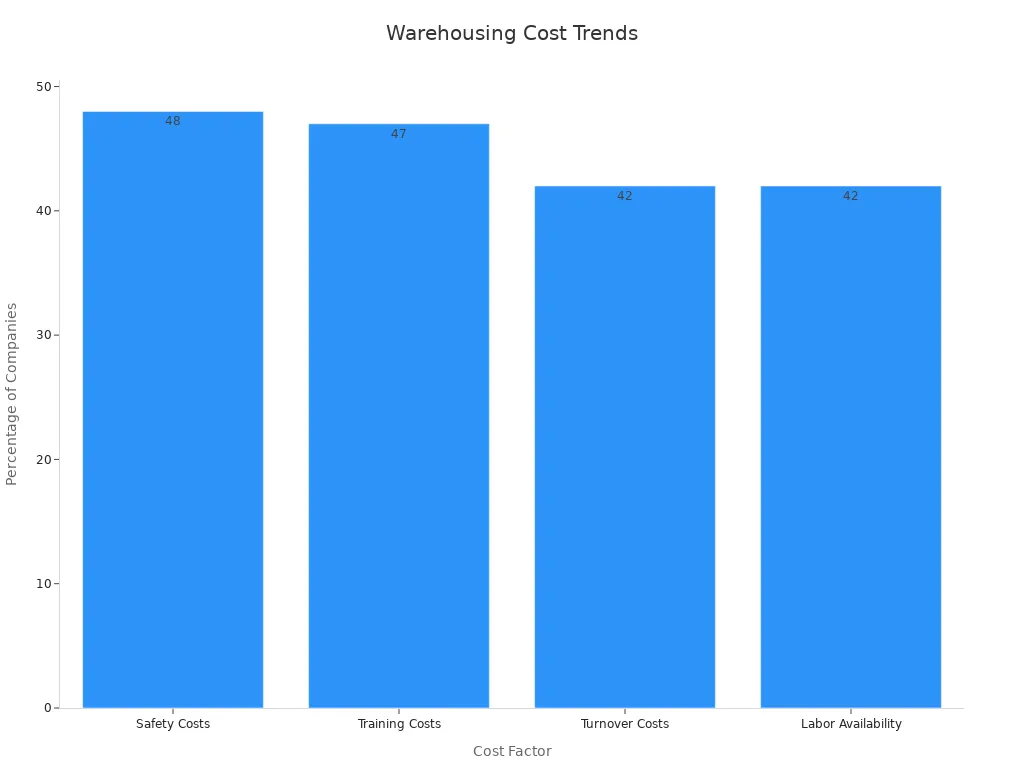
Businesses must weigh these factors carefully to strike a balance between cost efficiency and operational effectiveness.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are essential for modern warehousing operations, especially in the dynamic landscape of e-commerce. A scalable warehouse can seamlessly adjust its operations to accommodate fluctuating demand, preventing unnecessary costs or inefficiencies. This adaptability ensures businesses remain competitive in the face of rapid market changes.
Evidence Description | Key Points |
|---|---|
Scalability in warehouse management involves more than just handling more stock or shipping out more orders. | It encompasses the entire infrastructure of the warehouse, including people, processes, and technology. |
A scalable warehouse can adjust its operations seamlessly as demands change. | This prevents unnecessary costs or operational inefficiencies. |
As e-commerce continues to boom, many businesses are experiencing rapid increases in order volume. | Without scalable systems, businesses risk falling behind in order fulfillment. |
Investing in scalable solutions, such as modern Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), allows companies to handle growth without disruptions. These systems enable easy configuration and integration with other technologies, ensuring smooth operations even during peak seasons. Businesses that prioritize scalability in the Warehousing Game position themselves for long-term success.
Control and Oversight
Control and oversight are critical for maintaining operational efficiency and ensuring customer satisfaction. In-house warehousing provides businesses with direct control over inventory management, staffing, and order fulfillment processes. This level of oversight allows for quick adjustments to strategies and ensures alignment with business goals.
Outsourcing, while cost-effective, often limits control. Companies must rely on third-party providers to manage critical operations, which can lead to misaligned priorities. To mitigate this, businesses should establish clear KPIs and maintain regular communication with their partners. Hybrid models, which combine self-operation with outsourcing, offer a balanced approach by retaining control over core operations while delegating non-core tasks.
Tip: Businesses should evaluate their need for control based on their operational complexity and customer expectations. For companies prioritizing brand perception and customer experience, maintaining oversight through in-house or hybrid models is often the best choice.
Expertise and Technology
Expertise and technology play a pivotal role in shaping the efficiency and effectiveness of warehousing operations. Companies that invest in advanced systems and skilled personnel often gain a significant competitive advantage in the Warehousing Game. By leveraging cutting-edge tools and experienced teams, businesses can streamline processes, reduce errors, and enhance overall productivity.
Modern technologies, such as automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) and AI-driven inventory management, have revolutionized warehousing. These innovations not only improve operational accuracy but also free up valuable storage space. For instance, automation can increase pick accuracy to 99.9% and boost productivity by 66.67%. Additionally, businesses adopting these technologies report a 60% reduction in operational costs and an 85% improvement in storage utilization.
Statistic Description | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|
Reduction in operational costs | 60% | |
Increase in productivity | 66.67% | |
Improvement in pick accuracy | 99.9% | |
Storage space freed up | 85% |
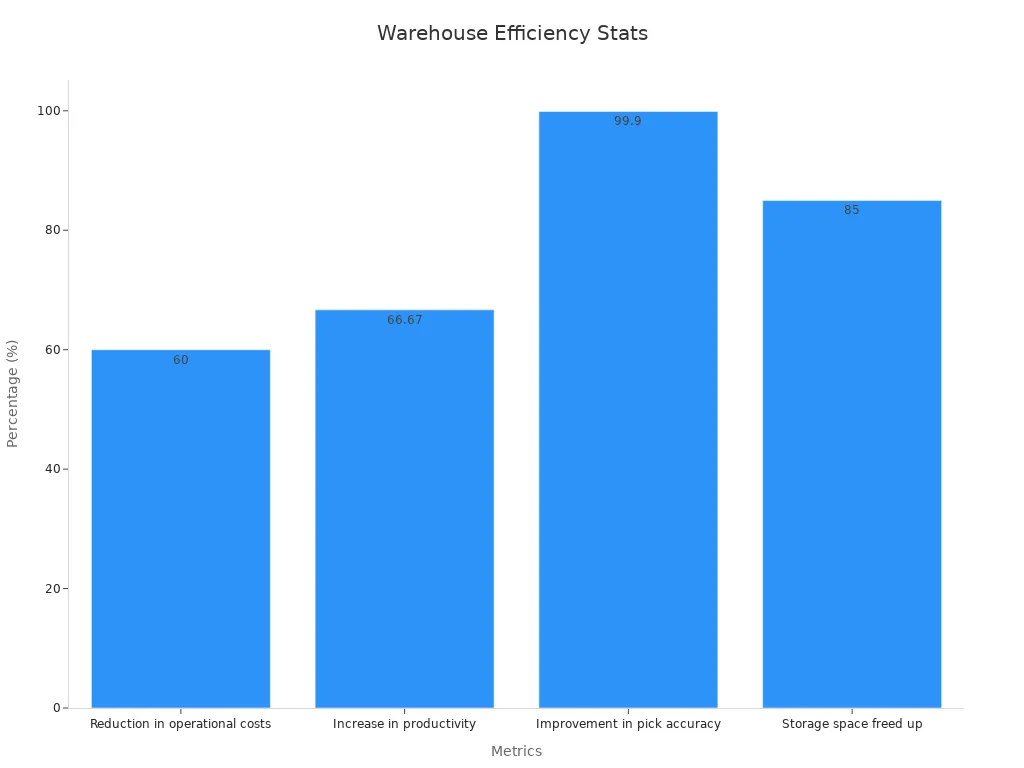
Skilled personnel further amplify the benefits of technology. Employees trained in warehouse management systems (WMS) and automation tools can optimize workflows and minimize downtime. This combination of expertise and technology ensures that businesses remain agile and responsive to market demands.
Tip: Companies should prioritize investments in both technology and workforce training to maximize the benefits of their warehousing operations.
Business Size and Growth Stage
The size and growth stage of a business significantly influence its warehousing strategy. Startups, for example, often opt for outsourced solutions to minimize costs and focus on core activities. As these businesses grow, their warehousing needs evolve, requiring more control and scalability.
Small businesses with limited order volumes benefit from outsourcing due to its flexibility and cost-effectiveness. However, mid-sized companies experiencing rapid growth may find hybrid models more suitable. These models combine the control of in-house operations with the scalability of third-party logistics providers. For instance, a company might manage its primary warehouse while outsourcing regional distribution to 3PLs.
Large enterprises, on the other hand, often invest in fully self-operated warehousing systems. This approach allows them to build proprietary capabilities and maintain strict oversight. Mature businesses also leverage advanced technologies to handle high order volumes efficiently.
Callout: Businesses should align their warehousing strategy with their current growth stage to ensure operational efficiency and cost management.
Understanding the relationship between business size and warehousing needs is crucial for long-term success. Companies that adapt their strategies as they scale can better navigate the complexities of the Warehousing Game.
Comparative Analysis: In-House vs. Outsourced Warehousing

Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency is a decisive factor when comparing in-house and outsourced warehousing. In-house warehousing demands significant upfront investments in infrastructure, equipment, and staffing. Businesses often face long ROI cycles, sometimes extending up to nine years. This can strain cash flow, especially for smaller enterprises. On the other hand, outsourced solutions offer a more cost-effective approach. Companies pay only for the space and services they use, avoiding the financial burden of maintaining underutilized facilities.
Metric | In-House Warehousing | Outsourced Solutions |
|---|---|---|
Cost-Effectiveness | High initial investment, long ROI (9 years) | Generally lower upfront costs |
Risk of Underutilization | High pressure to maximize space | Less pressure, can adjust space as needed |
Outsourcing also allows businesses to benefit from shared resources, such as labor and technology, further reducing operational costs. For companies seeking to optimize their budgets, outsourcing often emerges as the more economical choice.
Operational Effectiveness
Operational effectiveness varies significantly between the two models. In-house warehousing provides complete control over processes, enabling businesses to implement tailored strategies and make quick adjustments. This flexibility ensures that operations align closely with business goals. However, scalability remains a challenge. Expanding in-house operations requires time and resources, which can delay responses to market changes.
Outsourced warehousing excels in scalability. Third-party providers can quickly adapt to fluctuating demand, ensuring seamless operations during peak seasons. However, this comes at the cost of reduced control. Businesses must rely on their partners to maintain service quality, which may not always align with their priorities.
Metric | In-House Warehousing | Outsourced Solutions |
|---|---|---|
Scalability | Limited, difficult to adjust quickly | More scalable, can adapt to demand changes |
Control | Complete control over operations | Less control, dependent on third-party |
Flexibility | High flexibility, quick adjustments possible | Less flexible, requires negotiation |
Risk Management
Effective risk management is crucial for ensuring supply chain resilience. In-house warehousing allows businesses to maintain direct oversight, reducing risks associated with third-party dependency. However, it also exposes companies to challenges like underutilization and operational disruptions.
Outsourced solutions mitigate some risks by leveraging the expertise of third-party providers. Techniques like scenario planning and supplier risk management enhance preparedness for disruptions. For example, Monte Carlo simulations predict the likelihood of risks, while diversification strategies reduce dependency on single suppliers.
Technique | Description |
|---|---|
Risk Matrix | Evaluates risks based on likelihood and impact to prioritize them. |
Monte Carlo Simulation | Uses statistical models to predict the probability of different scenarios. |
Diversification | Engages multiple suppliers to reduce dependency on a single source. |
Businesses must weigh these factors carefully. While outsourcing reduces certain risks, it introduces others, such as data security concerns. A balanced approach, such as hybrid models, often provides the best risk mitigation strategy.
Strategic Alignment
Strategic alignment ensures that warehousing decisions support a company’s overarching goals. Whether a business opts for in-house or outsourced warehousing, aligning operations with its mission and objectives is critical for long-term success. Companies that prioritize alignment often experience smoother operations, better customer satisfaction, and improved profitability.
Consistency with Business Goals: Warehousing strategies must reflect a company’s priorities. For example, a brand focused on premium customer experiences may benefit from in-house warehousing, which offers greater control over quality. On the other hand, a cost-driven retailer might find outsourced solutions more suitable for maintaining competitive pricing.
Adaptability to Market Trends: Businesses that align their warehousing strategies with market demands can respond faster to changes. For instance, e-commerce companies experiencing rapid growth often require scalable solutions. Outsourced warehousing provides the flexibility to handle fluctuating order volumes without significant delays.
Integration Across Departments: Strategic alignment ensures that warehousing integrates seamlessly with other business functions, such as marketing and sales. A well-aligned strategy enables faster product launches, efficient inventory management, and timely order fulfillment.
Tip: Companies should regularly review their warehousing strategies to ensure they remain aligned with evolving business goals and market conditions.
Alignment Factor | In-House Warehousing | Outsourced Warehousing |
|---|---|---|
Control | High control over operations | Limited control, dependent on 3PLs |
Scalability | Requires significant investment to scale | Easily scalable based on demand |
Customer Experience | Tailored to brand standards | Relies on 3PL’s capabilities |
Strategic alignment acts as a compass, guiding businesses toward decisions that maximize efficiency and profitability. Companies that align warehousing with their goals position themselves for sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Choosing the Best Warehousing Solution
Assessing Business Needs
Selecting the right warehousing solution begins with a thorough evaluation of business needs. Companies must identify their priorities to ensure their choice aligns with operational goals and market demands. Several factors play a crucial role in this decision-making process:
Cost: Businesses should analyze rent rates, taxes, and hidden expenses to ensure the warehouse location fits within budget constraints.
Workforce Availability: Evaluating local demographics helps determine if skilled labor is accessible at reasonable costs.
Transportation Access: Accessibility to roads, highways, and public transport minimizes transportation expenses and ensures smooth logistics.
Proximity to Transportation Hubs: Warehouses near airports, railway stations, or ports reduce transit times and improve efficiency.
Market Proximity: Selecting a location close to suppliers and customers enhances responsiveness and reduces lead times.
Local Environmental Factors: Weather conditions and risks of natural disasters should be assessed to avoid disruptions in operations.
These considerations ensure businesses remain competitive in the Warehousing Game, balancing cost efficiency with operational effectiveness.
Evaluating Resources and Capabilities
A successful warehousing strategy depends on a company’s ability to leverage its resources and capabilities effectively. Businesses must assess their financial, technological, and operational strengths to determine the most suitable solution.
Performance Category | Methodology Used | Industry Focus |
|---|---|---|
Financial | Manufacturing, Third-party logistics, Retail |
Financial assessments help businesses understand their capacity to invest in infrastructure or outsourcing. Technological capabilities, such as automation and advanced Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), enhance operational efficiency. Operational expertise ensures smooth workflows and minimizes errors. Companies that prioritize these factors position themselves for long-term success.
Questions to Guide Your Decision
To navigate the complexities of warehousing decisions, businesses should ask key questions that clarify their priorities and constraints:
What is the projected order volume, and how does it fluctuate seasonally?
Does the company have the financial resources to invest in in-house warehousing, or would outsourcing be more cost-effective?
How important is control over operations, and can the business afford to delegate tasks to third-party providers?
Are there technological tools available to enhance efficiency, and does the workforce have the skills to utilize them?
What risks, such as data security or operational disruptions, are associated with each option?
Answering these questions provides a clear roadmap for selecting the best warehousing solution. Companies that align their decisions with their business needs and capabilities can master the Warehousing Game and achieve sustainable growth.
Retailers must weigh the strengths and weaknesses of in-house and outsourced warehousing to make informed decisions. In-house warehousing offers control and customization but demands significant investment and operational expertise. Outsourcing provides cost savings and scalability but limits oversight and flexibility. Aligning these choices with business goals ensures operational success and customer satisfaction.
To navigate the Warehousing Game effectively, businesses should create a decision-making checklist. This checklist might include evaluating order volume, financial resources, and growth projections. Consulting with industry experts can also provide valuable insights, helping retailers choose the best solution for their unique needs.
FAQ
What are the key cost differences between in-house and outsourced warehousing?
In-house warehousing requires significant upfront investments in infrastructure, equipment, and staffing. Outsourced warehousing, on the other hand, operates on a pay-as-you-go model, reducing initial financial strain. Businesses should evaluate their cash flow and long-term ROI goals before deciding.
How can a business decide if it needs a hybrid warehousing model?
A hybrid model works best for businesses balancing control and scalability. Companies with high order volumes in core regions but fluctuating demand in peripheral areas often benefit from combining self-operated hubs with outsourced regional support.
Is outsourcing warehousing safe for sensitive customer data?
Outsourcing can expose businesses to data security risks. To mitigate this, companies should partner with 3PLs that follow strict security protocols, such as encrypted systems and compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
What role does technology play in warehousing decisions?
Technology enhances efficiency and accuracy. Automated systems, such as Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and AI-driven inventory tools, streamline operations. Businesses should assess their technological readiness and consider outsourcing if they lack the resources to implement advanced systems.
How does business size influence warehousing choices?
Startups often outsource to minimize costs and focus on growth. Mid-sized companies may adopt hybrid models for flexibility, while large enterprises typically invest in self-operated systems to maintain control and build proprietary capabilities.
See Also
Understanding Robotic Automation's Role In Warehouse Efficiency
The Importance Of Warehouse Automation For Business Success
Improving Supply Chain Challenges In High-Tech Manufacturing
Transforming Supply Chain Management With Cloud Solutions
Boosting Warehouse Productivity Through Logistics Robotics Innovation
